Katja Ingrid Elbert-Avila, MD
- Associate Professor of Medicine

https://medicine.duke.edu/faculty/katja-ingrid-elbert-avila-md
Atrophy the entire skin surface muscle relaxant natural remedies buy 400 mg skelaxin visa, as well as hair muscle relaxant causing jaundice generic skelaxin 400mg, nails and mucosal surfaces ql spasms buy generic skelaxin from india, should be Scar Scales examined spasms pancreas best order skelaxin. In order to carry out the examination muscle relaxer kidney buy skelaxin 400mg online, you may require the patient to undress down to underwear bladder spasms 5 year old skelaxin 400 mg without prescription. If the patient has a widespread rash, it may Fissures Ulcers Crust seem obvious to them that you have to examine their skin in its entirety. They may however question the need for a full skin examination if they present with an isolated lesion. There may be other lesions the patient has not seen, perhaps on the back or buttocks. It is important to be aware of, and sensitive to , cultural and religious differences, and a chaperone may be required in some circumstances. Spatial relationship Describing a lesion Note the distribution and colour of lesions. This should be done by compressing the lesion between the fnger and thumb (in widespread rashes, this may not be necessary): Condition Condition Notes Notes Condition Condition Notes Notes Condition Condition Notes Notes Condition Condition Notes Notes Condition Condition Notes Notes You can download copies of the body map at: If your assessment indicates that more specialised A general physical examination including height, weight, temperature and investigations are required, refer the patient to a dermatology department. Mycology for fungal or yeast infection investigations skin scrapings, nail clippings, hair debris. Use a systematic approach to assessment: describe the lesion(s) eczema and their distribution, examine morphology, palpate the lesion(s), note any change in colour. Carry out relevant investigations or refer to dermatology if more specialised investigations are required. In both sexes, incidence peaks at 13?16 years, although it may continue into the 40s. Presentation Acne occurs on the face, chest and back depending on the distribution of sebaceous follicles in the individual. The precursor lesion of all acne lesions is the microcomedone Infammatory lesions: which, under the infuence of androgens, develops into non-infammatory. Papules and pustules the majority of patients with comedonal lesions (comedones) and infammatory lesions (papules and pustules). They are the well known little red Lesions of acne vary considerably with time, but in acne vulgaris spots or pustules on a red base. Most patients Papules develop rapidly over a few hours and frequently become notice a fuctuation in the number and severity of spots. Characteristically, small, deep ice-pick? scars occur, but more severe disease will leave gross changes with atrophy or keloid There is no evidence that diet infuences acne and it is not caused by formation. Traffc light Systemic symptoms (acne fulminans) this rare condition is almost Treatment always seen in young men. Symptoms include severe nodulocystic acne Treatment depends on severity (consider the possibility of scarring). Comedonal acne topical agents such as: Adapalene; Benzoyl Peroxide; Psychological impact the condition generally involves people in their Isotretinoin; Tretinoin. Before going to bed, the patient should cleanse the skin with soap and water or medicated wash then apply the weakest strength of topical agent. If the skin becomes sore, stop the treatment for a few days then restart on alternate nights. This allows the patient to adapt to the treatment and any irritation quickly resolves. In moderate to severe acne or unresponsive acne, systemic treatments are usually required in combination with topical treatments. If you have local guidelines on the management of common bacterial skin infections, their recommendations should be taken into consideration when prescribing treatment for cellulitis. Most patients can be treated at home but intravenous antibiotics, which may require the patient to be admitted to hospital, may be required if there are signs of systemic illness or extensive cellulitis. The co-existing condition that allowed entry of bacteria into the skin should be treated. Advice to patient After successful treatment, the skin may peel or fake off as it heals (post-infammatory desquamation). Traffc light If the infection is slow to settle, check that the patient does not have diabetes Cellulitis or is immune-defcient as he or she may require hospital admission. This is an infection of the subcutaneous tissues most commonly caused Cellulitis and allergic irritant contact dermatitis can look similar, by a group A, C or? Approximate age group More common in older people but can be seen in all age groups. It may be helpful to use a demarcation line to assess whether cellulitis is extending. The area will be erythematous and oedematous with localised pain and restricted mobility. The patient may also have systemic symptoms such as fever, malaise, chills or possibly rigors. The lesions tend to be symmetrical, commonly affecting the scalp, elbows, knees, sacral area and lower legs. The appearance will be quite different if fexural areas such as axillae, groins, sub-mammary or natal cleft are affected, presenting as smooth and non-keratotic with a shiny glazed appearance. Most patients have a few stable plaques but psoriasis can become unstable and extensive. A small proportion of patients will have joint involvement (psoriatic arthropathy). Chronic plaque psoriasis Guttate psoriasis Guttate/small plaque psoriasis Psoriasis this is an acute form of psoriasis which appears suddenly, often after a streptococcal throat infection. It is probably linked to several genes so occurrence within resolves spontaneously in about 2? It may be precipitated by hormonal changes, infection of psoriasis for the patient but it can occur in someone who has had such as a streptococcal throat infection or trauma. Here we describe two of the more common presentations: Treatment chronic plaque psoriasis and guttate or small plaque psoriasis. The majority of individuals with psoriasis can be treated with topical treatments. Approximate age group It can occur at any age but often begins between the ages of 15 and Chronic plaque psoriasis: treatment depends on the type, size and 25 years. Topical treatments include: emollient, vitamin D analogues or vitamin D analogue in combination with a potent topical steroid; tar preparations; saliyclic acid ointments; dithranol. Guttate psoriasis: as the condition usually resolves spontaneously, reassurance is all that is needed. Complete emollient therapy (see section 07) is useful if the skin is itchy or a mild topical steroid or weak tar solution may be indicated to give symptomatic relief. In some cases, ultra violet light treatment may be necessary: this would be administered in a dermatology department. Traffc light If more than 30% of the body surface area is affected by chronic plaque psoriasis, referral to dermatology should be considered. Erythrodermic psoriasis, where the entire skin surface is infamed, must be referred to secondary care. Generalised pustular psoriasis is an acute form of the disease which develops rapidly and may be associated with withdrawal of systemic or potent topical steroids. Sheets of erythema studded with sterile pustules come in waves, with an associated fever or malaise. The pain often continues until healing occurs but may go on for months or even years in older people (post-herpetic neuralgia). Treatment If the patient is seen in the prodromal phase with pain or abnormal sensation, or within 48 hours of the blisters appearing, treat with a 7-day course of an oral antiviral agents such as Aciclovir, Valaciclovir or Famciclovir. Antiviral agents are only effective when the virus is replicating and should only be given in the early phase of the disease (within 48 hours of the rash appearing). Adequate analgesia is important, such as paracetamol 1g every 4 hours or co-dydramol 2 tablets 4 hourly (max 8 in 24hrs). Advice to patient Reassure the patient that shingles cannot be caught, but chickenpox can Shingles (herpes zoster) be contracted from a patient with shingles by someone who has never Shingles occurs in people who have previously had chickenpox. Traffc light If there is ophthalmic involvement, rapid referral to ophthalmology is Approximate age group required to minimise potential complications of shingles involvement Can occur at any age. Presentation There is pain, tenderness or an abnormal sensation in the skin for several days before the rash appears. The rash will form groups of small vesicles on an erythematous background, followed by weeping and crusting. The rash is usually unilateral with dermatomal distribution and a sharp cut off at or near the midline. A good rule of thumb is to seek medical advice about all lesions which are not healing and may be enlarging. It slowly increases in size and, over time, the centre may ulcerate and crust (rodent ulcer). On examination, if you stretch the skin you will see a raised rolled edge like a piece of string sitting around the edge. It usually occurs in fair-skinned people who have worked or had hobbies out of doors. Well-differentiated tumours produce keratin, so the surface will be scaly or even horny and are often painful to touch. Common sites include bald scalp, lower lip, cheeks, nose, top of ear lobes and dorsum of the hand. They can also appear on non sun-exposed sites such as a site of previous radiotherapy or chronic scarring of burns and leg ulcers. If the lesion is superfcial (that is, it has not invaded downwards into the dermis), excision is more likely to result in cure. Change or irregular colour Malignant melanoma Minor features (score 1 point) A malignant melanoma is a malignant tumour of the pigment-producing 1 point. Oozing or bleeding of the skin cancers as it has the capability to metastisise through the 1 point. Suspect melamona if any major feature is present or there is a total score Approximate age group of 2. All age groups, particularly in those with fair or red hair who burn rather than tan in the sun. If urinalysis identifes protein or blood in the urine, specialist help should be sought as the patient may require systemic steroids or cyclophosphamide. Where no cause can be found (idiopathic), the patient should be reassured that the condition is self limiting and should resolve within 3? Vasculitis Advice to patient Vasculitis is an infammation of the blood vessels in the skin, usually due Bed rest will stop new lesions forming. Regular analgesia should be to the deposit of immune complexes in the walls of the vessels. Henoch-Schonlein purpura is a form of vasculitis and occurs mainly in the young (see section 05). Presentation the presentation will differ depending on the size and site of vessels involved. If the capillaries are involved, there will be a polymorphic rash with palpable purpura, as well as macules, papules, vesicles and pustules. If there is arterial involvement, livedo reticularis, nodules and ulceration of the lower leg may be present. Where there is arterial and venous involvement, there will be red, tender nodules or deep plaques in the subcutaneous fat. The patient may be feverish before developing a rash which will start with pink macules. The condition is communicable from fve days before the rash develops until around six days after. The spots can be very itchy and secondary infection may lead to pock-like scarring. However, an antiseptic-based emollient may reduce the risk of secondary infection. In adults or immunocompromised patients, aciclovir, valaciclovir or famciclovir will reduce the severity of the attack. Traffc light Adults who contract chickenpox can become very unwell with more severe symptoms. Chickenpox (Varicella) Varicella zoster virus causes chickenpox and shingles (see section 04 for shingles). By the age of 10 years most children, particularly in urban communities, will have been infected. Primary infection confers long-term immunity but the virus remains dormant in the dorsal root ganglion to be reactivated as shingles. Local dermatology nurses and dermatology departments will help with education, support and long-term management. The National Eczema Society, British Association of Dermatologists and the Primary Care Dermatology Society can also provide useful written Eczema (atopic) information. Atopy means an inherited predisposition to eczema, asthma or hay fever Traffc light and atopic individuals may have one or all of these conditions. The condition tends to be long term, but it will clear by puberty in 90% of individuals.
It has been suggested that psychological adjunctive therapy is more He was good in education but cannot continue his education due to efective and cost efective as compared to conventional therapy [24] spasms with cerebral palsy discount skelaxin on line. As he was the only child of his parents so Lam and Jones in 1999 [25] reported in their study that cognitive afer the death of his father he took the responsibility of his family and behaviour therapy techniques aim at managing and preventing stops education and started working muscle relaxant rub order skelaxin 400 mg on-line. His mother died 7 years ago at cognitive spasms between ribs purchase skelaxin paypal, afective and behavioral symptoms which are associated with the age of 70 spasms in hand order cheapest skelaxin. Behaviour Terapy for Bipolar disorder in his study and reported that Afer that he did not have any serious kind of physical and mental Cognitive behaviour therapy for bipolar disorder has following aims: illness spasms detoxification 400 mg skelaxin mastercard. X reported that he was good in studies in her childhood but process and common difculties associated with the bipolar cannot continue his education due to his father death spasms in back purchase skelaxin with amex. He did cognition and client was taught to improve his maladaptive behaviour not face any kind of birth complication at the time of his birth. His both parents were very caring and he did not have any conficting During frst few sessions, therapist builds repo with the client and relationships with his parents or anyone else. In next few sessions I identifed with his help that which thought pattern are problematic for him. According to him, he Before the onset of the sing and symptoms he reported himself really wanted to get rid of his problematic thoughts and associated to be slightly social and have only few friends. He reported himself of behaviours like he told during sessions that he is the victim of bad friendly nature and cooperative. His relationships with his neighbours luck and all that is happening to him is the result of bad circumstances were also good. Family history of the patients Trough a thorough investigations it was revealed that his poor socio economic condition has played signifcant role in his though pattern. According to his he During sessions I identifed more stressors in his life which were belongs to a very religious family and all the religious traditions are creating troubles for him. He is the dominant member of his family from which he wanted to get rid, I discussed with him that how we will and he sets the rules and regulation for his family. Mental status examination In next few sessions focus of the therapeutic session was on the cognitive restructuring of the client. His systematic identifcation of the problematic thought patterns which speech was pressured, loud and rapid and it was difcult to interrupt contribute to the onset and maintenance of the symptoms. He was tall and smart and well was made aware how negative thought patterns and their associated dressed. He was not maintaining proper eye contact with the therapist behaviours like aggression in his case were enhancing his problems like during the session. During the sessions he said many times that he is the stress, depression and mania symptoms. First of all we identifed Behavioural observation problem thoughts and behaviours then decided strategies to work on them. His main problems include sleep deprivation, stress, anger and Client appeared in a very sad mood. Follow up session were also conducted for accessing as he was speaking very fast, loud and he was changing topic of his level of achievement for achieving targets of psycho-therapy. He reported that he was not having proper sleep form many previous nights but he was looking very energetic. Client score on the mania rating scale is above cut was asked to calculate a regular bed time relative to daily demands and of score which show the high level of mania in client. Afer knowing all the client activities before sleep time, also indicate that he is not well socially adjusted. X in latter sessions to are many indicators in his drawing which shows his trends towards change his maladaptive behaviours. He techniques were applied on the client to cope with stress in future by seems to have confused thinking and distorted self-image. In drawing the person, feelings of inadequacy inferiority of social intellectualization, Psycho-education program was given to Mr. Tere is no psycho-education session client was made aware about the relationship evidence of neurological impairment including eye hand co-ordination between activities, physical feelings and mood. Subsequently he was trained Psychotherapies in the use of anxiety-control techniques (relaxation and breathing, self-instructions and cognitive distraction), sleep hygiene habits and Afer the administration of diferent psychological tests Mr. Cognitive behavioural therapy was applied In latter sessions he was trained in detecting distorted thoughts to Mr. As being a improvement of self-esteem techniques were taught to the client in psychotherapist I help him to identify which negative behavior patterns order to prevent relapses. Cognitive therapy is specifcally useful in improving life quality and functioning, increasing compliance, helping In the fnal session Mr. X reported of having less frequency of his early symptom recognition, decrease relapse and decrease depressive sign and symptoms. During the whole course of treatment the purpose of all the psychotherapeutic techniques applied to him to enhance Mr. X achieved improving his repertoire of social skills and assertiveness control, remission phase. Diagnosis was made afer having structured diagnostic helping him in gaining greater control on his mood by shifing thoughts interview with client. Monitoring of the client problematic thoughts and getting him involved in enjoyable activities, enhancing his self and behaviours was made throughout the therapeutic session. Afer therapy client that may occur in the context of an episode, these interventions are was recommended for follow-up session. Discussion Conclusion Bipolar disorder is turning out as a chronic, debilitating psychiatric The aim of the present study was to treat Mr. So it is concluded that psychotherapy is rates are found in Bipolar disorder, research has suggested that about very efective for the bipolar disorders and those patients who do not one third of patients diagnosed with bipolar disorder have attempted respond to medication can be best treated by psychotherapy. Given the chronicity and severity ethics of psychotherapy and counselling were maintained. Growing body of Following are the limitations of the study: literature exist which suggest that combined psychosocial interventions and psychopharmacological are best for treatment of adults having. This is a clinical case study and case studies always have limited Bipolar disorder [30]. The root cause of his disease was found his disturbing of bipolar disorder in whole life span. Only cognitive behavior therapy was applied in this case distractibility, racing thoughts and poor judgement and ups and down according to the need of client. As being a psychotherapist I taught him new alternative thought patterns and made him aware 4. Am J Psychiatry 163: 1173 harmful behaviours are removed and replaced with positive behaviours. Journal of Affective behavior in schizophrenia and its relationship to awareness of illness. American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of of a randomized clinical trial. Evidence-based research on the effcacy of psychologic interventions in bipolar 27. State related differences in the level of psychomotor activity in pa Official opponents: Prof. Ralf Hem tients with bipolar disorder Continuous heart rate and mingsen movement monitoring. Psychiatry Research 2016 Mar Correspondence: Department O, Psychiatric Center Copenhagen, Rigshospitalet, 30;237:166-74. Behavioral activities collected through smartphones and the association with illness activity in bipolar disorder. International Journal of Methods in Psy Dan Med J 2018;65(3):B5460 chiatric Research 2016 Apr 1. State tive disorder in the remitted or mild/moderate depressive related differences in heart rate variability in bipolar disorder. Journal of Affective Disorders 2012 Dec 10;141(2 Journal of Psychiatric Research 2017 Jan, 84, 169-173 * 3):457-63. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, In press, jective and objective symptoms in bipolar disorder the Accepted manuscript; doi: 10. Psychiatry Re As smartphone-based and heart rate-based electronic monitoring search 2014 Jun 30;217(1-2):124-7. Consequently, this dissertation is predominantly based on Daily electronic self-monitoring in bipolar disorder using studies conducted by the author. Psychological ing 12 articles on data from four original studies and two system Medicine 2015 Jul 29: 1-14. Smartphone data as an electronic bi discussion and review of the literature follows each of the two omarker of illness activity in bipolar disorder. The disorder is associated with a high risk of relapse and hospitalization, and on average, the risk of 2: Electronic monitoring of psychomotor activity and heart rate relapse increases with the number of previous affective episodes in bipolar disorder (23?25). Regarding clinical diagnosis, Electronic mental health: Mental health services provided through patients with bipolar disorder are often misdiagnosed, and the an electronic medium (E-mental health). Currently, due to the lack of objective tests, the via videoconferencing (virtual face-to-face). Furthermore, when patients Psychomotor activity: Consists of multiple domains, such as gross present in a remitted or depressive state, it may be difficult for motor activity, body movements, speech and motor response clinicians to determine whether the patients suffer from unipolar time. Patients may not recall prior Heart rate variability: Reflects the oscillation in the time intervals (hypo)manic episodes, and clinicians may not be sufficiently between consecutive heartbeats. In this way, a bipolar Application: A software program designed to run on mobile de disorder diagnosis could be overlooked. Thus, these issues call for less biased and more ob Smartphone-based electronic self-monitored data: Self-assessed jective markers of bipolar disorder. Psychomotor acterize bipolar disorder are accompanied by observable shifts in retardation during depression and increased motor activity during energy, activity, sleep and other behavioral aspects that may be mania were described in an eighteen-century monograph by quantified (14,15). Andres Piquer-Arrufat (65,66) and in more recent scientific arti Bipolar disorder is a common and complex illness with an cles (15,60,61,63,64,67?72). However, in most of the previous estimated prevalence of 1-2%, and it is one of the most important studies, psychomotor activity was assessed using clinical assess causes of disability worldwide (16,17). Bipolar disorder is associ ments or questionnaires, and the studies showed inconclusive ated with an elevated risk of mortality due to suicide and medical results (63,67?69,73,74). Electronic devices for collecting self-assessed features, such as Studies have shown that changes in the level of engagement mood, activity and medicine intake (32,124?128), and automati in social and communicative activities (60,81?83) and in speech cally generated features, such as heart rate, movement and other activity (84?87) represent central aspects of illness activity in behavioral aspects (15,61,79,83,114,129), have been used in bipolar disorder. Alterations in psycho lected data within laboratory or hospital settings, included small motor and speech activity are central features in the clinical sample sizes of patients who were followed for short periods, or presentation of bipolar disorder and are included in standardized did not monitor both self-assessed features and automatically clinical rating scales measuring the severity of depressive and generated features. With electronic devices, detailed data regarding complex Over the last decade, there has been a gradual paradigm shift psychopathological aspects of bipolar disorder that otherwise from a focus on affective episodes to an increasing focus on would be difficult to collect can be evaluated over prolonged interepisodic mood instability (26,89?91). A large proportion of time-periods, in naturalistic settings and in a relatively unobtru patients with bipolar disorder experience subsyndromal mood sive manner. Moreover, data collected using electronic devices swings on a daily basis (28,57,90,92,92,93), and mood instability could represent candidate markers of diagnosis and illness activi at a subclinical level is associated with impaired global functioning ty in bipolar disorder and further could allow early intervention and a high risk of relapse (89,92,94,95). However, despite the increasing focus on tures correlate with scores on the standardized clinical rating mood instability, the longitudinal patterns of mood instability and scales that are currently used as the gold standards to assess the possible differences in mood instability between bipolar disorder severity of depressive and manic symptoms. Lastly, the extent to which the use of smartphone-based continuous long-term monitoring and assessment of mood insta electronic self-monitoring affects clinically relevant outcomes, bility and other features that reflect illness activity may be clini and importantly, whether it may in fact have harmful effects, had cally advantageous because they would allow continuous detailed not been investigated. In bipolar disorder, several lines of embedded within mobile monitoring devices could provide evidence indicate the presence of autonomic dysfunction and enormous opportunities for new areas of research, development central autonomic disturbances (105?107). Furthermore, it has been suggested that bipolar disorder compared with healthy control individuals (111? mHealth interventions have the potential to minimize the tradi 121). In addition, an increased risk of cardiovascular disease is tional barriers of distance, time and costs (131,132). Biological markers, or biomarkers, refer to characteristics Data suggest that more than half of smartphone users seek that are objectively measured and evaluated as an indicator of health-related information from their phone, and more recently, normal biological processes, pathogenic processes, or pharmaco the use of sensors embedded within mobile devices to monitor logic response to a therapeutic intervention? (123). The increasing smartphones can deliver treatment interventions outside clinical number of articles published on the topic reflects the increase in settings. Strikingly, few smartphone applications have been evaluated in scientific studies (150,156). Reviews of smartphone applica Figure 1 tions for bipolar disorder reported that only 22% addressed priva cy issues, only 15% used best practice guidelines regarding treat ment advice and only 31% cited their information source (181,182). Prior to the work by the author, no studies combining the use of smartphone-based electronic self-monitoring and smartphone-based electronic automatically generated data in bipolar disorder had been published. In addition, no studies inves tigating the possible harmful effects of smartphone-based elec tronic monitoring had been published. Thus, questions regarding the associations between smartphone data and clinically rated depressive and manic symp toms, the safety of smartphone use and evidence supporting the use of smartphones as treatment interventions were unan swered. These types of charting instruments mood disorders are alterations in psychomotor activity enable the collection of detailed longitudinal information regard (14,183,184). The ability to discriminate between bipolar disorder ing daily mood swings and other symptoms relevant to bipolar and unipolar disorder is crucial as the two disorders have differ disorder when patients are outside the clinical setting, and they ent psychopharmacological treatments, courses of illness and are often used in the treatment of bipolar disorder. Differences in psychomotor activity during mood charting instruments can be viewed as a facilitating tool to depression and mania have been described (14,15,72,77), and help patients to gain illness insight, facilitate patient empower unbiased automatically generated assessments of changes in ment, and teach patients to recognize early warning signs of the affective states and severity could be useful in the diagnosis and recurrence of mania, depression and mixed states. However, this method cannot quantify in naturalistic settings may be useful for diagnosing and assessing subcomponents of activity patterns, such as activity energy ex state in bipolar disorder, but no studies of such measurements penditure, hourly variation of movement, intensity etc. Psychomotor activity may be correlated with other mood central to bipolar disorder could represent markers of diagnosis symptoms (64), but studies comparing psychomotor activity in and affective state and further allow for early diagnosis, monitor unipolar disorder and bipolar disorder have not adjusted their ing and treatment. With the use of electronic devices for monitor analyses for differences in the severity of mood symptoms. More ing, detailed fine-grained data can be collected unobtrusively over specifically, results from some studies suggest that bipolar de the long term in naturalistic settings. Prior to the work by the pression is more likely than unipolar depression to manifest with author, no investigations had examined whether the severity of psychomotor retardation and other atypical symptoms smartphone-based electronic self-monitored symptoms and (15,60,62,189). Additionally, psychomotor inhibition in unipolar electronic automatically generated features correlate with scores disorder has been associated with an increased risk of a later on the standardized clinical rating scales that are currently the bipolar course of illness (190). Concordantly, although the evi gold standards for assessing the severity of depressive and manic dence is poor, reviews suggest that psychomotor retardation is symptoms in bipolar disorder. Furthermore, few published stud more prevalent in bipolar disorder and may be a signature symp ies had examined whether electronic automatically generated tom (14,62,129).
Some statistics of this policy relative to the baseline economy are shown in Table 8 spasms 1983 purchase skelaxin 400mg mastercard. The policy is effective in expanding the use of modern contraceptives since the fraction of women using such methods increases from 33 percent to 84 percent spasms homeopathy right side purchase 400mg skelaxin with amex. Human capital and phys ical capital investments rise as expected muscle relaxant creams over the counter generic 400 mg skelaxin mastercard, and output per capita increases by roughly 2 bladder spasms 5 year old order skelaxin 400 mg free shipping. We do not report the decomposition of the full effect but such experiments are available upon request muscle relaxant skelaxin 800 mg buy skelaxin 400 mg on-line. Universal Policies: Sub sidy on the price of modern contraceptives; subsidy on the price of abortion; and subsidy on basic education (0-4 years) for all families back spasms 39 weeks pregnant cheap skelaxin online visa. Targeted Policies: Subsidy on the price of modern contraceptives for women with up to 8 years of schooling; subsidy on the price of abortion for women with up to 8 years of schooling; and subsidy on basic education for children with parents with up to 8 years of schooling. Children become relatively cheaper and parents respond to that by having more children. Although schooling also rises and inequality decreases, the net effect on output per capita of this policy is negative. In fact, output per capita would decrease if the government subsidized 4?8 years of education, 8?12 years of education, or 0?12 years of education. The main driver behind this fall in output is the rise in fertility when primary or secondary education is universally subsidized. Output per capita only rises when the government subsidizes higher education, but this policy is rather regressive and inequal ity rises relative to the baseline. Average welfare relative to the baseline rises in all three universal policies reported in Table 8 and its highest level is achieved when abortion is subsidized. From these policy experiments we can conclude that universal subsidies in early education are less effective than public investment in modern contraceptives or abor tion to raise per capita income and to control fertility. The largest reduction in inequality, measured by the ratio of the 90th percentile to the 10th percentile of income, also occurs when abortion is subsidized. Table 8 reports results for three different targeted policies: a subsidy on the price of modern contraceptives for women with up to 8 years of schooling (a primary degree); a subsidy on the price of abortion for women with up to 8 years of schooling (a primary degree); and a subsidy on basic education (0-4 years) 52 for the children of the parents with up to 8 years of schooling (a primary degree). A targeted subsidy on the price of modern contraceptives for women with up to 8 years of schooling (a primary degree) increases the share of women using such contra ceptive methods, but by less than the universal policy reported previously. The fraction of women using modern contraceptives increases from 33 percent to 70 percent with this policy, but it jumps to 84 percent when the universal policy is implemented. Investment in human and physical capital rise and output per capita increases by roughly 2. These numbers are bit less than in the universal policy, which is explained by the fact that in the baseline equilibrium there are also un wanted pregnancies among women with a secondary or a higher degree and a universal policy would increase the intensity of modern contraceptive use for all women, and not only those at the lower tail of the human capital distribution. Compared to the subsidy on modern contraceptive prices for women with the same amount of schooling, the abortion subsidy is much more effective in reducing unwanted fertility and total fertility, and consequently on increasing investment in human and physical capital. Finally, the last column of Table 8 reports results for the experiment in which basic ed ucation (0?4 years) is subsidized for all children of parents with up to 8 years of schooling. Educational attainment increases, and output per capita relative to the baseline increases by 3. Relative to the other two targeted policies, this targeted subsidy on education generates a larger impact on output per capita than the subsidy on the price of modern contraceptives, but smaller effect on income per capita when abortion is subsidized. Conventional macroeconomics wisdom ascribes family size to demand or the 52We implemented several other targeted policies. We choose to report results for this policy because it is the one in which the subsidy on education generates the largest positive effect on per capita income. Table 13 in Appendix B contains results with policies which target women with up to 4 years of schooling. This view has a major shortcom ing: micro development literature shows that improving access to modern contraceptives, legalizing abortion, and/or improving knowledge about the ef? Our paper contributes to the existing literature by embedding endogenously unwanted fertility in an otherwise standard quantity-quality overlapping generations model of population and growth with heterogenous households. Our theoretical model has several novel character istics: Fertility control is costly and families can (partially) insure against a fertility risk by using costly contraception. Given the number of children born, parents de cide how much education to provide and how much to save out of their young adulthood income. We calibrated and estimated the model to Kenya data, such that key empirical statistics are matched. Kenya is used as an illustration, but clearly the model is general enough and could be estimated using data for different developing countries. We show that the standard macro view is in part correct since aggregate fertility is indeed mainly driven by desired family size. The difference between the fertility rate of our baseline (2008 Kenyan economy) model, in which fertility is costly controlled through modern contraceptives, and a model in which fertility is fully controlled through costless contraceptives is just 0. However, access to modern contraceptives and abor tions indeed shapes the compositional pattern of fertility and consequently the human capital dynamics and savings of a society, and family planning interventions can have sizeable effects on individual outcomes and aggregate variables. This is due to the fact that the aggregate fertility measure hides important distributional issues since the gap be tween realized and wanted fertility can be three times larger for low?income families than high?income families. Our counterfactual exercises show that if modern contraceptive methods are freely provided to all women, then output per capita would increase by 13 percent relative to the baseline economy, and that would cost about 2. If abortion is freely offered then the rise in output per capita would be roughly 9 percent; such a policy would cost 0. Interestingly, our results suggest that with a small government budget (say, up to 0. We decompose the full effect of family planning interventions on the economy into three different channels: a general equilibrium channel (price movements), a wanted fer tility channel (how desired fertility changes with family policies), and the investment in education channel. For instance, fami lies usually target a higher wanted fertility rate when the fertility risk of unwanted preg nancies is reduced, which can mitigate some of the effects of family planning policies on 40 reproductive behavior, investment, and income levels. Knowing this could affect which plans policymakers will choose to pursue and implement. Our fertility model can be used to investigate important unresolved questions such as the role of access to modern contraceptives in affecting structural transformation, female labor force participation, and social security. Roberts, Chairman, Universities-National Bureau Committee for Economic Research, pp. New Evidence from Family Plan ning in Colombia,? Economic Journal, 120(545), 709?736. Table 9 contains summary statistics of these variables, and Table 10 reports correlations for them. Human capital attainment: Educational attainment of the total population aged 25 and over. The panel is unbalanced with some countries having only one observation and others having up tp 6. The panel is unbalanced with some countries having only one observation and others having up to 6. Percent of women using modern contraceptive method for the three years pre ceding the survey. The panel is unbalanced with some countries having only one observation and oth ers having up to 6. Table 11 provides the decomposition of the two supply policies (free modern contraceptives and free abortion) presented in Table 7, while Table 12 contains the decomposition of the two demand policies (no disutility 46 Table 10: Simple correlations. Finally, Table 13 reports statistics for the experiments in which the targeted group corresponds to all parents with up to 4 years of schooling. Targeted Policies: Subsidy on the price of modern contraceptives for women with up to 4 years of schooling; subsidy on the price of abortion for women with up to 4 years of schooling; and subsidy on basic education for children with parents with up to 4 years of schooling. Pregnancies that Pregnancies spaced less than 18 start less than 18 months after birth are associated with delayed months after a live birth are prenatal care and adverse birth outcomes, including preterm birth, associated with delayed prenatal care neonatal morbidity, and low birthweight. A comprehensive list of types of contraception and their relative effectiveness may be found here. The March of Dimes is a national voluntary health agency whose volunteers and staff work to improve the health of infants and children by preventing birth defects, premature birth and infant mortality. Founded in 1938, the March of Dimes funds programs of research, community services, education and advocacy. By 2012, the program increased the use of highly effective methods and a modest decrease in the rate of low birthweight had taken place statewide. The program has succeeded in saving money and reducing unplanned pregnancy, and participants have higher odds for achieving optimal birth spacing. Interpregnancy Intervals in the United States: Data from the birth certificate and the National Survey of Family Growth. Adverse birth outcomes in Colorado: Assessing the impact of a statewide initiative to prevent unintended pregnancy. Game change in Colorado: Widespread use of long-acting reversible contraceptives and rapid decline in births among young, low-Income women. Medicaid Family Planning Expansions: Lessons Learned and Implication for the Future. Interpregnancy intervals: Impact of postpartum contraceptive effectiveness and coverage. If you take all of your birth control pills on time, Sexually they are 99% effective. In the first 2-3 months you may have nausea, bleeding between periods, weight change, and/or breast pain. In 2002, the Uganda Population and Housing pregnancy, it should be preserved as a marriage gift. It also to be a haven of natural family planning, with strong focuses on decreasing the high total fertility rate from and visible opposition to contrary proposals. The latter proposal and the promotion of Large families and short birth intervals are closely contraceptives go against the teaching of the Roman associated with poverty and poor health. So, the mother, the unborn child, and the reaffirmed its acknowledgement of the genuine need living children are all negatively affected by frequent for birth control and child spacing. It acknowledged births, not to mention the entire household and the the presence of pregnancy-related risks to the mothers? country. However, its approach focuses health policy and development 127 volume 6 number 3 December 2008 Catherine Nakiboneka and Everd Maniple only on the use of artificial methods of family planning. With limited resources, high fertility depresses savings and makes it difficult for Literature Review most families to adequately feed, clothe, house, and the Global Policy Forum reported that, worldwide, educate their children (Namara, 2006). Therefore, roughly 125 million women indicate a desire to plan helping them to reduce unintended pregnancies would their families but are not currently using any slow population growth and reduce pressure on natural contraceptive method (Global Policy Forum, 2003). An average woman in the world now for limiting population growth as a means to acquire bears just 2. In fact, high fertility rate wipes learn the method; record keeping; partner cooperation; out development achievements and without action ability to observe periodic abstinence; the age of the taken, by 2013/14 the number of Ugandans living in users; level of education; culture and religion of the poverty was estimated to increase to 10. Trussell and Kost In Asia and South America, success in reducing (1987) explained that failure of a method may result fertility levels resulted from social and economic from the technical limitation of the method or simply development focused on raising the level of education from improper use. However, Aguilar diaphragms, condoms and cervical caps or chemical (1998) observed that some people use sexual barriers like spermicides. In America and Mexico, many Catholic priests procreation impossible (Karl, 1997: page 471). It also considers the national needs equally with their husbands in decisions concerning conditioned by limited resources especially in less children education, family income, and expenditure developed countries (Karl, 1985). In Pader District diaphragm before every sexual act, availability and of Uganda, most health units did not have signposts, cost of the method. The staff was government agencies educated the population about inadequate in number and training. In these units, clients found it difficult opportunity to clarify clients? misconceptions better. Low use of modern contraceptives due service enhance client perception of quality. These to strong adherence to the Catholic faith was also include reliability, accessibility, communication, reported in some parts of Uganda by Ayella (2005). In a diocesan development program survey health units in the dioceses formed the population. Eight health policy and development 131 volume 6 number 3 December 2008 Catherine Nakiboneka and Everd Maniple (or 31%) of the twenty six Lower level Health Units the majority of the respondents were peasant farmers. From Masaka District, children to provide labour, and are relied upon as the two hospitals and three (3/12 or 25%) lower level security in old age. From Rakai District, three want to control their fertility in order to accommodate (3/11 or 27%) lower level units were included and the demands of their work. A total of 200 respondents below shows the highest education level attained by were planned to be interviewed, i. Interviews were held with Table 2: Respondents? highest education attained clients on exit from the health units using interviewer administered questionnaires. Systematic random Level Frequency Total % sampling was used to interview every 5th client F M exiting. Key informants for the study, numbering 72, included the diocesan bishop, health coordinator, and None 12 10 22 10. Total 156 46 202 the study tools were pre-tested in one of the units in the diocese excluded from the study. Qualitative the majority of the clients (63%) had only attained data were collected and analysed manually and by up to primary school level of education. This them even illiterate people can use the cervical mucus ate into valuable study time. However, Table 1: Respondents? employment the most popular single method was injectable Depo Provera (depot Category Frequency Percentage medroxyprogesterone acetate) followed Peasant farmers 130 64 by breast-feeding.
Some of these include avoiding foods that may trigger episodes of nausea and vomiting spasms just before falling asleep buy cheap skelaxin 400 mg. Additionally muscle relaxant machine buy skelaxin 400mg line, supplements containing iron can be a source of nausea and vomiting in certain women spasms shown in mri purchase skelaxin paypal. Clinical data to support the safety and efficacy of these drugs are minimal and use of the following medications should still be exercised with caution (See Table 2) muscle relaxant definition purchase cheap skelaxin. Currently spasms 7 weeks pregnant discount 400 mg skelaxin with mastercard, no medications are approved for the treatment of nausea and vomiting in pregnant women muscle relaxant benzodiazepine cheap skelaxin 400 mg with mastercard. One other suggested therapy involves giving antihistamines in the morning to prevent nausea and vomiting. If hyperemesis is resistant to conventional treatment, then the use of ondansetron or corticosteroids may be considered. Table 2: Drugs Used in the Management of Nausea and Vomiting During Pregnancy Drug Pregnancy Risk Category Metoclopramide (Reglan) B Cyclizine (Marezine) B Ondansetron (Zofran) B Promethazine (Phenergan) C Prochlorperazine (Compazine) C Chlorpromazine (Thorazine) C Adapted from: Nelson-Piercy C. Treatment if Nausea and Vomiting in Pregnancy: When Should It Be Treated and What Can Be Safely Taken? Antihypertensive agents are used in women with a diastolic pressure of 100 mm Hg or higher (lower if end organ damage or renal disease is present) and in women with acute hypertension when pressures are greater than 105 mm Hg. The drug of choice for high blood pressure diagnosed during pregnancy is methyldopa. The sixth report of the joint national committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatmenrt of high blood pressure. Migraine the drug of choice for migraine headaches during pregnancy is acetaminophen. There appears to be no effect on the fetus as well as minimal effects on platelet function. Other typical medications used in migraine treatment are not recommended during pregnancy (See Table 4), which include the selective serotonin agonists. Although they have not been proven to be harmful to humans, there have been no well-controlled studies to validate their use. Ergotamine and dihydroergotamine are contraindicated in pregnancy because of their uterotonic effects. Testosterone Can cause birth defects Oral contraceptives Can cause birth defects Dutasteride Affects the sex organ development of the male fetus. Methotrexate Causes cleft palate along with multiple defects 15 Done by : Pharm. Health policies across disciplines and improving officials can leverage public health programs, social state and territorial public health services, and primary care services to improve care infrastructure. Provide behavioral and mental health rate declined 8 percent between 2007 and 2014 screening. Preterm infants are at greater risk of agencies and sectors to increase payment developing chronic conditions as adults, such as 1 for, availability of, and access to evidence diabetes and heart disease. There are significant racial and ethnic inequities at all economic levels in preterm birth and infant mortality rates. The preterm birth rate for African American women is 49 percent higher than the preterm birth rate for all other racial and ethnic groups. American Indian and Alaska Native women, who also have an infant mortality rate higher than the national average (8. Providing access to family planning services that include the full range of contraceptive options, counseling, preconception, and interconception care helps women prevent both unplanned and closely spaced pregnancies, both of which are associated with negative birth outcomes. Work with Medicaid and private insurance to reimburse providers for using screening protocols to detect substance misuse and addiction, maternal depression, and perinatal mood and anxiety disorders early in pregnancy, and to identify adverse outcomes in newborn and infant development. Educate providers and patients on evidence-based interventions for improving birth outcomes, including proper use of 17P (injectable progesterone), aspirin, group prenatal care, home visits, and non-medically indicated elective inductions and Cesarean sections. Data sources for monitoring and assessment include vital statistics, hospital discharge data, electronic health records, and health surveillance systems, such as birth defects surveillance and fetal infant mortality review. Provide continuous 2 quality improvement training using state and territorial datasets and expand maternal and child health surveys and surveillance projects to every state. This includes mobilizing community health and wellness resources, identifying individuals and communities of greatest need, and using proven practices to engage, inform, and deliver needed health and social services. Be advised that the statements are approved as a general framework on the issue at a point in time. Any given state or territorial health official must interpret the issue within the current context of his/her jurisdiction and therefore may not adhere to all aspects of this Policy Statement. Demonstrating Improvement in Maternal, Infant, and Early Childhood Home Visiting Program: A Report to Congress, March 2016. Black Mamas Matter: A Toolkit for Advancing the Human Right to Safe and Respectful Maternal Health Care. Demographic changes over the last two decades highlight the need for a reassess Frohwirth, Lindsay ment of why women decide to have abortions. Bivariate analyses examined differences in the reasons for abortion across subgroups, and multivariate logistic regression models assessed associations between respondent characteristics and reported reasons. Frohwirth is or ability to care for dependents (74%); that she could not afford a baby now (73%); and that she did not want to be a research associate, single mother or was having relationship problems (48%). Fewer than 1% said their parents? or partners? is research assistant, desire for them to have an abortion was the most important reason. Younger women often reported that they were Susheela Singh is vice president for research unprepared for the transition to motherhood, while older women regularly cited their responsibility to dependents. Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health, 2005, 37(3):110?118 Public discussion about abortion in the United States has and unreadiness for parenting. One compelling reason is that the who have abortions do so because of health concerns or fetal abortion rate declined by 22% between 1987 and 2002,7 anomalies, the large majority choose termination in response and another is that the demographic characteristics of to an unintended pregnancy. What personal, familial, social and economic factors or more children has increased, as have the proportions lead to the decision to end a pregnancy? In a 1985 study of 500 women in portion of women having abortions who were poor in Kansas, unreadiness to parent was the reason most often creased. Like school, work or other responsibilities, and that they could wise, a fuller appraisal of the life circumstances within which not afford a child. Fielding ran from December 2003 until March 2004, 2000, and to a 1987 survey of reasons for abortion. Quantitative Component Qualitative Component the design of the structured questionnaire was modeled We also conducted in-depth interviews with 38 women at after the one used in the 1987 U. The interview guide included all of the same top the wording as similar as possible to the language of that ics as the survey. Our eight-page questionnaire covered in detail the freestanding, in different regions of the country and in states reasons why the respondent chose to terminate her preg with differing restrictions on access to and Medicaid re nancy. If sen to represent varying city sizes and to capture a cross you have more than one reason, please list them all, start section of abortion patients. Multiple responses were allowed, and a space was ed 30?60 minutes and were anonymous. Finally, women were asked interview period began at the end of the structured survey about their demographic and social characteristics. We purposively sampled 11 facilities from the universe of known abortion providers that perform 2,000 or more Data Analysis abortions per year; such facilities performed 56% of all abor We used chi-square tests to examine differences in reasons tions in the United States in 2000. Multivariate sen to be broadly representative, rather than strictly sta logistic regression models re? In addition, we at least one facility in each of the nine major geographic di conducted a factor analysis of the closed-ended and write visions de? Census Bureau, and chose fa in reasons and subreasons to identify logical groupings. We therefore periods, parental consent regulations and use of state Med weighted? Of the 11 sites originally chosen, one clinic de 2004 survey was not nationally representative, individual clined to participate and was replaced by a similar facility. Because the sampling design in the questionnaire was pretested at a clinic that was not volved 11 primary sampling units, we used statistical tech part of the sample to assess how well women understood niques that accounted for the clustered design to calculate the informed consent process and the survey questions. Staff at the selected facilities asked women arriving for *In 1987, the question about ability to afford a baby did not offer speci? The most common a pregnancy termination to participate in the survey and, responses were used to create the options for the 2004 version. Percentage of women in various surveys of abortion patients, by selected of gestation, and 85% were at fewer than 13 weeks. Black 31 45 32 26 26 Fifty percent of women were below 200% of the federal Hispanic 19 11 20 7 13 poverty level in the 1987 survey of reasons, while in 2004, <9 weeks? gestation 61 39 u 55 50 <13 weeks? gestation 85 58 u 87 86 60% were below this level. We conducted all analyses using dren, and two-thirds were living below 200% of the feder Stata version 8. Marital status was similar between the two sam Of the 1,209 respondents, 4% gave no reasons and were ples. Furthermore, almost half of the women than of the others were nonwhite and had children. The audiocassettes of the in-depth interviews were pro fessionally transcribed, and the research team listened to every Reasons for Abortion tape while reviewing the transcription. Among the structured survey respon ed, and any information that could potentially identify re dents, the two most common reasons were having a baby spondents was removed. The edited transcripts were sys would dramatically change my life? and I can?t afford a baby tematically coded using categories based on the project focus now? (cited by 74% and 73%, respectively?Table 2). All coding proportion of women cited relationship problems or a de was done by one author and checked for validity by anoth sire to avoid single motherhood (48%). Twenty percent were 19 or the most common subreason given was that the woman younger, and 57% were in their 20s. Seventy-two percent could not afford a baby now because she was unmarried had never been married, and 59% had had at least one child. Thirty-eight percent indicated that having a baby Some 60% were below 200% of the federal poverty line, in would interfere with their education, and the same pro cluding 30% who were living in poverty (not shown). For example, or the lives of their other children (32 of 38 respondents), women who undergo abortions at hospitals may be more likely than oth ers to have sought an abortion for health reasons. Nine women cited health ing abortions for fetal or maternal health reasons to their facilities. Thus, underreporting of health reasons, while possible, is likely not substantial. Several questions were Reason 2004 1987 identical or virtually identical on the 1987 and 2004 sur (N=1,160) (N=1,900) veys of reasons for abortion and are thus comparable (Table Having a baby would dramatically change my life 74 78* 2). Roughly equal proportions of women in both sur Can?t afford a baby now 73 69 veys indicated that a baby would dramatically change their Unmarried 42 na Student or planning to study 34 na lives, that they could not afford a baby now, that they did Can?t afford a baby and child care 28 na not want to be a single mother or had problems with their Can?t afford the basic needs of life 23 na relationship, and that they were not ready for a child or an Unemployed 22 na Can?t leave job to take care of a baby 21 na other child. Currently or temporarily on welfare or public assistance 8 na However, the proportion of women indicating that they Don?t want to be a single mother or having relationship problems 48 52* had completed their desired childbearing increased sub Not sure about relationship 19 na Partner and I can?t or don?t want to get married 12 30*** stantially (and signi? To assess whether this shift was due to a Relationship or marriage may break up soon 11 16* change in mothers? propensity to give this reason (in ad Husband or partner is abusive to me or my children 2 3 Have completed my childbearing 38 28** dition to the change in population composition described Not ready for a(nother) child? 32 36 earlier), we strati? Thus, the over Physical problem with my health 12 8** Parents want me to have an abortion 6 8 all increase likely re? Note:na=not applicable, because portion of women indicating that having children or other survey questions were not comparable. This change, selves or possible problems affecting the health of the fetus however, appeared to be due solely to the change in pop as their most important reason in 2004, about the same as ulation composition (not shown). Only half a percent of women indicated that their who cited a physical problem with their health also in partners? or their parents? desire for an abortion was the creased over the period. Of the 1,160 women who gave 2004 than in 1987 said that having a baby would interfere at least one reason, 89% gave at least two and 72% gave at with their job or career (38% vs. Among women who gave at least that they and their partner could not or did not want to get two reasons, the most common pairs of reasons were in married (12% vs. In both surveys, 1% indicated that ability to afford a baby and interference with school or work; they had been victims of rape, and less than half a percent inability to afford a baby and fear of single motherhood or said they became pregnant as a result of incest. In both 1987 and 2004, un having completed childbearing or having other people de readiness for a child or another child and inability to afford pendent on them. In contrast, the proportions nancial instability, unemployment, single motherhood and reporting fear of single motherhood or relationship prob current parenting responsibilities. For example, one 25 lems, and reporting that a child would interfere with school or career, both declined, as did the percentage describing *We grouped some reasons slightly differently in Tables 2 and 3 to com bine reasons that are conceptually similar. Percentage distribution of women having an abortion, by their most impor ratios, 0. The fact that the odds ratios for women tant reason for having the abortion, 2004 and 1987 with one, two, and three or more children are similar sug Reason 2004 1987 gests that unreadiness is more strongly linked to initiating (N=957) (N=1,773) childbearing than to limiting the number of children. Not ready for a(nother) child?/timing is wrong 25 27 Fewer than half of the interview respondents said that Can?t afford a baby now 23 21 having a baby now would keep them from ful? Many women Would interfere with education or career plans 4 10*** who gave one of these reasons said they were too young to Physical problem with my health 4 3 Possible problems affecting the health of the fetus 3 3 have children and felt they were just starting out? in their Was a victim of rape <0. Most framed their decision in terms of the desire to Husband or partner wants me to have an abortion <0. Percentage of women reporting interference with school or career, and unreadiness for having a child, as a year-old woman, separated from her husband, said: reason for abortion, by selected characteristics; and odds Neither one of us are really economically prepared. Characteristic Interference with Not ready for school or career a(nother) child And with my youngest child being three years old, and me?constantly applying for jobs for a while now,?if I got % Odds % Odds (N=1,037) ratio (N=983) ratio a job, I?m going to have to go on maternity leave. These analyses included all women who mentioned each reason; they are not restricted to No. Women who had children were less likely than women with no children to give these reasons (odds ratios, 0. Notes:Chi-square tests measured differences across the entire distribu with children had reduced odds of citing this reason (odds tion. Percentage of women reporting that they could not afford another child, that I?m trying?I?m trying to do things for myself. How am I sup they did not want to be a single mother or had relationship problems, and that they posed to do something for another human?
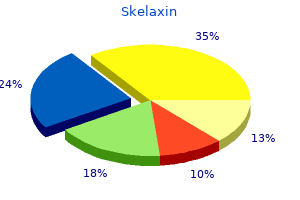
Separate oxygen muscle relaxant 4212 buy skelaxin online, air muscle relaxant injections neck skelaxin 400mg cheap, and suction facilities for the woman and the neonate should be provided in two separate locations muscle relaxant xanax 400 mg skelaxin free shipping. Gas outlets and wall-mounted equipment should be easily accessible but may be covered with a panel skeletal muscle relaxant quizlet discount generic skelaxin canada. Either a ceiling 40 Guidelines for Perinatal Care mount or a portable delivery light may be used spasms before falling asleep buy skelaxin 400 mg online, depending on the preference of the obstetric staff spasms right upper abdomen generic 400mg skelaxin mastercard. Proper care of the woman in labor requires sufficient space for a sphyg momanometer, stethoscope, fetal monitor, infusion pump, regional anesthesia administration, and resuscitation equipment at the head of the bed. The family area should be farthest from the entry to the room, and there should be a comfortable area for the support person. Equipment needed for labor, delivery, newborn resuscitation, and newborn care should be stored either in the room or in a nearby central storage or supply area and should be immediately available to the labor, delivery, and recovery room. For ease of movement, space below the foot of the bed should be ade quate to accommodate staff and equipment brought into the room. Standard major equipment held in this area for delivery should include a fetal moni tor, delivery case cart, linen hamper, and portable examination lights. A unit equipped for neonatal stabilization and resuscitation (described in Neonatal Functional Units? later in this chapter) should be available during delivery. The workable size of a labor, delivery, and recovery room measures 340 net ft2 (31. This room should be able to accommodate six to eight people comfortably during the childbirth process. Each labor, delivery, and recovery room should have the following equipment and supplies necessary for women in labor: Warming cabinets for solutions and blankets Inpatient Perinatal Care ServicesCare of the Newborn 4141. Adjustable lighting that is pleasant for the patient and adequate for examinations. A writing surface for medical records, computer hookup for medical record purposes, or both. Storage facilities for supplies and equipment There should be adequate space for support persons, personnel, and equipment, and room for the patient to ambulate in labor. Design or renovation should include planning for bedside and workstation information management sys tems and for computer management of medical information. Patients with significant medical or obstetric complications should be cared for in a labor, delivery, and recovery room that is specially equipped with car diopulmonary resuscitation equipment and other monitoring equipment neces sary for observation and special care. Rooms used for intensive care of patients at high risk in hospitals with no designated high-risk units are best located in the labor and delivery area and should meet the physical standards of any other intensive care room in the hospital, with a minimum of 200 net ft2 (18. When patients with significant medical or obstetric complications receive care in the labor and delivery area, the capabilities of the unit should be identical to those of an intensive care unit. Delivery can be performed in a properly sized and equipped labor, delivery, and recovery room. A comfortable waiting area for families should 42 Guidelines for Perinatal Care be adjacent to the labor, delivery, and recovery room, and restrooms should be nearby. Traditional delivery rooms and cesarean delivery rooms are similar in design to operating rooms. Vaginal deliveries can be performed in a labor, delivery, and recovery room or cesarean delivery room; cesarean delivery rooms are designed especially for that purpose and, therefore, are larger. Each room should be well lit and envi ronmentally controlled to prevent chilling of the woman and the neonate. The World Health Organization recommends that during delivery, rooms be kept at 25?C (77?F) or higher to prevent hypothermia, especially in low birth weight, premature infants. Cesarean deliveries should be performed in the obstetric unit or designated operating unit, and postpartum sterilization capabilities should be available in that area when appropriate. It is recommended that at least one family member is present at the time of delivery. Each labor, delivery, and recovery room should have the following equip ment and supplies necessary for normal delivery and for the management of complications: Equipment for administration of all types of anesthesia, including equip ment for emergency resuscitation of the patient. Designated area for neonatal resuscitation and stabilization (as defined in Neonatal Functional Units? later in this chapter). Scrub sinks strategically placed to allow observation of the patient Trays containing drugs and equipment necessary for emergency treatment of both the mother and the neonate should be kept in the delivery room area. Inpatient Perinatal Care ServicesCare of the Newborn 4343 Equipment necessary for cardiopulmonary resuscitation also should be easily accessible. Instruments should be prepared and sterilized in a separate room; alternatively, these services may be performed in a separate area or by a central supply facility. There also should be a room for the storage and preparation of anesthetic equipment; a room or unit for medication storage, preparation, and distribution; a clean workroom and supply room; and an environmental services room for house keeping supplies and equipment. Cesarean delivery rooms should additionally have available the following support areas: a control and nurse station, a soiled workroom, and a fluid waste disposal room or area. The postpartum unit should be flexible enough to permit the comfortable accommodation of patients when the patient census is at its peak and allow the use of beds for alternate functions when the patient census is low. Ideally, rooms are occupied by a single family and equipped for newborn care, and the patient and her neonate are admitted to the room together. Each room in the postpartum unit should have a handwash ing sink and, if possible, a toilet and shower. When this is not possible and it is necessary for patients to use common facilities, patients should be able to reach them without entering a general corridor. When the patient is breastfeeding, the room should have a handwashing sink, a mobile bassinet unit, and supplies necessary for the care of the newborn. Larger services may have a specific recovery room for postpartum patients and a separate area for patients at high risk. The equipment needed is similar to that needed in any surgical recovery room and includes equipment for monitoring vital signs, suctioning, administering oxygen, and infusing fluids intravenously. Bed Need Analysis Historically, the calculation of the number of patient rooms needed for all phases of the birth process was based on a simple ratio that involves the num ber of births, the average length of stay, and the accepted occupancy level. To best estimate patient room needs, each delivery service should thoroughly analyze functions, philosophies, and projections that will determine the types and quantities of rooms needed. An analysis of the present patterns of care 44 Guidelines for Perinatal Care should be reviewed, and consideration should be given to the following types of information: Present (and projected) number of women in the unit during peak periods, as well as the length and frequency of the peak periods. Anticipated changes in technology One planning method is to carefully analyze the activities that will occur in each type of room. For example, labor, delivery, and recovery rooms should not be used routinely to accommodate care, such as outpatient testing, when another room would provide a more appropriate setting. Rooms that allow adequate privacy are recommended for the entire birth process, from labor through discharge. Planning the number of labor, delivery, and recovery rooms requires that consideration be given to these additional questions: Will patients scheduled for cesarean delivery use labor, delivery, and recovery rooms or other types of patient rooms for their preoperative, recovery, and postpartum stays? If so, the length of stay and volume of all these activities must be considered in the calculation of bed need. Once the data have been accumulated, the following normative formula can be used to calculate the number of rooms needed by type of room (note that patient episodes?cases or activities?is used rather than the number of births): Number of patient episodes (considering all activities, such as admission, observation, and transitional care, in this room) For more precise estimates, computerized simulation models are available commer cially. However, many of these software packages are expensive and require a significant investment of time for adequate training and use. Often this software will be purchased by a hospital planning department and models developed for each service as needed. Alternatively, some expert consulting firms that special ize in maternal?child services can provide an on-site assessment of obstetric capacity and perform a bed need analysis using their own proprietary simula tion software. Consistency of nursing care and efficiency of staffing may be enhanced by having a mix of neonatal patients in a single area. Local circumstances should be considered in the design and management of these care areas. If resuscitation takes place in the labor, delivery, and recovery room, the area should be large enough to allow for proper resuscitation of the newborn without interference with the care of the mother. Items contaminated with maternal blood, urine, and stool should be kept physically distant from the neonatal resuscitation area. The thermal environment for infant resuscitation should be maintained by use of an infant warmer or overhead source of radiant heat. When delivery of a preterm infant is anticipated, the temperature of the room should be increased. This space may be used for multiple purposes, including resuscitation, stabilization, observation, examination, or other infant needs. These areas should have adequate suction, oxygen, compressed air, and electrical out lets to accommodate simultaneous resuscitation of twins. A separate resuscita tion room also should have an electrical outlet to accommodate a portable X-ray machine, if needed. Electrical outlets should conform to regulations for areas in which anesthetic agents are administered. Physical separation of the mother and her newborn during this period should be avoided. This evaluation may take place within one or more areas, including the room in which the mother is recovering, the labor, delivery, and recovery room, or the mother?baby unit. No special or separate isolation facilities are required for neonates born at home or in transit to the hospital. The capacity required depends on the size of the delivery service and the duration of close observation. The number of observation stations required depends on the birth rate and the length of stay in the observation area. The admission and observation area should be well lit and should contain a wall clock and emergency resuscitation equipment similar to that in the designated resuscitation area. When the admission and observation is in a labor, delivery, and recovery room, the neonate remains in the room with the mother for breastfeeding. Healthy neonates are never separated from their healthy mothers, and they are kept with their mothers in the labor, delivery, and recovery room at all times. In facilities where the mother must be transferred from the delivery room to a postpartum room, the newborn also is admitted 48 Guidelines for Perinatal Care to the postpartum room. Neonatal Care Units Within each perinatal care facility there may be several types of units for newborn care. These units are defined by the content and complexity of care required by a specific group of infants. As in the resuscitation and stabilization area and the admission and observation area, equipment for emergency resus citation is required in all neonatal care areas. Recommendations regarding the intensity of care are made in the following paragraphs. A separate newborn nursery is available for infants who require closer observation or whose mothers cannot care for them. In addition to providing care for healthy term infants, a level I neonatal unit can provide care for late preterm infants born at 35?37 weeks of gestation who are physiologically stable. These neonates are not ill but may require frequent feeding and more hours of nursing care than healthy term neonates. Level I units in hospitals without higher level units also have the equipment and per sonnel to stabilize newborns who are ill or are born at less than 35 weeks of gestation until they can be transferred to a higher level facility. Because relatively few staff members are needed to provide care in the newborn nursery and bulky equipment is not needed, 24 net ft2 (2. Bassinets should be at least 3 ft (approximately 1 m) apart in all directions, measured from the edge of one bassinet to the edge of the neighboring bassinet. In this type of setting, one neonatal registered nurse is recommended for every 6?8 neonates requiring routine care, and the nurse should be available in each newborn-occupied area at all times (see also Nurse?Patient Ratios? earlier in this chapter). During decreased patient occupancy, central nurseries use nursing staff inefficiently. The newborn nursery should be well lit, have a large wall clock and a sink for handwashing, and be equipped for emergency resuscitation. One pair of wall-mounted electrical outlets is recommended for every two neonatal sta tions. One oxygen outlet, one compressed-air outlet, and one suction outlet are recommended for every four neonatal stations. Cabinets and counters should Inpatient Perinatal Care ServicesCare of the Newborn 4949 be available within the newborn care area for storage of routinely used supplies, such as diapers, formula, and linens. If circumcisions are performed in the nurs ery, an appropriate table with adequate lighting is required. Sick neonates who do not require intensive care but who require 6?12 hours of nursing care each day should be cared for in a special care nursery. A special care unit also may be used for convalescing neo nates who have returned to specialty facilities from an intensive care unit in an outside facility or have been transferred from a higher level of care within the institution. The neonatal special care area is optimally close to the delivery area, cesarean delivery room, and the intensive care area (if there is one in the same facility) and away from general hospital traffic. It should have radiant heaters or incubators for maintaining body temperature, as well as infusion pumps, cardiopulmonary monitors, and oximeters. In facilities where the special care unit is the highest level of neonatal care, equipment should be available to provide continuous positive airway pressure and, in some units, equipment may be available to provide short-term (less than 24 hours) assisted ventilation.
400mg skelaxin visa. 7 Natural Muscle Relaxants for Muscle Tension.
References
- McGettigan P, Henry D. Cardiovascular risk and inhibition of cyclooxygenase: a systematic review of the observational studies of selective and nonselective inhibitors of cyclooxygenase 2.
- Peacock JF, Greven CM, Couz JM, et al. Reactivation toxoplasmic retinochoroiditis in patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation: is there a role for chemoprophylaxis? Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995;15:983-987.
- Van Veenendaal MB, Liem KD, Marres HAM. Congenital absence of the trachea. Eur J Pediatr 2000;159:8-13.
- Luukkonen P, Mikkonen U, Jarvinen H. Abdominal rectopexy with sigmoidectomy vs. rectopexy alone for rectal prolapse: a prospective, randomized study. Int J Colorectal Dis 1992;7:219-22.
- Michelet FX, Deymes J, Dessus B. Osteosynthesis with miniaturized screw plates in maxillofacial surgery. J Maxillofac Surg 1973;1:79-84.
- Colen S, Haverkamp D, Mulier M, van den Bekerom MP. Hyaluronic acid for the treatment of osteoarthritis in all joints except the knee: what is the current evidence? BioDrugs 2012; 26(2):101-12.
- Baas P, Fennell D, Kerr KM, et al. Malignant pleural mesothelioma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 2015;26(Suppl 5):v31-v39.
- Chapple CR, Kaplan SA, Mitcheson D, et al: Randomized double-blind, active-controlled phase 3 study to assess 12-month safety and efficacy of mirabegron, a-(3)-adrenoceptor agonist, in overactive bladder, Eur Urol 63(2):296n305, 2013.