Archana Dixit MD, MRCOG
- Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
- West Middlesex University Hospital NHS Trust
- Isleworth, Middlesex, UK
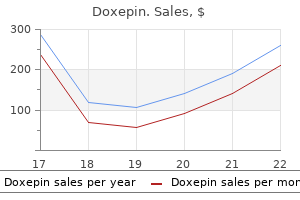
Increase in chronic or recurrent rhinitis anxiety symptoms nausea cost of doxepin, rhinoconjunctivitis and eczema among schoolchildren in Greece: three surveys during 1991-2003 anxiety symptoms jaw pain cheap doxepin 75 mg with visa. Changes in frequency of asthma attributable to atopy anxiety yellow pill buy 75mg doxepin, during 23 years (1987-2009) anxiety early pregnancy generic doxepin 25 mg with amex, in Greece anxiety 4 weeks pregnant buy genuine doxepin online. A Greek cohort study Bacopoulou F anxiety level test generic doxepin 75mg without prescription, Veltsista A, Vassi I, Gika A, Lekea V, Priftis K, Bakoula C. Priftis K, Panagiotopoulou-Gartagani P, Tapratzi-Potamianou P, Zachariadi-Xypolita A, Sagriotis A, Saxoni-Papageorgiou P. Major allergen triggers that are implicated Parietaria pollen in the development or exacerbation of Grass pollen allergic disease Olea europea pollen House dust mites Mold spores (primarily alternaria, cladosporium) References: A 10-year aerobiological study (1994-2003) in the Mediterranean island of Crete, Greece: trees, aerobiologic data, and botanical and clinical correlations. Prevalance of atopic sensitization among young adults from different parts of Greece. Skin test reactivity to various aeroallergens in atopic subjects from Central and Southern Greece. In our country with more than double the number of physicians required for our population, it becomes obvious why such a problem exists. In this regard, our International Scientifc Organizations should help by writing in large print on Membership certifcates, that this is not a Specialty Title. More important yet, our patients need to be trained (by allergists too) to recognize alternative witchcraft from some modes of alternative medicine that appear to help some patients with mild allergic problems, associated with an overload of undue stress. Mild cases excluded, long term control and management rests with specialists as well. There are no organized courses on allergy diagnosis and treatment during General Practitioner specialization. Efforts required for improved patient care are underway to introduce diploma courses in allergy at some centers. Trends in the prevalence of asthma symptoms and allergic diseases in Israeli adolescents: results from a national survey 2003 and comparison with 1997. Prevalence and risk factors for allergic rhinitis and atopic eczema among schoolchildren in Israel: results from a national study. Hospital admission trends for pediatric asthma: results of a 10 year survey in Israel. Major allergen triggers that are implicated House dust mites in the development or exacerbation of Olive pollen allergic disease Cypress olive Parietaria (pellitory) Grass pollens References: Waisel Y et al. Safety and effcacy of allergen immunotherapy in the treatment of allergic rhinitis and asthma in real life. Comparison of positive allergy skin tests among asthmatic children from rural and urban areas living within small geographic area. Emergency room visits of asthmatic children, relation to air pollution, weather, and airborne allergens. They continue to treat their patients as advised, with further follow up and treatment in allergy clinics as needed. Differences in parentaland self-report of asthma, riniti and eczema among Italian adolescents. Verlato G, Corsico A, Villani S, et al Is the prevalence of adult asthma and allergic rhinitis still increasingfi Changes in prevalence of asthma and allergies among children and adolescents in Italy: 19942002. Exposure to indoor allergens and association with allergy symptoms of employees in a work environment. Surveys on the prevalence of pediatric bronchial asthma in Japan: a comparison between the 1982, 1992, and 2002 surveys conducted in the same region using the same methodology. Major allergen triggers that are implicated House dust mite in the development or exacerbation of Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica) pollen allergic disease Other pollens Fungi Animal danders References: Miyamoto T, et al. Allergic identity between the common foor mite (Dermatophagoides farinae Hughes, 1961) and house dust as a causative antigen in bronchial asthma. The annual socio-economic costs of Some data available at: allergic diseases Statistics by Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Japan, 2006. In recent years there has been greater awareness and recognition of the importance of the specialty of allergy. Additionally, Japanese Society of Allergology and Japanese Medical Association conduct training workshops and seminars to educate the general practitioners. Enhancements required for improved More standardized allergens need to be made available in Japan. There is no consensus on the diagnosis of drug allergy, and a preventive strategy for drug allergy is needed. Education on allergic diseases at school for children and their parents are needed, especially to treat food allergy and anaphylaxis appropriately. Insurance coverage for allergic diseases is insuffcient and this needs to be addressed. Most certifed allergists practice in urban areas, so there is a need for better allergy services in rural areas. For 13-14yrs old (wheeze ever, current wheeze (within the last 12 months), and physician diagnosis of asthma are 25. Major allergen triggers that are implicated Salsola in the development or Chenopodium album exacerbation of allergic disease Bermuda grass Dermatophagoides pteronnysinus German cockroaches Reference: Salsola pollen as a predominant cause of respiratory allergies in Kuwait Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. More epidemiological studies are needed to ascertain the extent of the allergic disease burden. We need more allergists working in country areas, because the majority of allergists are working in Riga, the capital of Latvia. Currently, the Credentialing Committee of the immunology National Specialist Register, Academy of Medicine Malaysia, has taken up the matter and initiatives are underway to form the Clinical Immunology Credentialling Subcommittee (which will include Allergy) and create a training program for paediatricians and physicians. Enhancements required for improved Patient care would be enhanced by the recognition of clinical immunology and allergy as a medical (internal patient care medicine and paediatrics) sub-speciality. Better training in allergy is required at the undergraduate level and for General Practitioners. The creation of specialist centers, and epidemiological studies to assess the socio-economic burden of allergic diseases, are needed. More education is required, targeted appropriately for specialists, pediatricians, general practitioners, allied health workers and patients. Allergists work immunology service provision between in the third level hospitals and private allergy and asthma clinics in cities. Promote the need for health insurance system to cover the costs of allergic disease, including immunotherapy. Rural immunology service provision between areas are neighboring urban areas where allergy services are provided, and most patients would have to urban and rural areas travel less than 150 miles for an allergy service. Enhancements required for improved We need to include allergy teaching in medical university programs and to recognize allergy as a specialty. Asthma in every ffth child in Oslo, Norway: a 10-year follow up of a birth cohort study. Lifetime prevalences and association with sex, age, smoking habits, occupational airborne exposures and respiratory symptoms. Allergy adjuvant effect of particles from wood smoke and road development or traffc. There are great geographical differences in the availability of immunotherapy provision between urban and rural areas services, and this is more seldom offered in rural areas. Enhancements required for improved the lack of a formalization of allergology may be the reason for the fragmented education about allergic patient care diseases, for both undergraduate medical students and specialists in Norway. The competence should be linked to service at an allergy center for 1-2 years, and a structured education in allergology. General practitioner training in allergy Though we hold continuous medical education lectures sponsored by the pharmaceutical industry, and we diagnosis and treatment hold a National congress every 2-3 years, there is a lack of knowledge within our general practitioners. We have made history by starting the frst allergy and clinical immunology trainingprogram in Panama in 2010. We have have a plan to gradually grow the specialty and society for the better management of allergies in our country. However, in recent years through several diagnosis and treatment courses we are trying to change this situation. However, there is a large patient care defcit in the training of doctors in immunlogy and allergy. Sensitization to common aeroallergens in children with allergic respiratory diseases at a tertiary hospital. In 1972, these allergists formed the Philippine Society of Allergology and Immunology, thus formalizing the existence of the distinct subspecialty in the country. General practitioner training in allergy Allergy and Immunology is part of the medical curriculum, both in Internal Medicine and Pediatrics in all diagnosis and treatment medical schools. This would be facilitated by arranging for new allergists to spend patient care time studying in centers abroad, and by easier, affordable access for clinicians to information and education about allergy. Epidemiological studies are required to assess prevalence of allergic diseases on a regular basis. Research grants are needed to support the implementation of management guidelines for allergic diseases. Tendencies in epidemiology of allergic diseases in Russian Federation during last 10 years (in Russian). Adult asthma prevalence, morbidity and mortality and their relationships with environmental and medical care factors in Singapore. A population-based questionnaire survey on the prevalence of peanut, tree nut, and shellfsh allergy in 2 Asian populations. Association of ambient air-pollution levels with acute asthma exacerbation among children in Singapore. Utilization of healthcare resources for asthma in Singapore: demographic features and trends. There are no allergy practicing nationally subspecialty fellowships, and most allergists have done their subspecialty training in overseas institutions. Many physicians with little allergy specialist training practice allergy, eg, dermatologists, otolaryngologists. General practitioner training in allergy the conditions are very common, and general practitioners manage them at primary level and refer the diagnosis and treatment problem cases. Allergy practice in patient care institutions is carried out by specialists and academics, although the bulk of care is conducted at the primary care level. The greatest challenge is the small critical mass of specialists due to the small population. This is based pollutants that are implicated in the on an environmental impact study. The Allergy Society of South Africa also conducts diagnosis and treatment congresses and workshops for General Practitioners. We also have an urgent need for epidemiological studies to assess the economic impact of allergic disease. Association between sensitization to outdoor spider mites and clinical manifestations of asthma and rhinitis in the general population of adults. Neither General Practitioners nor Pediatricians receive specifc training about the diagnosis and treatment of allergic diseases during their education. If General Practitioners have a special interest they usually attend an allergy department for one month during postgraduate training. Some regions have allergy urban and rural areas services only in Private Hospitals but not in Public Hospitals. Proceedings of 4th Scientifc Sessions, Allergy and Immunology Society of Sri Lanka. A descriptive pilot study of allergic rhinitis Proceedings of 4th Scientifc sessions, Allergy and Immunology Society of Sri Lanka. Proceedings of 4th Scientifc sessions, Allergy and Immunology Society of Sri Lanka. Atopy, allergic diseases and soil-transmitted nematode infections in children in Sri Lanka. In addition, adrenaline auto-injectors are not available for most patients with anaphylaxis, and this inadequacy needs to be addressed. There is a clear geographical variation between southern and immunology service provision between northern Sweden with much higher density of services in southern Sweden. Determination of multiple allergenspecifc IgE by microfuidic immunoassay cartridge in clinical settings. Prevalence of asthma, allergic rhinitis and eczema among university students in Bangkok. Vichyanond P, Sunthornchart S, Singhirannusorn V, Ruangrat S, Kaewsomboon S, Visitsunthorn N. Boonsawat W, Charoenphan P, Kiatboonsri S, Wongtim S, Viriyachaiyo V, Pothirat C, Thanomsieng N. Survey of the prevalence of asthma, allergic rhinitis and eczema in schoolchildren from Khon Kaen, Northeast Thailand. More specialists immunology service provision between are available in urban than in rural areas. Most of the studies have concentrated on the prevalence of asthma in both children and adults from different regions of the country. General practitioner training in allergy General practitioners do receive training in allergy diagnosis and treatment but the level of knowledge is not diagnosis and treatment at the desired level. This training is received during medical school at the level of undergraduate training. The creation of specialist centers with good communications between these centers and primary care (the hub and spoke model) would greatly enhance patient care. Epidemiological studies are needed to assess the socio-economic burden of allergic diseases. American Lung Association, Epidemiology and Statistics Unit, Research and Program Services. Allergic Rhinitis is estimated to affect approximately 60 million people in the United States, and its prevalence is increasing.
Participants should claim only the credit com m ensurate w ith the extent of their participation in the activity anxiety 9 code doxepin 25mg with mastercard. Coinfection Sept11 G enital D erm atology N icholas V an W agoner anxiety 8 weeks pregnant buy 75mg doxepin mastercard, M D anxiety knee pain generic doxepin 10 mg with mastercard, PhD U niv anxiety yoga poses generic 25 mg doxepin otc. Isolation or detection of other organisms such as Group A streptococcus anxiety symptoms gad cheap doxepin online mastercard, Group B streptococcus anxiety symptoms heart flutter buy doxepin 25 mg low price, Staphylococcus aureus, and others may be associated with certain specific clinical syndromes or risk of infection in the neonate. Proper handling, transport, processing and plating of specimens with selective, non-selective and enriched media, and incubating under specific environmental conditions will facilitate the recovery of fastidious genital tract pathogens such as Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Processing of specimens: See Specimen Processing Procedure a) Direct Examination: Not indicated. Introduction Many women carry Group B streptococcus (Streptococcus agalactiae) in their vagina or large bowel. This organism may be transmitted to the neonate as it passes through the birth canal, resulting in potentially devastating systemic disease in the newborn. Processing of Specimens: See Specimen Processing Procedure a) Direct Examination: Not indicated. References National consensus statement on the prevention of early onset of Group B Streptococcal infection in the newborn. Canadian Pediatric Society and the Society of Obstetricians and Gynecologists of Canada. Introduction the most common causes of adult vaginitis are Candida albicans, Trichomonas vaginalis, and bacterial vaginosis which can be diagnosed using a wet mount and gram stain. For pre-pubescent and post-menopausal patients, laboratory diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis has not been validated and interpretation of gram stain results needs to take this into account. Processing of Specimens: See Specimen Processing Procedure a) Direct Examination: i. Place a cover slip on the slide and examine under the microscope using the 40X objective. Gram stain: Examine for the presence of yeast, clue cells and organisms associated with bacterial vaginosis. Observe for the presence of the following morphotypes: Large gram-positive bacilli (Lactobacillus spp. Calculate a total numerical score by summing the scores for the three components as indicated in the following table and examples: LactobacilliNugent Scorespp. Introduction Vaginal infections are occasionally caused by Staphylococcus aureus and beta-hemolytic streptococci (not S. Toxic-shock syndrome may be associated with vaginitis or vaginal colonization due to S. Introduction Urethritis is usually caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae or Chlamydia trachomatis. Gonococcal urethritis can be diagnosed with excellent specificity by Gram stain of the urethral exudate. Reporting Results Gram stain: Quantitate and report the presence or absence of pus cells and gram negative diplococci. Introduction Irritation and cellulitis of the penis can be caused by organisms that cause typical wound infections. Reporting Gram stain: Report with quantitation presence of pus cells and organisms. Introduction Bacterial infections of the seminal tract have been postulated to potentially play a role in male infertility. However, bacteria in these concentrations may also represent contamination given the circumstances of sample collection and colonization of the peri-urethral orifice. However, most cases of endometritis follow childbirth, and it has been demonstrated that in the postpartum period, whether or not there is endometrial infection, significant numbers of anaerobes and other organisms from the cervical and vaginal flora may be found in the uterine cavity. Although any organism may cause infection of the placenta, the most common organisms associated with this syndrome include S. Reporting Results Gram stain: Report with quantitation the presence of the pus cells and organisms. Propionibacterium acnes: Time-to-Positivity in Standard Bacterial Culture From Different Anatomical Sites. Anaerobic thioglycolate broth culture for recovery of Propionibacterium acnes from shoulder tissue and fluid specimens. Optimal culture incubation time in orthopedic device-associated infections: A retrospective analysis of prolonged 14-day incubation. Introduction the most common bacterial causes of genital ulcers are syphilis (Treponema pallidum). Processing of Specimens: See Specimen Processing Procedure a) Direct Examination: Gram stain of secretions. Examine for the presence of branching gram positive bacilli suggestive of Actinomyces species. Mazzulli Seminal Fluid change to use pipette instead of swab to March 28, 2014 Dr. Incubate plates Add Strep anginosus grp to non-seminal tract pathogens September 29, 2015 Dr. The randomisation was done by blocks Biostatistics and Data Science of four or six for each site. The primary outcome was (Prof L Myers PhD),Tulane T vaginalis infection by intention to treat, at test-of-cure 4 weeks after completion of treatment. The analysis of the University School of Public primary outcome per nucleic acid amplifcation test or culture was also stratifed by bacterial vaginosis status. This trial Health and Tropical Medicine, Tulane University, is registered with ClinicalTrials. Although planned enrolment had been 1664 women, the study was of Infectious Diseases stopped early because of funding limitations. Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center, Funding National Institutes of Health. Parasitic Diseases and Malaria, Centers for Disease Control and Introduction and preterm delivery) in women. The purpose of this study was to re-evaluate the sexually transmitted infection worldwide. A single 2 g dose of oral metronidazole examine treatment diferences by bacterial vaginosis status. A meta-analysis of six published studies metronidazole is superior to single-dose metronidazole for found that multiple doses of metronidazole resulted in fewer the treatment of trichomoniasis in women, irrespective of treatment failures than single-dose treatment. We found that women receiving the 7-day-dose and willingness to be randomly assigned to either of the metronidazole treatment were half as likely to be T vaginalisstudy groups. A secondary aim was to examine to be randomised, and inability or unwillingness to return treatment diferences by bacterial vaginosis status. An openindependent Data Safety and Monitoring Board monitored label design was used to simulate real-world conditions the data every 6 months, with a priori stopping rules. Because of the this assay was allowed for investigational use only, and sensitive nature of the surveys both at enrolment and was performed by use of the direct tube sampling system. After eligibility screening and written informed consent, the cultures were considered T vaginalis-positive if any the participants were asked to take a survey, provide live trichomonads were detected, and T vaginalis-negative urine for pregnancy testing, and self-collect vaginal after three negative pouch readings. A list containing the envelope number asked to take the frst dose at the clinic under direct and allocation group was kept in an electronic fle that observation by study staf and were ofered crackers or was not accessed until the end of the study. For the participants in the were kept at each site, and study staf pulled envelopes treatment group, the remaining pills were dispensed in a sequentially and documented the treatment group, container with a child-proof cap. All patients, clinicians, and study staf were their sexual partners of their exposure to T vaginalis aware of the allocation, but the treatment group was and to encourage them to seek treatment. Participants in the treatment, symptoms during follow-up, and side-efects treatment group were also advised on the importance of of the medication (including nausea, vomiting, and taking all doses of the medication. It provides an intuitive interface for 270 completed treatment 270 completed treatment validated data entry, audit trails for tracking of data manipulation and export procedures, automated export procedures for seamless data downloads to common 312 included in intention-to-treat analysis 311 included in intention-to-treat analysis statistical packages, and procedures to import data from 270 included in per-protocol analysis 270 included in per-protocol analysis external sources. We measured the baseline characteristics associated Figure:Trial profle with trichomonas infection. Intention-to-treat analyses for Outcomes all randomised participants were stratifed by baseline the primary outcome was a T vaginalis-positive result at bacterial vaginosis status. Allocation was masked from technicians treat population, by reclassifying all missing results as at all sites. The proportion of patients with follow-up these events did not difer signifcantly by study group. Amsel criteria37 had been used been favoured over 7-day-dose treatment, because to test for bacterial vaginosis at the clinics. Symptoms for adherence to treatment is not an issue, especially if the bacterial vaginosis and trichomoniasis are often similar,7 patient is under direct observation by a clinician. Indeed, in this study selfmetronidazole for trichomoniasis, providing further reported adherence was higher among patients receiving rationale for recommending 7-day-dose metronidazole as the single dose compared with patients receiving the frst-line treatment for trichomoniasis. The majority trichomoniasis should be upheld even for those women of women who enrolled were African American. More studies of women with asymptomatic7 tested for T vaginalis with culture, we found a reduced trichomoniasis are needed. The diference We chose to use an open-label study design to factor in between groups might be due to chance, and reviews43,44 real use conditions, although masking participants to have found that multiple doses of metronidazole are safe treatment is often preferred. Strengths of the study were that study design, treatment duration and follow-up times randomisation appeared to work well, as baseline were diferent for each treatment group, which could characteristics were similar by group (table 1), loss to have resulted in diferences in sexual exposure. Moreover, the reported sexual behaviour might not be accurate, we intention-to-treat, modifed intention-to-treat, and other used computer-assisted interviews, which have been sensitivity analyses were consistent with each other. Treatment of trichomonal vaginitis with a single oral Hologic and GlaxoSmithKline. Molecular testing for Rhonda Whidden, Meghan Whitfeld, Christen Press, Jim Alosi, Trichomonas vaginalis in women: results from a prospective U. Center we thank the laboratory staf, including Catherine Cammarata, Judy Burnett, and Denise Diodene. The infuence of bacterial the prevalence and incidence of four curable sexually transmitted vaginosis on the response to Trichomonas vaginalis treatment among infections in 2012 based on systematic review and global reporting. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment bacterial vaginosis is improved by a standardized method of Gram guidelines, 2015. Metronidazole for vaginal evidence-based care of symptomatic trichomoniasis and trichomoniasis. Coexistence in vaginal wet mount preparations from 40 Kissinger P, Rice J, Farley T, et al. In addition to the determination of diagnostic parameters, the culture of vaginal content and a Papanicolaou cytology test were also performed. Among the diagnostic clinical criteria, the presence of clue-cells was positive in 275 women (99. Culture of the vaginal content permitted the identifcation of Gardnerella vaginalis in 96. Oncotic colposcopy revealed a very scarce presence of lactobacilli, which were present in only 8 cytological exams (2. These fndings indicate the need for further studies that might better elucidate the interrelations between the microbiological fndings and the clinical expression of bacterial vaginosis. Bacterial vaginosis in pregnancy: diagnosis, screening, vaginal fuid of pregnant women with bacterial vaginosis. Nonspecifc vaginitis: diagnostic criteria and microbial and epidemiologic associations. Bacterial vaginosis in sexually experienced and non-sexually and Chlamydia trachomatis infection with adverse pregnancy experienced young women entering the military. Comprehensive Endotoxin and interleukin-1 alpha in the cervical mucus and gynecology. After a period clitoris, labia minora and labia with thick seams and G there may be minimal majora. If you are maintains a normal healthy use cold compresses concerned about the health, acidic environment. For more information about Is my vaginal discharge labias and normal variants normalfi These types of not usually transmitted through bacteria seem to overgrow in sexual intercourse and are not much the same way as considered a sexually Candida. As information and knowledge is constantly changing, readers are strongly advised to confirm that the information complies with present research, legislation and policy guidelines. True accepts no responsibility for difficulties that may arise as a result of an individual acting on the advice and recommendations it contains. It is most 1,3 common in women aged 20-30 and in pregnancy as oestrogens promote its growth. Vaginal microbial flora in women with and without vaginal discharge registered in general practice. The management of women of reproductive age attending non-genitourinary medicine settings complaining of vaginal discharge. Comprehensive guide on the assessment, investigation and management of women presenting to nongenitourinary medicine settings with infective vaginal discharge. Useful short overview on the management of chlamydia and management issues you should cover with the patient. Prospective study of almost 500 women examining symptoms in Chlamydia trachomatis. This review covers near patient diagnosis and indicates pH is an under-utilised test. It looked at pH with culture of Streptococci, Gardnerella vaginalis and mixed organisms compared to yeasts and normal flora. This study examined 252 women with vaginal discharge in an Australian sexual health centre.
Order 75mg doxepin. 10 Signs of Emotional Abuse.
High-dose therapy and autologous mediated immune responses by 8-methoxypsoralen and stem cell transplantation in relapsing cutaneous lymphoma anxiety and chest pain discount 25 mg doxepin mastercard. High-dose stage: a report from the Scandinavian mycosis fungoides therapy and bone marrow transplantation in cutaneous Tgroup anxiety dreams generic 10mg doxepin otc. Photochemotherapy of allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation in adSezary syndrome anxiety symptoms over 100 order 75 mg doxepin overnight delivery. The dosimetry characteristics of a dual-field Stanford technique treatment of mycosis fungoides: adjuvant topical mechlorethto a customized single-field Stanford technique for total amine after electron beam therapy anxiety symptoms 9 weeks buy doxepin 25mg free shipping. Di Guglielmo R anxiety in children doxepin 10mg without prescription, Miliani A anxiety symptoms tongue buy cheap doxepin 75 mg on-line, Avanzi G, Cozzolino F, Duminuco assessment in patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Effectiveness of topical naloxone, an opioid antagmycosis fungoides: results of a 10-year follow-up. Systemic chemotherapy and extracorposin in treatment-refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: final real photochemotherapy for T3 and T4 cutaneous T-cell results from a phase 2B, international, multicenter, registralymphoma patients who have achieved a complete response tion study. On one side are academicians, pharmaceutical companies, and government agencies, who claim the disease is usually mild and virtually always easily cured. On the other side are chronic Lyme disease patients and their doctors, who say that infection may survive the standard four weeks of antibiotic treatment, and that its impact may be debilitating and difficult to treat. This report adds another dimension to the debate by focusing on Lyme disease as a business model. An examination of patents, marketing agreements, and revenue streams reveals the potential for the appearance of conflict of interest for many of the individuals setting Lyme disease policy. These policies, created in part to enable the analysis of data required for product approval, have also served to disenfranchise large numbers of infected patients no longer meeting the official standard for diagnosis with the disease. Untreated by physicians and uncovered by insurance companies, these patients have become increasingly ill. In the pages that follow we will detail the straightforward path of revenue and its relationship to multinational pharmaceutical companies, venture-backed biotechnology firms, government agencies, and academicians. As long as the status quo is allowed to stand, large numbers of people exposed to this rapidly emerging infection will continue to go undiagnosed and untreated for Lyme disease, and will be placed at severe risk for lifelong health problems, including arthritis, neurological impairment, psychiatric illness, cardiac illness, gastrointestinal disease, and more. It is most commonly transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected Ixodes scapularis or Ixodes pacificus tick in its ecosystem of choice-the shaded, woody areas of the suburban United States. Though most people still associate Lyme with the single infection caused by the Bb spirochete, recent studies show it can be far more complex. Ticks that carry Borrelia burgdorferi may also carry co-infections such as Ehrlichia and Babesia, leading to a broader definition of Lyme disease in recent years. This creates a dynamic situation with many opportunities for exposure for each individual. But throughout the rest of the state, we see many more cases in other counties, such as Fairfield County, Litchfield County, and New Haven County. In a study done by Matthew Carter and associates at the Connecticut Department of Health, you can see that through an active surveillance, they identified about 1,000 cases among 400 physicians who maintain an active Lyme disease surveillance. With almost 11,000 practicing physicians in Connecticut, the number of cases reported was only about 10 percent of the expected reporting. Atypical forms of this rash, taking on a large variety of forms, are seen far more commonly. The rash can be very small or very large (up to twelve inches across), and can imitate such skin problems as hives, eczema, sunburn, poison ivy, fleabites, and so on. But most practitioners, even those in endemic areas, simply are unaware of the complexity and diverse presentation. The Great Imitator When, due to these diagnostic errors, patients are treated insufficiently or not at all, they become extremely ill. Since the Lyme spirochete can infect virtually any organ in the body, it can mimic many other diseases. Professionals also agree that Lyme disease patients who have gone undiagnosed and now suffer later stage disease may continue to experience debilitating symptoms following a month-long course of antibiotics. All agree that these symptoms-arthritic, neurological, and multisystemic-can last for months, years, or throughout life. While some contend Lyme is underdiagnosed and others that it is overdiagnosed, most recognized authorities believe that initial diagnosis of Lyme disease can be based on blood tests alone. Common Misconceptions on the Part of Physicians Even in the face of this consensus, misunderstandings abound. The First Scientific Controversy: Persistence of Infection Much of the medical mainstream, including the Yale-based physicians who originally studied Lyme disease, contend most cases can be successfully treated with 30 to 60 days of antibiotics, which they contend kills the Lyme spirochete. If symptoms continue, say these physicians, they are probably caused by something other than the Lyme bacteria. Alternatively, they suggest, illnesses unresponsive to a month or two of antibiotic treatment are caused by an unrelated problem, like chronic fatigue syndrome, psychiatric illness, lupus, multiple sclerosis, or fibromyalgia. Moreover, these same physicians question long regimenrs of expensive antibiotics, labeling them as unnecessary and sometimes dangerous. The very sickest patients, who almost universally continue to decline under such treatment protocols, have found their way to a group of clinicians and researchers whose studies and experience stand in powerful opposition to the findings and opinions at Yale. These doctors, including such experts as psychiatrist Brian Fallon of Columbia Presbyterian and Dr. Willy Burgdorfer, the National Institutes of Health scientist who discovered the Lyme spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, say that an audit of the peerreviewed literature reveals no evidence that infection cannot survive the standard 4 weeks of antibiotic treatment. Instead, these clinicians and researchers contend, patients with continuing symptoms are usually ill because the Borrelia burgdorferi spirochete has never been eradicated from the body. W hile the results are not yet in, it may be that all such studies are problematic to one degree or another based on the range of co-infections, known and unknown, and hundreds of borrelia sub-strains, each responding differently to the variety of antibiotics in the arsenal available today. Indeed, While double-blind studies of simple antibiotic protocols have been inconclusive, dozens of peer reviewed studies in microbiology and cell biology journals nonetheless indicate that active, ongoing spirochetal infection is the cause of the persistent symptoms in chronic Lyme disease. To determine this, they studied 63 patients with erythema migrans, the signature skin lesion of Lyme disease, removing the active edge of the rash for biopsy and examining growth in test tube cultures. Preac-Mursic of the University of Munich in Germany cultivated Borrelia burgdorferi from biopsies of the iris and skin as well as samples of cerebrospinal fluid after antibiotic therapy for Lyme borreliosis. Although the patients in this study, by and large, tested negative by Western blot-although they lacked diagnostic antibody titersfihey still had subclinical or clinical disease. Those same spirochetes, grown in fibroblasts cultured in a test tube and then treated with antibiotics, survived as well. Cornell University scientist Rheinhard Staubinger, for instance, infected 16 dogs with Borrelia burgdorferi by tick bite. Four months (120 days) after tick exposure, 12 dogs were treated with antibiotics for 30 days while 4 control dogs were not treated at all. In experiments performed both in vivo and in vitro and presented in the peer-reviewed literature, it has been shown that different strains respond differently or not at all to the host of antibiotics used to treat Lyme disease. Although some medications may be useful for treating Borrelia burgdorferi alone, they may be ineffective against the co-infections. For instance, amoxycillin will be ineffective against Ehrlichia (which requires doxycycline or another antibiotic in the tetracycline family) as well as Babesia (often treated with Mepron. Given these facts, say the clinicians, it is easy to see why a month of low-dose doxycycline or amoxycillin might fail to do the trick when tick-borne disease has been undiagnosed and untreated in an individual for years. According to one theory still under investigation, Bb spirochetes under environmental stress lose their cell walls, becoming resistant to conventional antibiotics. One line of research suggests that when under pressure from its environment, the Lyme disease spirochete loses its cell wall. In doing so, it becomes resistant to the majority of antibiotics, which are engineered to work by attaching to bacterial cell walls. When a given environmental stressor including antibiotic therapyis halted, the spirochetes may come out of hiding and revert to conventional, cell-walled forms. Clinicians say they can treat the cell-wall-deficient forms of the Lyme disease spirochete with Flagyl, an antibiotic that causes them to convert to cell-wall forms, which are vulnerable to conventional antibiotics. Borrelia burgdorferi is undergoing a period of rapid evolution, according to molecular biologists at the University of Utah Medical School, the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, and the Institute for Genomic Research in Rockville, Maryland. These observations lead one to the conclusion that certain subsets of patients with Lyme disease may require prolonged antibiotic treatment and that presently available chemotherapeutic modalities may be suppressing but not eradicating the infection. If a doctor sees Lyme disease as underdiagnosed and thus treats all comers, the actual diagnosis might remain unrecognized and untreated while unnecessary use of antibiotics might lead to antibiotic-resistant infections in the human blood reservoir at large. On the other hand, if a doctor sees Lyme disease as overdiagnosed and thus hesitates to treat, patients will go on to develop late stage, disseminated Lyme disease. By the time such individuals are finally diagnosed, they are often simply too sick to respond to a single month of antibiotics. The overdiagnosis-underdiagnosis debate and the issue of chronicity are key to the quagmire of Lyme disease politics and the conflicts of interest that result. The reason is this: Redefinition in these areas was a prerequisite for launch of Lyme disease products, including vaccines and diagnostic tests. Eugene Shapiro, Steere proved the Connecticut syndrome-named for its epicenter in the town of Lyme-was caused by the bite of an Ixodes tick. Years later, government scientist Willie Burgdorfer of the Rocky Mountain Laboratories discovered that the tick transmitted Lyme disease through a spirochetal bacterium, Borrelia burgdorferi, named after its discoverer. Lyme Disease and Diagnosis But though the critical microbe had been found, the effort to diagnose Lyme remained a challenge, in large part due to the absence of a gold standard laboratory test-one that could culture Bb spirochetes from the blood. These bound antibodies can then be detected when a second solution, which contains antibodies to human antibodies, is added to the preparation. Linked to these second antibodies is an enzyme, which changes color when a certain chemical is added to the mix. To distinguish the false positives from the true positives, the Western blot (also known as an immunoblot) is used. In this test, the laboratory looks for antibodies directed against a wide range of Bb proteins. This is done by first disrupting Bb cells with an electrical current and then "blotting" the separated proteins onto nitrocellulose, nylon, or other synthetic membranes. The current causes the proteins to separate according to their mass, measured in kilodaltons (kDa). If the patient has antibodies to a specific Bb protein, a "band" will form at a specific place on the immunoblot. A layer of complexity is added to analysis because the Western blot report usually contains two parts: IgM and IgG. These are immunoglobulins (antibody proteins) produced by the immune system to fight infection. IgM is produced fairly early in the course of an infection, while IgG response comes later. The IgG response, according to the traditional model, tends to start several weeks after infection and peak months or even years later. Similarly, IgG response can remain strong or decline with time, again regardless of treatment. Assuming normal amounts of variation found in nature, it is a given that unusual banding patterns will occur. Raising the Bar Back in what now seems like the prehistory of Lyme disease testing, the year 1991, these unavoidable variables were magnified by a system mired in chaos. There was, at the time, no agreed-upon standard for what constituted a positive Western blot. Different laboratories used different antigen preparations made from different strains of the Bb spirochete to run the test. Some required a certain number of bands to constitute a positive result, while others required more bands or less. In a study published in February of that year with Frank Dressler and colleagues from Germany, he performed immunoblots on several dozen patients with well-characterized Lyme disease and a strong antibody response. By looking at the resulting blot patterns and doing some fairly involved statistical analysis, the team determined which bands showed up most often and which best distinguished Lyme disease patients from control subjects who did not have Lyme disease. They found that by requiring 2 of the 8 most common IgM bands in early disease and 5 of the 10 most common IgG bands after the first weeks of infection, they could make the results the most specific, in their view, without sacrificing too much sensitivity. This flew in the face of a general consensus that different bands on a Western blot have different relative importance. But these bands correspond to common proteins in many bacteria, not just Borrelia burgdorferi, and so are of limited diagnostic usefulness, especially in the absence of other, more species-specific bands. But it is also the most commonly appearing band in control subjects, probably because people are exposed to a variety of spirochetes throughout life and so their sera might cross-react with this protein. As a rheumatologist, it was only natural that his patients present with a frank arthritis of Lyme, often with a swollen joint. But the study did not include patients from other disciplines, including those who might show up at the office of a gastroenterologist, neurologist, or opthalmologist. Even more puzzling was the omission from consideration of bands at 31 and 34 kDa, corresponding to OspA and OspB, among the most species-specific proteins of the organism. Often absent in early disease, Osps A and B tended to come into prominence as patients become increasingly ill. Prior to referral, 409 of the 788 patients had been treated with antibiotic therapy. The most common reason for lack of response to antibiotic therapy was misdiagnosis. If so, it would mean he had developed a test far beyond the state of the art for 1993, not to mention today. It is difficult to accept uncritically his claim that the antibody testing protocols he uses are so far and away superior to any other without the same independent testing other labs are subjected to . The reasoning is circular: the presumption is that his tests are superior because they render the highest correlation between seropositivity and actual Lyme disease, but the definition of "actual Lyme disease" in the study is derived almost exclusively from the test results generated at his lab. Although false negative serologies are widely recognized as common in early Lyme disease, it is often claimed that they are extremely rare phenomena later in the course of the illness. This approach systematically excludes all patients from areas that have not been investigated for B. Response to treatment required for diagnosis: Of the patients thought to have active Lyme disease, at least 52 had already been antibiotically treated before evaluation by the authors.
This chapter reviews the literature on health economic models published since then that have evaluated population H anxiety fever 75mg doxepin free shipping. The models studied a variety of populations and made different assumptions anxiety symptoms 6 weeks cheap doxepin 75 mg, but all found population H anxiety symptoms go away when distracted buy 75mg doxepin otc. Savings related to dyspepsia were rarely considered in these models anxiety medicine for dogs order 25mg doxepin otc, and none of the studies used data from randomized controlled trials anxiety symptoms rocking purchase 10 mg doxepin mastercard. Summary of economic models that have evaluated population Helicobacter pylori screening and treatment to prevent gastric cancer Reference Country Perspective Population Duration H anxiety symptoms twitching buy doxepin 10 mg on line. Summary of economic models that have evaluated population Helicobacter pylori screening and treatment to prevent gastric cancer (continued) Reference Country Perspective Population Duration H. Summary of the methodology of economic models for population Helicobacter pylori screening and treatment to prevent gastric cancer Reference Type Systematic Discounting Method of Type of Dyspepsia of review of incorporating analysis cost savings model literaturefi Impact of population Helicobacter pylori screening and treatment on dyspepsia after 2 years. Considering these cost savings may make such programmes even cheaper and mean that population H. Other limitations of the current health economic literature are that less than half of studies conduct a probabilistic analysis to evaluate the uncertainty in the data modelled, and even fewer present the data in a way that is meaningful to health-care decision-makers. This type of analysis is needed for other populations using other assumptions relevant to local populations. Although this is a valid approach, it could be argued that societal costs are more important for a 117 national screening programme. Finally, it is important to emphasize that nearly all models reported benefit in terms of life-years saved. This will overestimate the benefit of the programme as most of the life-years saved will be in the elderly, many of whom have other comorbidities that may limit their quality of life. Future economic models should use current systematic review data on the efficacy of H. Uncertainty in the data should be evaluated using probabilistic analyses, and there is no model currently published that fulfils all these criteria. Significance of Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric cancer: implications for screening. The feasibility and results of a population-based approach to evaluating prostate-specific antigen screening for prostate cancer in men with a raised familial risk. Effect of repeated invitations on uptake of colorectal cancer screening using faecal occult blood 118 testing: analysis of prevalence and incidence screening. Effect of population screening and treatment for Helicobacter pylori on dyspepsia and quality of life in the community: a randomised controlled trial. Population-based and opportunistic screening and eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Efficacy and optimum dose of omeprazole in a new 1-week triple therapy regimen to eradicate Helicobacter pylori. Modelling cost-effectiveness of Helicobacter pylori screening to prevent gastric cancer: a mandate for clinical trials. Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer: what are the benefits of screening only for the CagA phenotype of H. Clinical and economic effects of population-based Helicobacter pylori screening to prevent gastric cancer. The cost-effectiveness of population Helicobacter pylori screening and treatment: a Markov model using economic data from a randomized controlled trial. The cost-effectiveness of screening for Helicobacter pylori to reduce mortality and morbidity from gastric cancer and peptic ulcer disease: a discrete-event simulation model. Cost-effectiveness analysis of Helicobacter pylori screening in prevention of gastric cancer in Chinese. Cost-effectiveness analysis between primary and secondary preventive strategies for gastric cancer. Exploring the cost-effectiveness of Helicobacter pylori screening to prevent gastric cancer in China in anticipation of clinical trial results. Illustrating economic evaluation of diagnostic technologies: comparing Helicobacter pylori screening strategies in prevention of gastric cancer in Canada. Impact of Helicobacter pylori eradication on dyspepsia, health resource use, and quality of life in the Bristol Helicobacter Project: randomised controlled trial. Randomised controlled trial of effects of Helicobacter pylori infection and its eradication on heartburn and gastro-oesophageal reflux: Bristol Helicobacter Project. A community screening program for Helicobacter pylori saves money: 10-year follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. Long-term follow-up of 1,000 patients cured of Helicobacter pylori infection following an episode of peptic ulcer bleeding. Search strategy for economics of Helicobacter pylori test and treat to prevent gastric cancer 1. Gastric cancer is also the third leading cause of cancer death in both sexes worldwide, with an estimated 723 000 deaths in 2012. Gastric cancer is one of the leading cancers in many areas of Latin America, particularly in Central America and in the Andean countries. An improved understanding of the natural history of the infection will enable the development of tests for an early diagnosis, or even better, the identification of patients at risk of developing gastric cancer. Most of these factors interact with receptors in gastric epithelial cells to signal different cellular pathways that eventually lead to changes in the expression of genes involved in inflammation, cellular proliferation, invasion, and metastasis. Decades of gastric inflammation may also induce epigenetic changes, such as methylation of genes, that would also lead to carcinogenesis. Considerations All the bacterial or cellular factors described above represent potential biomarkers for risk, early diagnosis, or prognosis for gastric cancer, but there are important considerations in the selection of candidates. The utility of biomarker tests is optimized when they are applied in the right context. Gastric cancer is a multifactorial disease, and a proper combination of markers, including host genetic factors 122. In fact, very few cancer biomarkers already in clinical use have high sensitivity and specificity, and for many of them, whether they really improve cancer outcome is currently questioned. It is in these countries where identification of patients at risk and early disease detection are most needed, but it is also in these countries where resources for health are limited. Regional gastric cancer mortality rates the regional gastric cancer mortality rate is a geographical marker for populations at risk and an important criterion in the selection of populations at greater need of targeted intervention programmes. Most studies to date on the utility of the pepsinogen test have been performed in Asian countries, where evidence shows that it is a useful serological test to identify patients with gastric atrophy. In cardia gastric cancer cases with low PgI levels, the risk increased to an odds ratio of 11. Few studies have been performed in Latin America, and most of them with a small sample size. The study also suggested that serology for CagA antibodies may improve the efficacy to detect atrophic gastritis. Differences between these two Latin American studies are that the gastric cancer mortality rate in Costa Rica is about 2. In another study, conducted in Mexico in 180 healthy volunteers, atrophy was measured in multiple biopsies from antrum and corpus. Thus, more studies are needed in Latin America to better establish the performance of the test and to define cut-off values for the population. Since the test detects atrophic gastritis, it is not effective for screening of diffuse gastric cancer, and performance would vary depending on the proportion of diffuse gastric cancer in the population. Diffuse Intestinal the prevalence of pre-neoplastic lesions would also affect the performance of the test. In addition, the pepsinogen test is still too expensive to use in communitybased screening programmes, particularly in countries in Latin America and Asia that present the highest mortality rates. Still, pepsinogen tests currently represent the most reliable and practical test to screen populations and identify those who deserve close followup by means of invasive endoscopic methods. In particular, patients with atrophic antral gastritis present with low levels of circulating G-17. Current national programmes in Asia Japan and the Republic of Korea, the Asian countries with the highest gastric cancer mortality rates, have national or regional screening programmes to identify early gastric cancer cases. Japan uses barium X-ray as a government-sponsored nationwide programme in asymptomatic individuals older than 40 years. In the Republic of Korea, the National Cancer Screening Program recommends biennial screening for individuals older than 40 years, with direct upper-gastrointestinal series or endoscopy. Novel approaches There are several recent studies searching for markers that may distinguish normal individuals from those with pre-neoplastic lesions, which take advantage of what is being learned about the natural history of gastric cancer. Although they are still far from clinical use or from being recommended in population screening programmes, such markers should be considered for studies in large groups in regions with high gastric cancer mortality rates, particularly in Asia and Latin America, to better elucidate their potential use in a particular population. Clearly, much has been learned about genetic polymorphisms as risk factors for gastric cancer in Asia, particularly Japan and China, but an effort should be made to study this in other human groups with high gastric cancer mortality rates, including other countries in Asia and Latin America. The study of microbiota in the stomach may also show some utility as a marker of risk or prognosis for gastric cancer. Given the diversity of microbiota structure across individuals and across populations, regional studies are needed to gain insight into its diversity in each population. Other considerations It should be kept in mind that gastric cancer is a multifactorial disease and that a proper combination of markers may improve their utility to identify patients at risk. The utility of a biomarker test is optimized when it is applied in the right context. At present none of the suggested biomarkers for gastric cancer has been approved for clinical use, and they are even farther from being ready for use for large-scale screening. When planning for a community screening programme, important points to consider are that the test should be validated for accuracy and high predictive value in the population being studied, and it should be non-invasive, simple, cheap, and accessible. Suggested strategies for Latin America In Latin America, no population strategies have been suggested so far, despite the fact that the region contains areas with gastric cancer mortality rates among the highest in the world. A first approach should consider that the pepsinogen test has not proven as efficient in Latin America as in Asia to detect atrophy. Also important is the reported increasing trend in different countries of the diffuse type of gastric cancer, for which no precancerous lesions have been described yet. Still, an initial selection by country and by district or county might help better target screening programmes. Latin America is a region with limited resources for public health, and an initial screening should be simple and cheap. Probably, after initial selection of districts, screening could be performed in adults older than 40 years for H. How the study of Helicobacter infection can contribute to the understanding of carcinoma development. Asthma is inversely associated with Helicobacter pylori status in an urban population. Hypothesis: the changing relationships of Helicobacter pylori and humans: implications for health and disease. Effect of Helicobacter pylori infection combined with CagA and pepsinogen status on gastric cancer development among Japanese men and women: a nested case-control study. The utility of serologic tests as biomarkers for Helicobacter pyloriassociated precancerous lesions and gastric cancer varies between Latin American 130 countries. Serum pepsinogen levels, Helicobacter pylori CagA status, and cytokine gene polymorphisms associated with gastric premalignant lesions in Costa Rica. Helicobacter pylori cytotoxin-associated genotype and gastric precancerous lesions. Helicobacter pylori CagA seropositivity and gastric carcinoma risk in a Japanese American population. Seroprevalence of cytotoxin-associated gene A positive Helicobacter pylori strains in Changle, an area with very high prevalence of gastric cancer in south China. Relationship between Helicobacter pylori iceA, cagA, and vacA status and clinical outcome: studies in four different countries. Prospective study of Helicobacter pylori biomarkers for gastric cancer risk among Chinese men. Progression of chronic atrophic gastritis associated with Helicobacter pylori infection increases risk of gastric cancer. Correlation between gastric histology and serum levels of gastrin-17 and pepsinogen I: a multicentre 131 study. Importance of atrophic gastritis in diagnostics and prevention of gastric cancer: application of plasma biomarkers. Dinis-Ribeiro M, da Costa-Pereira A, Lopes C, Barbosa J, Guilherme M, Moreira-Dias L, et al. Predicting the development of gastric cancer from combining Helicobacter pylori antibodies and serum pepsinogen status: a prospective endoscopic cohort study. Prescreening of a high-risk group for gastric cancer by serologically determined Helicobacter pylori infection and atrophic gastritis. Implications of serum pepsinogen I in early endoscopic diagnosis of gastric cancer and dysplasia. Pepsinogen A, pepsinogen C, and gastrin as markers of atrophic chronic gastritis in European dyspeptics. The epidemiology of low serum pepsinogen A levels and an international association with gastric cancer rates. Noninvasive versus histologic detection of gastric atrophy in a Hispanic population in North America. Gastric cancer incidence estimation in a resource-limited nation: use of endoscopy registry methodology. Systematic review of the prevalence of gastric intestinal metaplasia and its area-level association with smoking. Gastric parietal cell antibodies, Helicobacter pylori infection, and chronic atrophic gastritis: evidence from a large population-based study in Germany. Screening of atrophic gastritis and gastric cancer by serum pepsinogen, gastrin-17 and Helicobacter pylori immunoglobulin G antibodies. Interleukin-1beta and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist gene polymorphisms and gastric cancer: a meta-analysis.
References
- Rosenberger P, Shernan SK, Mihaljevic T, et al. Transesophageal echocardiography for detecting extrapulmonary thrombi during pulmonary embolectomy. Ann Thorac Surg 2004; 78:862-866.
- Minami Y, Iijima T, Yamamoto T, et al. Diffuse pulmonary hamartoma: a case report. Pathol Res Pract 2005; 200(11-12):813-6.
- Chatterjee S, Sardar P, Biondi-Zoccai G, et al. New oral anticoagulants and the risk of intracranial hemorrhage: Traditional and Bayesian meta-analysis and mixed treatment comparison of randomized trials of new oral anticoagulants in atrial fibrillation. JAMA Neurol 2013;70:1486-90.
- Keenan JP, Solum NO: Quantitative studies on the release of platelet fibrinogen by thrombin. Br J Haematol 1972;23:461-466.