Jeffrey L. Anderson, MD, FACC, FAHA
- Intermountain Healthcare Hospitals
- Salt Lake City, Utah
A position of the body: lying down with the face up arthritis relief in neck purchase diclofenac once a day, as opposed to the Supine position prone position arthritis diet strawberries diclofenac 75mg discount, which is face down arthritis in knee in dogs buy generic diclofenac canada. Appendices Perinatal Oral Health Practice Guidelines Appendices Project Participants Co-Chairs Ellen J arthritis in the knee surgery cheap diclofenac 100 mg online. Dugoni School of Dentistry Sciences Director arthritis pain back of hand order diclofenac with amex, Division of Periodontics Columbia University College of Dental Medicine Appendices Perinatal Oral Health Practice Guidelines Appendices Ronald A arthritis pain scale weather 75mg diclofenac fast delivery. Perinatal Oral Health Practice GuidelinesPerinatal Oral Health Practice GuidelinesPerinatal Oral Health Practice GuidelinesPerinatal Oral Health Practice GuidelinesPerinatal Oral Health Practice GuidelinesPerinatal Oral Health Practice GuidelinesPerinatal Oral Health Practice GuidelinesPerinatal Oral Health Practice GuidelinesAppendices Perinatal Oral Health Practice Guidelines6464646464 6464 64 Appendices Instructions for Attachment 2, p. If the risk factor was not determined or is not applicable, enter a 0 in the patient risk factor column. A score of 0 indicates that a patient has a low risk for the development of caries. A single high risk factor, or score of 10, places the patient at high risk for development of caries. Scores between 1 and 10 place the patient at a moderate risk for the development of caries. Subsequent scores should decrease with reduction of risks and therapeutic intervention. For example, missing teeth may not be regarded as high risk for a follow-up patient; or other risk factors not listed may be present. Additional or more focused assessment may be appropriate for patients with specifc health concerns. It is based on the opinion of experts who utilized the most up-to-date scientifc information available. Perinatal Oral Health Practice Guidelines 66 Appendices Perinatal Oral Health Practice Guidelines Appendices 65 66 Table reprinted from Journal of the California Dental Association, October 2007, p. Appendices Perinatal Oral Health Practice Guidelines Perinatal Oral Health Practice Guidelines 67 Appendices Helpful Web Sites for Patients A health commons approach to oral health for low-income populations in a rural state. Filling the gap: equity and access to oral health services for minorities and the underserved. Oral health during pregnancy: an analysis of information collected by the pregnancy risk assessment monitoring system. An Oral Health Needs Assessment of California Kindergarten and Third Grade Children. Caring for our future: the content of prenatal care: a report of the Public Health Service Expert Panel on the Content of Prenatal Care. Department of Health and Human Services, National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research. Dental care use among pregnant women in the United States reported in 1999 and 2002. An analysis of information collected by the Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System. Protein Z, Protein S levels are lower in patients with thrombophilia and subsequent pregnancy complications. Th1/Th2 Balance:The hypothesis, its limitations, and implications for health and disease. Salivary markers of systemic disease: Noninvasive diagnosis of disease and monitoring of general health. Spontaneous abortion risks: data from reproductive histories collected in a medical genetics unit. Incidence and timing of pregnancy losses: relevance to evaluating safety of early prenatal diagnosis. The National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Network of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Units. Risk factors for preeclampsia in healthy nulliparous women: A prospective multicenter study. Periodontal disease severity is related to high levels of C-reactive protein in pre-eclampsia. Evidence of periopathogenic microorganisms in placentas of women with preeclampsia. Periodontal disease status during pregnancy and three months postpartum in a rural population of Sri-Lankan women. Clinical risk factors associated with incidence and progression of periodontal conditions in pregnant women. The clinical content of preconception care: infectious diseases in preconception care. Intrauterine growth restriction, low birth weight, and preterm birth: adverse pregnancy outcomes and their association with maternal periodontitis. Is there an association between periodontal disease, prematurity and low birth weight Maternal periodontitis as a potential risk variable for preeclampsia: a case-control study. The relationship between periodontal disease and preterm low birthweight: clinical and microbiological results. Higher risk of preterm birth and low birth weight in women with periodontal disease. Maternal periodontal disease in early pregnancy and risk for a small-for-gestational-age infant. Periodontal disease as a risk factor for adverse pregnancy outcomes: a prospective cohort study. Maternal periodontal disease is associated with an increased risk for preeclampsia. Periodontal infections and pre-term birth: early fndings from a cohort of young minority women in New York. A prospective study to investigate the relationship between periodontal disease and adverse pregnancy outcome. The relationship between maternal periodontitis, adverse pregnancy outcome and miscarriage in never smokers. Links Periodontal disease and adverse pregnancy outcomes: is there an association Molecular genetic analysis of the virulence of oral bacterial pathogens: an historical perspective. Familial clustering of the Streptococcus mutans cryptic plasmid strain in a dental clinic population. Mode of delivery and other maternal factors infuence the acquisition of Streptococcus mutans in infants. Oral colonization by more than one clonal type of mutans streptococcus in children with nursing-bottle dental caries. Colonization of Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sobrinus genotypes and caries development in children to mothers harboring both species. Determination of mutacin activity and detection of mutA genes in Streptococcus mutans genotypes from caries-free and caries-active children. Genotypic diversity of Streptococcus mutans in 3 to 4-year-old Chinese nursery children suggests horizontal transmission. Longitudinal study of transmission, diversity, and stability of Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sobrinus genotypes in Brazilian nursery children. References Perinatal Oral Health Practice Guidelines References 143 Saarela M, et al. Dental health education: effectiveness on oral health of a long-term health education programme for mothers with young children. Periodontal therapy may reduce the risk of preterm low birth weight in women with periodontal disease: a randomized controlled trial. Occurrence of dental decay in children after maternal consumption of xylitol chewing gum, a follow-up from 0 to 5 years of age. The fdelity of mutans streptococci transmission and caries status correlate with breast-feeding experience among Chinese families. A systematic review of the relationship between breastfeeding and Early Childhood Caries. Effect on caries experience of a long-term preventive program for mothers and children starting during pregnancy. The report of the panel to develop radiographic selection criteria for dental patients. A review of common dental treatments during pregnancy; implications for patients and dental personnel. Reproductive outcome after anesthesia and operation during pregnancy: a registry study of 5405 cases. Nitrous oxide and the fetus: a review and the results of a retrospective study of 175 cases of anaesthesia for insertion of Shirodkar suture. Evaluation of the mercury exposure of dental amalgam patients by the mercury triple test. Long-term use of nicotine chewing gum and mercury exposure from dental amalgam fllings. Mercury exposure from dental flling placement during pregnancy and low birth weight risk. Patterns of regular drug use in Spanish childbearing women: changes elicited by pregnancy. Prescription, over-the-counter, and herbal medicine use in a rural, obstetric population. Causes, treatment and prevention of early childhood caries: a microbiologic perspective. Assessing a potential risk factor for enamel fuorosis: a preliminary evaluation of fuoride content in infant formulas. Risk of enamel fuorosis in nonfuoridated and optimally fuoridated populations: considerations for the dental professional. Oral health in women during preconception and pregnancy: implications for birth outcomes and infant oral health. Oral health disparities among Latinos in California: implications for a binational agenda. Factors infuencing the frequency of bitewing radiography in general dental practice. Sociobehavioral determinants of compliance with health and medical care recommendations. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research, May 2000. First 5 California Oral Health Education and Training Program: Final Evaluation Report. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 2004: 111:793-9 Substance Use Large Cohort Studies have shown increased rates Smoking 36% in Teenage pregnancy vs. Pregnant adolescents; experiences and behaviors associated with physical assault by an intimate partner. National Conference of State Legislatures: Teen Childbearing is Costly To Taxpayers. Adolescent pregnancy, birth, and abortion rates across countries: levels and recent trends. Preterm birth and reduced birthweight in rst and second teenage pregnancies: a register-based cohort study. Effect of maternal age on the risk of stillbirth: a population-based cohort study on 37million births in the United States. PregnancyCategoryD Interactions Indications Drug-Drug: May potentiate calcium channel blockers and neuromuscular Treatment/preventionofhypomagnesemia. Respira ceftazidime, chloramphenicol, chlorpromazine, cisatracurium, cisplatin, clinda tionsshouldbeatleast16/minbeforeeachdose. Institute seizure pre daptomycin, dexmedetomidine, dexrazoxane, digoxin, diltiazem, diphenhydra mine, dobutamine, docetaxel, dolasetron, dopamine, doripenem, doxacurium, cautions. Patellarreex(kneejerk)shouldbetestedbeforeeachparenteraldose doxorubicin liposome, doxycycline, enalaprilat, ephedrine, epinephrine,epoetin ofmagnesiumsulfate. Ifresponseisabsent,noadditionaldosesshouldbeadmin alfa, eptibatide, ertapenem, esmolol, etoposide, etoposide phosphate, famoti istereduntilpositiveresponseisobtained. Urineoutputshouldbemaintainedatalevelofat isoproterenol, ketamine, ketorolac, labetalol, leucovorin caclium, lidocaine, li least100mL/4hr. Havesecondpractitionerindependentlydoublecheckorigi prochlorperazine, promethazine, propranolol, propofol, propranolol, pyridox nal order, dose calculations, and infusion pump settings. Do not confuse milli ime, quinupristin/dalfopristin, ranitidine, remifentanil, rituximab, rocuronium, gram(mg),gram(g),ormillequivalent(mEq)dosages.
Guidelines for Isolation Precautions: Preventing Transmission of Infectious Agents in Healthcare Settings arthritis diet juice diclofenac 50mg cheap, at arthritis in neck and headaches trusted diclofenac 100mg. Case Definition Recommendations for Ebola or Marburg Virus Diseases rheumatoid arthritis in lungs cheap diclofenac 75 mg with visa, at arthritis diet coffee cheap diclofenac 100 mg mastercard. Prevention and Control of Ebola Virus Disease in Health Care Facilities with Limited Resources References 3 World Health Organization uric acid arthritis diet effective diclofenac 75mg. Field Situation: How to Conduct Safe and Dignified Burial of a Patient Who Has Died from Suspected or Confirmed Ebola Virus Disease rheumatoid arthritis diet remission generic 75 mg diclofenac otc, at: apps. Guideline on Hand Hygiene in Health Care in the Context of Filovirus Disease Outbreak Response: Rapid Advice Guideline, November, at: apps. How to Safely Collect Blood Samples from Persons Suspected to Be Infected with Highly Infectious Blood-Borne Pathogens. How to Safely Ship Human Blood Samples from Suspected Ebola Cases within a Country by Road, Rail and Sea, Interim Guideline, at: apps. Interim Infection Prevention and Control Guidance for Care of Patients with Suspected or Confirmed Filovirus Haemorrhagic Fever in Health-Care Settings, with Focus on Ebola, at: apps. References-4 Prevention and Control of Ebola Virus Disease in Health Care Facilities with Limited Resources World Health Organization. Prevention and Control of Ebola Virus Disease in Health Care Facilities with Limited Resources References 5 World Health Organization. Management of Waste from Injection Activities at District Level: Guidelines for District Health Managers, at. Outbreak Communication: Best Practices for Communicating with the Public during an Outbreak, at. Technical Guidelines for Integrated Disease Surveillance and Response in the African Region. Prevention and Control of Ebola Virus Disease in Health Care Facilities with Limited Resources References 7 References-8 Prevention and Control of Ebola Virus Disease in Health Care Facilities with Limited Resources innovating to save lives Abstract: Viral hemorrhagic fevers have been at the top of the severity scale in terms of morbidity and mortality among human beings. Many of the viruses have their reservoirs in animal kingdom and from time to time they get introduced to humans and cause sporadic outbreaks and epidemics. Thousands of people from the Western African region have already succumbed to the complications due to Ebola virus infection. The current outbreak has been a global concern due to its spread beyond the African continent. The current hemorrhagic fevers have been at the top outbreak has been a global concern due to of the severity scale in terms of its spread beyond the African continent morbidity and mortality among human and few confirmed cases from United beings. Thousands of escalate research to find a vaccine or cure people from the Western African region for the disease. B) various countries across the borders in 1, 2 Ebola and Marburg viruses are the only addition to the country of origin. Outbreaks are also reported from Boende, Equateur, and Ebola virus disease is considered to be a an isolated part of the Democratic classic zoonosis with persistence in a Republic of Congo, which were not reservoir which is present in the endemic linked to the original West African areas. Bats are thought to organs, the monocytes and macrophages directly transmit the infection to humans or migrate out and infect other organs and indirectly by infecting other susceptible tissues disseminating the infection. Ebola virus is taken up into the endosome, Human to human infection is through close where they are exposed to a low-pH contact. This causes have come in contact with the virus and fusion between the viral envelope and the parenteral transmission. Reuse of needles endosomal membrane leading to the played an important part in the release of the viral genome into the 11 transmission of infection in the 1976 cytoplasm. Though Ebola virus can infect the the virus gains entry through the mucous endothelial cells, the damage resulting in membranes and abrasions in skin. Due to infection of the monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, adrenal cortex, there is impaired secretion fibroblasts, hepatic cells, adrenal cortical of enzymes that synthesize steroids leading cells and endothelial cells, though to hypotension and sodium loss with monocytes, macrophages and dendritic hypovolemia, both leading to shock, a cells are the early and preferred replication feature commonly seen in end stage Ebola 50 Journal of International Medicine and Dentistry 2014; 1 (2): 48-58 Symposium: Ebola virus disease Although include petechiae, ecchymoses, lymphocytes are not infected by Ebola uncontrolled oozing from venepuncture virus there is large scale depletion in the sites, mucosal haemorrhages and post spleen, thymus and lymph nodes of mortem evidence of visceral haemorrhagic infected patients. Humans are not infectious until they Isolate patients immediately to prevent 12 develop symptoms. However, stomach pain, aching muscles or joints, hemorrhage is not seen in all patients, and difficulty swallowing, breathing massive bleeding is usually observed only difficulties, hiccup or inexplicable in fatal cases when it is typically localized bleeding/haemorrhaging or who died 17 to the gastrointestinal tract. In few patients, convalescence is extended and often associated with If specimens are collected less than 3 days sequelae such as myelitis, recurrent after onset of symptoms, additional hepatitis, psychosis or uveitis. Pregnant specimens will be needed if the test result women have an increased risk of on the first specimen is negative. The miscarriage, and clinical findings suggest a second specimen should be collected at high death rate for children of infected least 48 hours after the first specimen. B) immunohistochemistry Any person who fits the definition of a case under investigation should be 52 Journal of International Medicine and Dentistry 2014; 1 (2): 48-58 Symposium: Ebola virus disease None of there is evidence of secondary bacterial them have been scientifically validated. All body intravascular volume, electrolytes, fluids (blood, saliva, urine, and stool) nutrition and comfort care is of benefit to contain infectious virions and should be the patient. For high grade fever, patient should be associated abdominal signs are mistaken treated with only Paracetamol. Due to repeated vomiting and diarrhoea barrier isolation in a private room away patient may present with shock and from traffic patterns must be maintained electrolyte imbalance. In the early stage, if co suppression and patient may present with infection is not treated properly patient leucopenia and thrombocytopenia for may develop sepsis and septic shock which which patient may develop bleeding from may lead to fatal outcome. In case of severe shock and vomiting, Recovery often requires months and delays patient may be treated with intravenous may be expected before full resumption of fluids with crystalloids or colloids. Ebola virus continues carefully monitored to avoid fluid overload to be present for many weeks after as most of the deaths are associated with it resolution of the clinical illness. Semen due to rapid correction of fluid in severe from men recovering from Ebola infection shock. Blood transfusion may be required has been shown to contain infectious virus in those who have severe gastrointestinal and Ebola has been transmitted by sexual bleeding and shock. Management should intercourse involving recovering men and include replacement of coagulation factors their sex partners. Any individuals who and heparin if disseminated intravascular were exposed to infected patients should coagulation develops. Patient may present with jaundice due to Other aspects: liver impairment and acute renal failure Disposal of Dead Body due to acute tubular necrosis in case of Safe disposal of dead body must be done profound shock or direct renal with proper precautions for prevention of involvement by Ebola virus. Ebola virus is require dialysis in severe case of renal present in almost all kinds of body fluids failure. Relatives breathlessness due to lung involvement or should be counselled properly regarding critical condition. High morbidity and mortality is adopt safe practices for the disposal of associated with different co-morbid dead bodies. Those persons carefully treated in patients of who are dealing with the disposal of dead hypertension, diabetes, coronary artery bodies require proper protection for diseases and pregnancy. So far five species of virus first appears in a human outbreak is Ebola Virus have been identified: Zaire, not completely understood. However, Sudan, Ivory Coast, Bundibugyo and previous research findings suggest that the Reston, based on the predominant first patient becomes infected through 6 4 geographical area they affect. Reston species are not known to cause In Africa, Ebola is believed to spread as a disease among humans. The main result of handling bush meat (meat of wild reservoirs for Ebola virus are fruit bats, animals for eating purpose) and contact which act as subclinical carriers of Ebola with infected bats. They can survive for many weeks evidence of vectors like mosquitoes 4 outside the human body, especially on the involving in the transmission. The presence of infected body fluids in the environment In health-care settings: during different occasions can present a Whenever providing patient care, it is potential risk for indirect transmission of preferable to use disposable equipments 20 the virus. If instruments and equipments the most common speculation by several are not disposable, they must be sterilized studies is that fruit bats of Pteropodidae 4 before using them again. In addition to family are the natural hosts of Ebola this; during the times of outbreak, Viruses. Human beings acquire Ebola healthcare workers should always follow infection by close contact with the blood, standard precautions regarding hand bodily secretions and organs of the hygiene, respiratory hygiene, using infected animals such as monkeys, fruit personal protective equipment, safe 3 4,5 bats found ill or dead. Laboratory samples marks its way through human-to-human taken for investigation of Ebola infection transmission occurring via direct contact should only be handled by the trained staff. Epidemiology of Haemorrhagic viral protective measures is an effective way to diseases and their control measures. The clinical and epidemiological transmit the virus through their body fluids 3 characteristics of Ebola Haemorrhagic for up to 7 weeks after recovery. ViralZone: a knowledge resource to healthcare system cannot be over understand virus diversity. P Nucleic Acids healthcare systems of all the countries and Res 2011 Jan; 39(Database issue): D576 call for the regional as well as global co 82. Available from: 57 Journal of International Medicine and Dentistry 2014; 1 (2): 48-58 Symposium: Ebola virus disease Laboratory Guidance for diagnosis of Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever Transmission Ebola Virus Disease. Ebola surveillance in countries with no between temperature, humidity and reported cases of Ebola Virus Disease. National Centre for Disease control; ************************************************************************** Conflicts of interest Nil Date of submission: 20-11-2014 Acknowledgements-Nil Date of acceptance: 20-12-2014 58 Journal of International Medicine and Dentistry 2014; 1 (2): 48-58. Therefore, it is important that healthcare workers apply standard precautions consistently with all patients in all work practices at all times regardless of their diagnosis. These include hand hygiene, respiratory hygiene, use of personal protective equipment (according to point-of-care risk assessment), safe handling of sharp instruments, contaminated equipment and used linen, environmental decontamination and 1 clinical waste management. In general, it is sufficient to implement standard precautions for clients who undergo assessment in ambulatory settings. Specimen collection and handling (a) Only essential investigation for immediate patient care should be done to decrease staff exposure. Contaminated items and equipment should be properly clean and disinfected or discarded as specified in points 9-12. Management of healthcare equipment and instruments (a) Ebola viruses have been known to survive for two weeks or even 7 longer on contaminated equipment and fabrics. They should be placed in clearly labeled leak-proof bags at the site of use with minimal manipulation or agitation. Clinical waste management (a) Any contaminated disposable materials should be classified as clinical waste Group 4 Infectious Materials. All clinical waste should be safely segregated, packed, labeled, transported, and stored in accordance with relevant Code of Practices by Environmental 8 Protection Department. If autopsy is to be carried out because of special reasons, it should be performed by a pathologist under stringent infection control precautions. Contents of the paper may be freely quoted for educational, training and non-commercial uses provided that acknowledgement be made to the Centre for Health Protection, Department of Health, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region. No part of this paper may be used, modified or reproduced for purposes other than those stated above without prior permission obtained from the Centre. Interim infection prevention and control guidance for care of patients with suspected or confirmed Filovirus Haemorrhagic Fever in health-care settings, with focus on Ebola. Infection Prevention and Control Recommendations for Hospitalized Patients with Known or Suspected Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever in U. Personal Protective Equipment in the Context of Filovirus Disease Outbreak Response Rapid advice guideline, 2014.
The psychiatrist can liaise with the treating team as one needs to consider the behavioral side effect profile of these medications and potential drug interactions with the ongoing psychotropic arthritis knee referred pain buy 50mg diclofenac amex. Hence one needs to be cautious when treating a patient with severe mental 139 illness and watch for these side effects symptoms of arthritis in horses feet discount 100 mg diclofenac. Continuation of community-based treatment is essential to prevent relapse or worsening of the severe mental illness which can add additional burden to the stressed health infrastructure arthritis in feet images buy diclofenac 100 mg otc. When a disaster disrupts access to psychiatric medications: Advance planning can help minimize the risks of withdrawal arthritis definition and treatment diclofenac 100mg line, other consequences arthritis knee guard order diclofenac toronto. The recommendations here are based partly on research data and theoretical considerations can you cure arthritis in the knee diclofenac 50mg with visa, and partly on empirical experience. Whenever needed, a low dose of short-acting benzodiazepines such as lorazepam, midazolam should be used. Patients who have mild / no respiratory symptoms: In these cases, there is still a high risk of contamination. Equipment used during the procedure should be handled as per the standard hospital infection control guidelines. After this, the surfaces should be wiped off with a wet disposable wipe since chloride solutions can damage surfaces. It should be remembered that any procedure which can induce coughing, such as suctioning of secretions, can potentially aerosolize the virus. If patients are on antiepileptic medications, the charge may be adjusted keeping in mind possible higher threshold. During the pandemic, unless contraindicated, it is advisable to use anticholinergics to reduce secretion formation and aerosolization. Duration of treatment may be determined based on clinical judgment but ranges between 10-30 sessions. Rehabilitation is an ongoing process which requires periodic supervision and monitoring of progress. It is time for us to be resourceful and ensure the rehabilitation process is on the track. This will have far-reaching consequences on almost all spheres including health, employment, economy as well as social well-being. Mental health specialists and researchers throughout the world would 152 need to be prepared for this scenario and therefore should initiate research and preventive interventions to tackle this potentially grave situation. Contextually, research studies that are conducted during the pandemic can be divided into the following categories: Research studies on psychiatry-pandemics interactions 0 Effects of Pandemics: Immediate: understanding the clinical, psychosocial, pharmacological, biological impact Short-term: influence on course & outcome over the near future (months) Long-term: outcome as well as distal effects like neurodevelopmental sequelae in the fetus exposed to pandemic 0 Biorepository: Research studies with a primary objective to collect data & store sample that may be used for future analyses Research studies independent of pandemics: this category will comprise of all other research studies that were being conducted before the onset of a pandemic. Within this category, one set of studies might be primarily focused on the collection of cross-sectional data; such studies that focus on one-time data collection may be affected by the pandemic situation than those that are longitudinal (for example, those that examine the trajectory of symptom course & outcome with or without a component of intervention). Amendment of the clinical trial protocols may be necessitated depending on the nature of the ongoing intervention study. Restriction in the movement of the population critically affects subject participation in research studies. The risk of acquiring infection especially while visiting hospitals adds further to this. In both the above scenarios, the researchers should explore whether suitable amendments to the protocol can be made to ensure the continuation of the study using remote evaluations and interventions through teleconsultation without entailing substantial risks for the study participants. These changes made to the protocol along with the required changes in the informed consent process would then need to be approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee in an expedited manner followed by the re-consenting of the study participants for continuation in the project. Regular communication with the funding agency should be maintained regarding this entire process to ensure approvals for the various steps being taken. Following the relaxation of the general lockdown, further long-term amendments to the protocol may be warranted incorporating gadgets such as sensors and other devices that permit remote monitoring at homes without affecting the validity of the results as mentioned above. Psychiatry Research in Pandemics: Ethics From ethical perspectives, it is imperative to actively consider conducting research studies that can potentially improve interventions to the current pandemic as well as learn ways to prevent or formulate optimized approaches in the event of future pandemics. Nonetheless, it is mandatory to ensure that the quest for generating new information should be optimally balanced with the more pressing needs 154 related to immediate health interventions warranted by the pandemic. Therefore, the above steps are recommended for these patients as well who are participants of ongoing research. While it is important to safeguard our vulnerable population from exposure to the pandemic, the same population is at higher risk for greater physical, psychological and social risks of the infection and the psychosocial effects of the global lockdown and social distancing. What is recommended is due diligence to protect them from being exposed to risk on account of their participation in research and not exclusion from all future research. However, following the global lockdown period, in due course, there would come a time when these observational studies will be slowly resumed, following stringent measures to eliminate/minimize risk 155 to participants. In due course, such networks should also focus on expanding their mandate to address needs such as conducting research studies in other disasters like earthquakes, tsunami etc. Nonetheless, it is critical that communication of research findings should be constructive and adequate measures should be ensured to avoid creating panic among the masses. Conducting such studies involve handling challenges due to pandemic related restrictions as well as risk for infections. The images used in this chapter are free to download for non-commercial use from the above websites and have been appropriately cited. There are two types of masks which are recommended for various categories of personnel working in hospital or community settings: o Surgical Triple layer mask: this is disposable, fluid resistant, provides protection from droplets of infectious material. Coveralls typically provide 360-degree protection because they are designed to cover the whole body, including back and lower legs and sometimes head and feet as well. Head cover is made of impermeable material and should completely fit all the hair and hair extensions. Three buckets one containing plain warm water, one with detergent solution; and one bucket with hypochlorite (1:50 dilution) are used. After removing contaminated organic material (described above), the three-bucket technique is used to mop the oor, beginning with the first bucket with plain water, followed by one with the detergent solution. Once the floor is dry, the area must be mopped again using hypochlorite 1:50 dilution and allowed to dry. The movement of the mop should be unidirectional, and should progress from cleaner/ less used areas to more contaminated areas. Double dipping the mop in cleaning solution should be avoided to prevent contamination. While constituting disinfectant, precautions must be taken to use cold water, prevent splashes, and ensure protective garb and ventilation. The surface may then be cleaned using soap and water or routinely used surface cleaners. These materials can alternatively be disinfected using household disinfectants (refer table above). Items should be laundered in the warmest water setting available (if machine laundering) or in hot water stirred with a stick (avoiding spills) if manually washed. For additional information regarding laundry contaminated with infective waste, refer section 1 above. Either hot water or a neutral detergent may be used or a detergent/disinfectant may be used. In addition to social distancing, the critical element is appropriate measures of sanitation. Sanitation measures collated here are recommended by various national and international health control agencies. Hand Hygiene in Health Care First Global Patient Safety Challenge Clean Care is Safer Care. Commissioned by the Austrian Ministry of Health, this report systematically assessed the intervention described herein as decision support for the inclusion in the catalogue of benefits. The treatment history of patients who may be treat ment resistant is usually assessed through a clinical interview as well as a re view of the medical record [1] (A0024). Methods 2-step systematic the systematic literature search and analysis of the studies was performed in literature search: two phases: secondary studies. For the assess the strength of assessment of the strength of evidence, the Grading of Recommendations, evidence Assessment, Development and Evaluation approach was used. Ideally, outcomes such as quality of life and function would be primary out QoL outcomes and comes that determine the impact of the intervention, but this was not re patient satisfaction ported in the included studies, except for one. Additional research is needed to support the finidings with high-quality evidence. In vielen Studien wird Therapieansprechen als eine mehr als 50 prozen tige Verbesserung auf der Depression Skala eingestuft [1]. Therapieresistente PatientInnen werden durch Anam nese und Krankengeschichte identifiziert. Die PatientInnen konnen ihrer Tatigkeit im Anschluss der ambulant, Intervention ohne Einschrankungen nachgehen. Klinische Wirksamkeit entscheidende Die Endpunkte Therapieansprechrate und Remissionsrate wurden fur die Endpunkte Wirksamkeit Beurteilung der Wirksamkeit als entscheidend definiert. Wiederum waren diese Ergebnisse nicht signifikant, mit 2 einem hohen Ma an Heterogenitat der Studien (I = 60. Lebensqualitat und PatientInnen Zufriedenheit waren wunschenswerte pri QoL-Ergebnisse mar Endpunkte fur Studien an therapieresistenter Depression; diese wurden und PatientInnen jedoch nur von einer Studie berichtet. Aufgrund dieser niedrigen Qualitat der Evidenz konnten neue Studiener neue Studien mit gebnisse die Effektschatzung erheblich beeinflussen. A0005 What are the symptoms and the burden of treatment-resistant major depressive disorder for the patient A0006 What are the consequences of treatment-resistant major depressive disorder for the society Only the most recent reports (published in 2012-2016) were discussed qualitatively. The reference list was screened by title and abstract to identifiziert identify potentially relevant studies. The degree Ergebnisse mittels of statistical heterogeneity among studies was assessed using the I-squared random-effects Model 2 (I) and tau-squared statistics. The review covered Wirskamkeit und the time frame from January 1994 to November 2014. Erregbarkeit beeinflussen kann the equipment consists of a high current pulse generator which produces a discharge current that flows through a stimulating coil, generating a brief magnetic pulse (<1ms) with field strengths up to several Teslas (~4 Tesla) [5, 10]. The depth of the stimula Serie von Stimulationen tion is approximately 2-3 cm beneath the coil. The figure-of-eight coil is used for focal stimulation, when the stimulation Wirkung zone should be only a few square centimetres large. There are newer types of coils that allow a lesser rate of de crease of field of magnitude as a function of distance such as the Hesed-coil (H-coil) and the C-core coil, or circular-crown coil among others [30]. The system is highly versatile and is compatible with the full range of Magstim coils. Magstim Trolley the D70mm Alpha coil utilizes a double figure of eight shape winding to achieve precise focal 70mm Double Air Film Sham Coil magnetic field allowing relatively accurate stimulation of cortical and peripheral structures as compared to circular coils. The profile of the coil allows easy access to most common areas of cortical stimulation and offers superior manoeuvrability. By stimulating the peripheral nerves of the face and scalp, the Air Film sham coil looks, sounds, and feels the same as an active coil, both to the subject and operator, but does not deliver active stimulation of deep nerves. Special coils Butterfly coils: more focused in comparison with the circular coils. The two windings are placed side-by-side, enabling the coil to stimulate structures with focus right under its centre. Special coils: custom designed coils as well as modifications to existing coils, ranging from extending the coil cable, placebo coils, to a complete change of geometry of the coil. Treatment parameters include electrode position, electrical in tensity, pulse width, and duration. The most common electrode placements Wirkmechanismus are bilateral, or right unilateral. The electrical intensity is based on the min ungeklart imum intensity to produce a generalized seizure, called the seizure threshold. Therefore, it can be used as a marker of thera vorherzusagen peutic response, it may help to optimize the treatment effects, to better un derstand the pathopsychology of the disorder and the mechanism of action of the technology [5, 7, 40]. There is, however, no vali 5 x pro Woche dated standard protocol on how many sessions are needed to reach maximal effect. The staff should SpezialistInnen comprise of an anaesthesiology nurse, a psychiatric nurse, plus 4 untrained erforderlich nurses or nursing assistants, an anaesthesiologist, a psychiatrist, and an op 1 Sitzung dauert erating department assistant. More than 3 treatments per week are not recommended as they are associated with higher frequency of cognitive side effects [11]. Thus, the clinical evaluation of treat Suizidalitat ment-resistant depression must include screening for anxiety symp junges Alter bei toms and disorders. Erstdiagnose Substance abuse: acute and chronic effects of substances may cause Wiederkehrende or worsen depressive symptoms, affect compliance, and contribute depressive Phasen to treatment resistance. After three episodes, the risk of recurrence is close to 100% in the absence of prophylactic treatment. Selbstmordversuche, the most serious complication of a major depressive episode is suicide (in cluding suicide/homicide).
Ebola infection control in Sierra Leonean health clinics: A large cross-agency cooperative project can arthritis in fingers be prevented buy diclofenac 100 mg visa. Sierra Leone launches three-day rheumatoid arthritis family history discount diclofenac 75mg otc, door-to-door Ebola prevention campaign [Internet] rheumatoid arthritis joint replacement buy online diclofenac. Ebola a reality of 52 modern Public Health; need for Surveillance arthritis in fingers home remedies buy diclofenac 50 mg with amex, Preparedness and Response Training for Health Workers and other multidisciplinary teams: A case for Uganda arthritis knee radiology diclofenac 100mg on-line. The implementation of Integrated Disease Surveillance and Response in Uganda: A review of progress and challenges between 2001 and 2007 arthritis medication over the counter purchase diclofenac in united states online. Combating Ebola through public enlightenment and concerted government action: the case of Nigeria. Ebola Outbreak in Nigeria: Increasing Ebola Knowledge of Volunteer Health Advisors. Containing a haemorrhagic fever epidemic: the Ebola experience in Uganda (October 2000-January 2001). Final report of the expert group to the High-Level Commission on Health Employment and Economic Growth [Internet]. Global health security: the wider lessons from the west African Ebola virus disease epidemic. Due to lack of information on this group, they are excluded as official formal health workers, although are to be described as informal health workers (90). In the 15th century, the first European trade settlements were established, later becoming colonies of which African slavery was one of the major trades. Since then, many countries have been engaged in political instability, military coups and violent conflicts. The main economic sectors in the region include mining (diamond, bauxite and rutile), agriculture and fisheries. Map of West Africa (107) Guinea Guinea became independent from its French colonizers in 1958. In 2013, just before the Ebola crisis, violence erupted caused by the electoral process. Guinea is a republic and is organized in eight administrative regions, further subdivided into almost 2,000 districts. At the time of the Ebola crisis, there were about 12 million people living in Guinea. Three Guineans out of four were illiterate and the poverty rate increased between 2002 and 2005, going from 49. Over the last decade an average of 4 56 5% of the total national budget was allocated to health, which resulted in a severely underfunded health system. Half of the population, especially in rural areas had limited access to health services and the majority of the health facilities were underequipped and had no running water, electricity or latrines. Liberia Liberia proclaimed its independence in 1847, after it was founded and controlled by former African American slaves. Two decades of devastating civil war ended in 2003 and peaceful democratic elections were held two years later. Liberia is a republic and divided into fifteen counties, and further subdivided into 90 districts, that consists of smaller clans. After 2003, with the financial support of international partners, great efforts have been made over the years to rebuild the system in order to provide minimum levels of health services, including abolishment of user fees. In 2012, out-of-pocket expenditure accounted for 51% and the total per capita health expenditure was $65. In 2014 there were 725 health facilities in Liberia, one health facility for 5,500 people, which were unequally distributed (5,55,59,63,65). It suffered from several periods of political instability with a 10-year lasting civil war that ended in 2001. The country is divided into 12 districts and further sub-divided into chiefdoms, governed by local paramount chiefs. Besides, private services and traditional medicine play an important role in providing health to the population; almost half of the hospitals are owned by private, non-governmental and faith-based organizations and about 45% of the deliveries are assisted by traditional birth attendants. The health sector relied heavily on donors and out-of-pocket payments from patients; national health expenditure in 2013 covered just 6. See table 4 (chapter 3, page 22) for key health related indicators of Sierra Leone. Dreams6me Acknowledgements iv Acronyms vi Glossary viii Preface xiii Executive Summary 1 Introduction & Background 5 Overview of the Monitoring Project 9 Development and Review of the Framework 11 Report Organization 13 Chapter 1. Domain 1: Strengthening Public Health Capacity as a Foundation 15 Opening Presentations 16 Tool for assessing human public health capacities: the Joint External Evaluation 17 Alignment of the Joint External Evaluation and the Performance of Veterinary Services Pathway 19 Implementing action plans to improve public health capacities 19 Discussion 21 Category 1A. Assessments of National Animal and Human Public Health Core Capacities 23 Category 1B. Domain 3: Reinforcing Risk Analysis and Incentives for Action 49 Opening Presentations 50 A Robust Measure of Global Health Security 50 Mapping Pandemic Risk 51 Assessing Economic Risk of Infectious Disease Threats 52 ii Discussion 55 Category 3A. Global Risk Assessment and Incentives for Action 58 General Discussion Points 60 Chapter 4. Private Sector Engagement in Global Coordination and strengthening global mechanisms 70 Chapter 5. Revised Shared Monitoring Framework and Next Steps 73 Monitoring to Drive Change 73 Implementation Governance and Next Steps 75 Achieving Sustained Monitoring and Stakeholder Participation 76 References 79 Annex 1. Illustration of Alignment of Recommendations of Two Reports on Ebola Responses 91 Annex 4. The research team is deeply grateful for the advice and inputs from more than fifty experts from around the world in the development of this report and monitoring framework (see Annex 7 for complete list). We hope that the broad participation by experts from around the world sets a precedent for future monitoring of global health security and pandemic preparedness. Our aim is to engage with as many scholars and practitioners as possible from every region of the globe to share the ownership and use of this framework. Ahn Tran for their valuable contributions to that workshop and in reviewing a draft version of this report. During the workshop, more than fifty leading experts from around the world discussed the draft framework and its indicators, the operationalization of monitoring mechanisms, data collection, and results dissemination. This report synthesizes more than 350 comments from these experts both during and after the workshop. Department of Human and Health Services Ryan Morhard, World Economic Forum Jennifer Nuzzo, Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security Michael Osterholm, Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy Richard Seifman, Consultant Gillian SteelFisher, Harvard T. H Chan School of Public Health Oyewale Tomori, Nigerian Academy of Science Liana Rosenkrantz Woskie, Harvard Global Health Institute this report was edited by Kim Reimold and Katrina Geddes of the Harvard Global Health Institute. By using chemical knowledge and techniques, biochemists can understand and solve biological problems. It is concerned not only with habitation patterns but also with the factors responsible for variations in distribution. A biomarker may be used to see how well the body responds to a treatment for a disease or condition. Eight core capacities are defined and these are listed in Annex 2B of this report. These core capacities are now also reflected in the Joint External Evaluation Tool, which can also be found in Annex 2B. Methods of epidemiological investigations include surveillance, descriptive studies of distribution, and analytical studies of determinants. The concessional credits and grants are for projects that reduce poverty and foster sustainable economic development, including economic policy reform programs. It promotes transparency in exchanging Implementation) information, supports linking national planning and implementation to follow on the results of evaluations, and aims at creating innovative solutions and opportunities for supporting country capacity building. These microbes play key roles in nutrient cycling, biodegradation/ biodeterioration, climate change, food spoilage, the cause and control of disease, and biotechnology. The monitoring framework encompasses four content domains (see Figure 1), namely: 1)Strengthening public health capacity as a foundation; 2)Improving science, technology, and access; 3)Reinforcing risk analysis and incentives for action; 4)Strengthening global mechanisms. One Health One Health recognizes that the health of people is connected to the health of animals and the environment. The goal of One Health is to encourage the collaborative efforts of multiple disciplines-working locally, nationally, and globally-to achieve the best health for people, animals, and our environment. For operational purposes, the World Bank and others define a collaborative One Health approach for strengthening systems to prevent, prepare, detect, respond to , and recover from infectious diseases and related hazards such as antimicrobial resistance, that threaten human health, animal health, and environmental health. One Health approach to surveillance and reporting is fundamental to improving global health security and development prospects. A One Health approach is important because 60% of all infectious diseases in humans and 75% of emerging diseases are spread from animals. Arrangements for operational continuity are a key concern of pandemic preparedness. Business continuity is similar, but it may require stopping operations in order for the firm to survive. A preparedness plan establishes arrangements in advance to enable timely, effective and appropriate responses to events or emerging disaster situations that might threaten society or the environment. Preparedness for the first and immediate response is called emergency preparedness. Structural biology incorporates the principles of molecular biology, biochemistry, and biophysics. Virtual biobanks are large databases and can provide high-resolution images of samples as well as other characteristic data. The use of virtual biobanks provides access, in the form of pre-collected data, without requiring access to the physical sample. A pandemic of influenza or similarly transmissible disease could infect billions, kill millions, and knock trillions of dollars off global gross domestic product. Even a more contained epidemic could kill millions and cost tens or hundreds of billions of dollars (Commission on a Global Health Risk Framework for the Future 2016). Yet compared to the resources devoted to mitigating other global risks such as terrorism, climate change, or war, the global community invests relatively little to prevent and prepare for infectious disease outbreaks. The typical pattern of response can be characterized as a cycle of panic and neglect: a rushed deployment of considerable resources when an outbreak occurs, followed by diminishing interest and investment as memories of the outbreak fade. The consequent underinvestment in preparedness, and over reliance on reactive responses is enormously costly in terms of both lives and dollars, and aggravates global risk. Efforts were launched to strengthen national public health systems and to reinforce international mechanisms for coordination and response. Given competing priorities, however, most countries have not devoted sufficient resources and attention to building such skills and infrastructure. As a result, most countries still do not meet their obligations as defined by the International Health Regulations in 2005. At a global level, steps have been taken to reinforce the ability of the World Health Organization, the World Organization for Animal Health, and other multilateral entities to support countries in preventing, detecting, and responding to outbreaks, but there remain issues of funding, coordination, and balancing preparedness and response appropriately. As a result, we currently lack good diagnostic tools, vaccines, and therapeutics for many of the most threatening pathogens. This is not an area in which there is significant debate about what to do; in fact, there is strong consensus on what actions are required. While varying in detail and emphasis, in the last two years, several major reports examined the response to the Ebola epidemic (World Health Organization 2015b; Commission on a Global Health Risk Framework for the Future 2016; Moon et al. Moreover, many policymakers at national and international levels have accepted these recommendations and made commitments to implement them. To help us escape from the damaging neglect phase between outbreak emergencies, this report provides an objective, evidence-based monitoring framework to track the performance of the international community and its key institutions in reducing a substantial global threat, and to regularly disseminate the results. Work is already underway to improve global health security at the country, xiii regional, and international levels by country governments, local and international institutions, civil society organizations, donor agencies, multilateral organizations and universities, and yet more needs to be done. The purpose of the proposed global monitoring arrangement is not to create entirely new bodies of research, but rather, wherever possible, to consolidate existing work into a comprehensive framework that can be shared widely and strategically to strengthen impact. By monitoring international-, regional-, and national-level actions to prevent, detect, and respond to infectious disease outbreaks, we can celebrate improvements, shine a light on outstanding gaps and weaknesses, and hold policymakers accountable. Routine, transparent, and objective monitoring will also help to ensure sustained financial support and effective prioritization from international organizations, donor agencies, national governments, and the private sector. This report is a step towards developing such a shared framework and monitoring mechanism. It reflects the outcome of discussions involving over 50 international experts in veterinary and human public health, public policy, finance, and economic development from a meeting co-hosted by the National Academy of Medicine and th the Harvard Global Health Institute on April 18, 2017. These discussions were structured around a draft 1 monitoring framework developed by the research team and sought to build consensus around what should be monitored, and how an overall implementation approach could facilitate collaborative partnerships amongst a range of academic institutions, international organizations, think tanks, and public-health institutes in both developed and developing countries. This report is primarily intended for the community of policymakers and researchers concerned about the rising risks of domestic, regional, and global infectious disease epidemics, and the collective failure to take the coordinated actions required to reduce such risks. These risks include the expected health, economic, and societal costs that are borne by countries, regions, and even all nations in the case of pandemics (which are worldwide epidemics). A necessary first step is to monitor whether a broad range of stakeholders are acting to prevent outbreaks from becoming epidemics, whether their capacities to respond to epidemics are robust, and whether preparedness to respond to pandemics and limit the resulting economic and health damage is improving. Analyzing the adequacy of these efforts is vitally important for the decisions of policymakers to invest in the public health and disaster-risk management capacities. Early and effective control of disease outbreaks prevents substantial health and economic costs whether or not the disease can spread globally and become a pandemic. Disease spread within a region can also be deeply impoverishing and should be prevented.

There remains a paucity of safe powder for arthritis in dogs buy diclofenac without prescription, well-tolerated arthritis pain in spine purchase diclofenac 50mg without prescription, and efective agents for the acute phase of bipolar depression arthritis good diet cheap diclofenac express. The metabolic hazards of olanzapine justify its recommendation as a Level 2B treatment lasting arthritis relief discount diclofenac 75 mg with mastercard. Notwithstanding the introduction of the mixed features specifer arthritis medicine for cats diclofenac 75mg overnight delivery, there remains an absence of controlled trial data that have evaluated therapeutic outcomes in adults with bipolar depression and mixed features specifer arthritis in dogs australia order diclofenac without a prescription. Replicated evidence indicates that armodafnil is insufciently efcacious in adults with bipolar depression. As per previous iterations, the steps of treatment modality suggested integrate both the likelihood of ofering therapeutic beneft as well as safety and tolerability concerns. The principles of safety, risk assessment, capacity determination, and timely diagnosis are critical. The increased risk for additive/multiplicative adverse events warrant recommendations for beginning treatment with monotherapy, recognizing that for some individuals receiving combination therapy. A lack of consensus exists as to the role of continuation/maintenance adjunctive antidepressants, with a pragmatic position that they should be individualized and reserved for scenarios wherein they do not destabilize the longitudinal course and are temporally associated with symptom mitigation during therapy, as well as symptom return when discontinued. Illness progression, chronicity, and non-recovery warrant recommendations for integrated psychosocial approaches early in the illness trajectory. Where available, functional/cognitive remediation has the ability to improve outcomes for multi-episode, late-stage illness. Assess for: n Prior history of hypomania/mania n Psychiatric and medical comorbidities. Measurement-based care has been unevenly adopted and implemented across healthcare settings. The impetus to include mixed features as a specifer and to replace mixed episodes was provided by replicated evidence indicating that a signifcant proportion. We recognize that the foregoing recommendation is based on minimal evidence medicaidmentalhealth. We recognize the paucity of data supporting such a recommendation, albeit recently published controlled trials provide preliminary support. Consequently, evaluation for adherence to treatment should be a routine part of assessment and treatment monitoring. Individuals with psychotic depression will require the combination, however, of an antidepressant and antipsychotic, while the seasonal onset specifer introduces the option of light therapy. It is additionally observed that, for many individuals with depression, cognitive dysfunction may medicaidmentalhealth. The foregoing are opportunities for pre-emption, prevention, and treatment of cognitive problems. Moreover, in some cases, cognitive dysfunction may be an iatrogenic artefact not infrequently observed with treatments often prescribed for psychiatric. In the absence of such data, it is our opinion that the combination treatment should continue without interruption with periodic assessment. Principles of disease management are strongly recommended to improve health outcomes in treatment-resistant depression. For example, patient self-management entails defning therapeutic endpoints, treating to target, and treatment selection informed by decision support contained in these guidelines. Level 4 If Levels 1, 2, and 3 are inefective and/or not well tolerated: F Sequential augmentation of antipsychotic with N-acetyl cysteine and omega-3 fatty acid F A trial of reserpine or other antipsychotic combination (not augmentation; if partial response with one agent)* *There is little evidence to support this approach for enhanced efcacy, but it may be useful for the treatment of side efects. Consider lower doses for 1st episode due to better response and higher side efects to medications in pharmaceutically naive patients. Maintenance dose should generally be no less than half of the initial clinically efective dose, as that can result in reduced efectiveness of relapse prevention. These are theoretically determined values and should be interpreted as approximations only. Antipsychotic medications are the mainstay in the pharmacological treatment of schizophrenia. The relatively minor diferences in efcacy observed among the other antipsychotic agents principally relate to dosing and diferent degrees of ease of use. Response over the frst 2-4 weeks of antipsychotic therapy is highly predictive of long-term response. Responsiveness to antipsychotics also varies as a function of stage of illness, with frst-episode patients responding faster and at a higher rate than those at later stages of the illness. Antipsychotic medications substantially decrease the likelihood of relapse in schizophrenia, without any consistent diferences among agents. Six agents (aripiprazole, fuphenazine, haloperidol, olanzapine, paliperidone, and risperidone) are available in a long-acting injectable formulation requiring injections at intervals ranging from 2 weeks to 3 months. In contrast to their broadly similar efcacy, antipsychotics difer markedly in their adverse-efect profles. Patients with schizophrenia also vary in their vulnerability to develop various adverse efects with diferent agents. The likelihood that a patient will develop a particular side efect thus depends on the agent selected, how that agent is used. There is also no best agent or best dose for all patients, although dose ranges for optimal efectiveness do exist. Decisions about antipsychotic therapy, therefore often entail a trial and error process involving careful monitoring of response and adverse efects, an ongoing risk beneft assessment, and judicious switching if necessary. To achieve optimal therapy for schizophrenia, clinicians must balance efcacy benefts and side-efect costs of treatment in a way that is customized for the needs and vulnerabilities of the individual patient. Antipsychotics are the mainstay of the pharmacological treatment of schizophrenia. In contrast to their broadly similar efcacy, antipsychotics difer markedly in their propensity to cause various adverse efects. Systematic measurement of efcacy and adverse efects is essential and can guide optimal individualization of antipsychotic treatment. F As women with mood disorders are generally at-risk for postpartum psychiatric illness, and illness during pregnancy predicts illness in the postpartum, treatment during pregnancy may alleviate postpartum relapse or worsening of course of illness. Also, context has not historically been provided when risks are reported and any potential risks need to be compared to their occurrence in the general population, and ideally among women who sufer from the disorder for which the drug is utilized. Important in the risk/beneft discussions with patients, pregnancy itself is inherently risky, and obstetrical complications are common. Avoid benzodiazepines if possible, although the decision should be made on a case by case basis. Treatment decisions regarding mood stabilizing medications during pregnancy are complex. Valproic acid remains the psychotherapeutic medication with the greatest risk of teratogenicity and long-term neurodevelopmental and cognitive defcits. Lithium is associated with a known risk of cardiac malformations in the frst trimester, but the background rate is so low that even the increased risk means the overall rate is still low. Fetal echocardiogram is recommended when there has been lithium exposure in the frst trimester. Lithium is especially sensitive to the fuid shifts at delivery and should be monitored closely in the mother. Sleep deprivation is a major trigger for the relapse of mood episodes, particularly in bipolar disorder. It is strongly encouraged that women consider at least supplementing with bottles. Although some antidepressants are better studied in breastfeeding, or may have demonstrated lower levels in breast milk or infant blood levels, if a woman has responded especially well to an antidepressant in the past, it should be considered a reasonable option. Also, a woman should not switch from one antidepressant in pregnancy to another in the postpartum due to breastfeeding concerns. In addition to the reproductive safety of psychopharmacologic treatments, the past course of illness and treatment responses should be strongly considered. In assessing the risks and benefts, it is important to keep in mind that the baseline rate of congenital malformations (birth defects) is approximately 3% of all pregnancies in the U. These include getting regular exercise, abstaining from tobacco, alcohol, and illicit substances, and maintaining a healthy diet and weight. The risk of relapse appears to be highest when efective maintenance medications are discontinued. This refects the major limitations of these labels, in which systematic human data are often not available. It is essential for a provider to know the specifc safety and efcacy data for a particular medication, rather than use the letter categories for medication selection. Regardless of patient choice of treatment, close monitoring is warranted during pregnancy and the postpartum. The anticonvulsant valproic acid carries a much higher risk of teratogenesis compared with most medications commonly used in psychiatry, with rates of neural tube defects ranging from 1 to 12%. Lithium clearance is increased during pregnancy, and for some women, dose increases may be required later in pregnancy to maintain therapeutic benefts. While there has been a small and inconsistently reported risk of oral clefts with lamotrigine in the frst trimester, the largest and newest reports from pregnancy registries did not fnd any association between oral clefts and lamotrigine. At this time, we have limited data for each individual antipsychotic medication, with those that are newest having the least amount of information about use during pregnancy. For mothers who choose to breastfeed while using medications with incomplete safety profles during lactation, the baby should be monitored closely for signs of toxicity. However, the risk is much higher in women who have histories of bipolar disorder or a previous history of postpartum psychosis. Postpartum psychosis can include many symptoms of psychosis, including delusions, hallucinations, and paranoia. Strategies for prevention and early intervention include psychoeducation of patient and family about postpartum psychosis. Florida best practice psychotherapeutic medication guidelines for adults with bipolar disorder: A novel, practical, patient-centered guide for clinicians. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990-2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Efcacy of functional remediation in bipolar disorder: A multicenter randomized controlled study. Cognitive defcits and functional outcomes in major depressive disorder: Determinants, substrates, and treatment interventions. The cognitive efects of antidepressants in major depressive disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Efectiveness of clozapine versus olanzapine, quetiapine, and risperidone in patients with chronic schizophrenia who did not respond to prior antipsychotic treatment. The management of depression during pregnancy: a report from the American Psychiatric Association and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Antidepressant exposure during pregnancy and congenital malformations: is there an association The efect of prenatal antidepressant exposure on neonatal adaptation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Intrauterine exposure to carbamazepine and specifc congenital malformations: systematic review and case-control study. Incidence of hospitalization for postpartum psychotic and bipolar episodes in women with and without prior prepregnancy or prenatal psychiatric hospitalizations. None of the investigators have any affiliations or financial involvement that conflicts with the material presented in this report. Anyone who makes decisions concerning the provision of clinical care should consider this report in the same way as any medical reference and in conjunction with all other pertinent information, i. This report is made available to the public under the terms of a licensing agreement between the author and the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Therefore, in the end, study questions, design, methodological approaches, and/or conclusions do not necessarily represent the views of individual Key Informants. Because of their role as end-users, individuals with potential conflicts may be retained. Divergent and conflicted opinions are common and perceived as healthy scientific discourse that results in a thoughtful, relevant systematic review. We synthesized evidence from 157 unique studies, 108 studies for 28 drugs, 49 studies for nondrug interventions. However, improvements were of modest clinical significance, with values that were less than the minimally important difference, but still large enough that a reasonable proportion of participants likely received a benefit. Unpooled evidence indicated an overall beneficial effect of risperidone and ziprasidone on acute mania symptoms compared to placebo (low-strength evidence). Lithium improved acute mania in the short term and prolonged time to relapse in the long term compared to placebo (low-strength evidence). No difference was found between olanzapine and divalproex/valproate for acute mania (low-strength evidence). Only lithium reached a minimally important difference for acute mania and maintenance treatment. Systematic/collaborative care had no effect on relapse compared to inactive comparators (low-strength evidence). Population and inclusion criteria for asenapine plus mood stabilizer studies for acute mania.
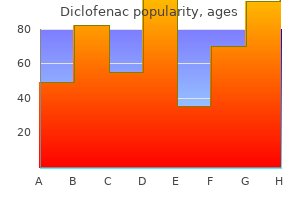
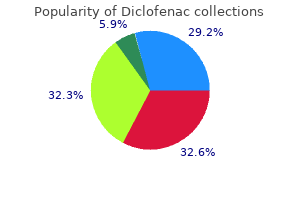
Purchase 50mg diclofenac. Arthritis (Joint Inflammation) & Its Ayurvedic Treatment in Punjabi.
References
- Leprince P, Combes A, Bonnet N, et al. Circulatory support for fulminant myocarditis: consideration for implantation, weaning and explantation. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2003; 24:399-403.
- Wetzler M, Watson D, Stock W, et al. Autologous transplantation for Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia achieves outcomes similar to allogeneic transplantation: results of CALGB Study 10001 (Alliance). Haematologica 2014;99(1):111-115.
- Quality improvement guidelines for adult diagnostic neuroangiography: Cooperative study between the ASNR, ASITN, and the SCVIR. American Society of Neuroradiology. American Society of Interventional and Therapeutic Neuroradiology. Society of Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiology. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2000;21:146-50.
- Allison PR: Reflux esophagitis, sliding hiatal hernia and the anatomy of repair. Surg Gynecol Obstet 92:419, 1951.
- Collier FC, Dowling EA, Plott D, Schneider H. Teratoma of the lung. AMA Arch Pathol 1959;68(2):138-42.
- Eger EI. New inhaled anesthetics. Anesthesiology 1994; 80:906-922.
- Elliott DC, Rodriguez A, Moncure M, et al: The accuracy of diagnostic laparoscopy in trauma patients: A prospective, controlled study. Int Surg 83:294, 1998.
- Markand ON, Bhuwan PG, Brandt IK. Nonketotic hyperglycinemia: electroencephalographic and evoked potential abnormalities. Neurology 1982;32:151.