Eva Escobedo, MD
- Professor of Radiology
- UC Davis Medical Center
- Sacramento, California
This can mean taking the opportunity to enjoy what life has to offer medicine klonopin buy generic divalproex on line, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and good relationships and participating in all sorts of activities medications you cannot crush generic divalproex 250mg without prescription, including play treatment 4 syphilis order 500mg divalproex fast delivery, travel symptoms 4dpiui cheap divalproex express, sports symptoms for mono divalproex 500mg with amex, career and other activities that are sustaining or inspiring medications 5 songs order divalproex cheap. At the various stages of life, issues can arise for a person with a bleeding disorder or their family that impact on their ability to enjoy their life. It could be as simple as knowing how to arrange the necessary documents and treatment product to travel. Or for parents, how best to help a child to play and have fun while dealing with the potential for bruises and bleeds. Haemophilia Foundation Australia also has a Youth Program run by young people affected by bleeding disorders. With knowledge and planning most people live well with haemophilia and lead active and independent lives. Important Note: this booklet was developed by Haemophilia Foundation Australia for education and information purposes only and does not replace advice from a treating health professional. Always see your health care provider for assessment and advice about your individual health before taking action or relying on published information. However, no mutation has been directly linked with functional 23 changes in viral pathogenicity. Importantly, these viral isolates 27 show significant variation in cytopathic effects and viral load, up to 270-fold differences, 28 when infecting Vero-E6 cells. Although multiple in vitro studies or clinical trials on inhibitors or drugs were 51 carried out, no effective cures or vaccines have been found so far (Cao et al. So far, no recombination events were detected (Yu, 60 2020), although this could be at least partially due to the fact that most viral isolates were 61 sequenced with short-reads platform. The transmembrane spike (S) glycoprotein mediates 62 viral entry into host cells through homotrimers protruding from the viral surface. The S 63 protein includes two domains: S1 for binding to the host cell receptor and S2 for fusion of 64 the viral and cellular membranes, respectively (Tortorici and Veesler, 2019). This is crucial in our understanding of the viral infectious 74 mechanisms and dictates the strategy of drug and vaccine development in preparation for 75 the next stage of the pandemic. Super-deep sequencing of the 11 79 viral isolates on the Novaseq 6000 platform identified 1-5 mutations in the coding 80 sequences among the viral isolates. We infected Vero-E6 cells with 11 viral isolates and quantitatively 82 assessed their viral load at 1, 2, 4, 8, 24, and 48 hours post infection (P. These patients therefore constitute 1st and 2nd 99 generations of the viral victims based on their epidemiological history. The 11 patients 100 include 8 males and 3 females, with ages ranging from 4 months to 71 years old. There 101 are no clear criteria in selecting these patients other than the fact that they were all 102 admitted into Zhejiang University-affiliated hospitals in Hangzhou. Luckily, all of the patients have recovered as of the 105 time of writing this article. A summary of the epidemiological information of the 11 patients involved in 108 this study. Moreover, in cases where the viral populations are not homogenous, the 118 depth could help us to characterize alleles with very low frequency. Previously, only one 129 viral isolate identified in Australia had the T22303G mutation. Observations of these two single nucleotide variants can only be 134 coincidental, albeit very unexpected. Taken together, despite only 11 146 patient-derived isolates being analyzed in this study, we observed abundant mutational 147 diversity, including several founding mutations for different major clusters of viruses 9 148 now circulating globally. This diverse mutational spectrum is consistent with their 149 relatively early sampling time and relative proximity to Wuhan city, where the first viral 150 strain was identified. The full mutational diversity of the virus in Wuhan city in the early 151 days is still unknown to this day, due to limited sampling (Lu et al. If a mutation was observed in the context of a mixed population, the respective 157 percentages of the top two alleles are provided. We used iqtree (see Materials and Methods) to construct a 170 1000-times bootstrapped maximum-likelihood phylogenic tree of the 736 viral sequences 171 based on 835 parsimony informative sites (Fig. The 1000-times bootstrapped maximum likelihood tree was 180 constructed to demonstrate the phylogenetic context of the 11 viral isolates. Specifically, we note the 190 following three biggest clusters in our phylogenetic analysis: 1. Three nucleotide 191 mutations C241T (silent), C14408T (silent), and A23403G (D614G in S) found a group 192 of 231 viral sequences (Fig. Several smaller monophyletic clusters, 201 defined by different sets of founding mutations (bootstrap supporting value >95), can be 202 observed. When integrating the characterized 11 viral isolates into the phylogenetic 208 analysis, they are dispersed across the entire phylogenetic space. The rest of 213 the group either have few mutations or novel mutations that do not cluster with any 214 known sizable groups, reflecting the extensive diversity within our 11 samples. Theoretically, one usually needs not often invoke selection 223 arguments in explaining the origin of these mutations, as the human to human infection 224 process is a series of repeated naturally-occurring bottlenecking events, in which the 225 seeding viral population can be as little as hundreds of viral copies (Forni et al. We first examined whether the viral isolates could successfully bind to Vero-E6 243 cells as expected (Fig. We then infect the Vero-E6 cells with 245 all 11 patient-derived viral isolates and harvest the cells at 1, 2, 4, 8 (in quadruplicates), 16 246 24, and 48 (in duplicates) hours P. Cycle 251 threshold values, C, were used to quantify the viral load, with lower values indicatingt 252 higher viral load. We 254 failed to detect any significant signals from our negative controls, hence we simply 255 assigned a C value of 40 for all them. During these early hours, 258 viral particles are binding to gain access into the cells, and replications would rarely 259 occur (Schneider et al. Therefore, different viral isolates, which are defined by different mutations in 274 their genomes, exhibit a significant variation of viral load when infecting Vero-E6 cells. P-values were 290 calculated between consecutive time points using the t-test and adjusted p-values are 291 shown. Mean Ct values of selected viral 296 isolates are displayed and color-coded, respectively. Pearson correlations were 302 calculated and p-values were adjusted accordingly; only correlations with adjusted 303 p-value < 0. Due to the extremely wide variety of clinical 313 symptoms shown in the patients, establishing a genotype-phenotype link in patients 314 would be very difficult. The in vitro cell line provides an ideal system to examine the 315 mutational impact of different isolates of viruses, when all other confounding factors are 22 316 removed. A diverse collection of mutations was 320 identified in the 11 viral isolates, including two sets of founding mutations for two major 321 clusters of viruses currently infecting the world population. In addition, 19 of the 31 322 identified mutations are novel, despite the relatively early sampling dates, indicating that 323 the true diversity of the viral strains is still largely underappreciated; 2. This could 334 be due to the founding effect of mutations, in which case the T22303G mutation was not 335 transmitted out of the China during the early days; 3. Investigating the functional 339 impact of this tri-nucleotide mutation would be highly interesting. We note that in the 340 current database, another trinucleotide mutation (G28881A, G2882A and G28883C) has 341 been identified, which also results in two missense mutations at the protein level (Fig. Furthermore, characterizations 351 of all founding mutations in the major geo-based clusters of viruses could be very useful 352 in helping determining if there are actionable pathogenicity differences to aid the current 353 battle against the virus. Finally, similar to flu, drug and vaccine development, while 354 urgent, need to take the impact of these accumulating mutations, especially the founding 355 mutations, into account to avoid potential pitfalls. A summary of the epidemiological information of the 11 patients involved in 359 this study. If a mutation was observed in the context of a mixed population, the respective 364 percentages of the top two alleles are provided. The 1000-times bootstrapped maximum likelihood tree was 370 constructed to demonstrate the phylogenetic context of the 11 viral isolates. P-values were 386 calculated between consecutive time points using the t-test and adjusted p-values are 387 shown. Mean Ct values of selected viral 390 isolates are displayed and color-coded, respectively. Pearson correlations were 396 calculated and p-values were adjusted accordingly; only correlations with adjusted 397 p-value < 0. As the pandemic continued to 417 spread, the probability of transmission outside of Hubei Province increased. The 418 epidemiological exposure to Hubei Province was not a prerequisite for suspected cases. The supernatant was collected 433 after centrifugation at 3000 rpm at room temperature. Before infecting Vero-E6 cells, all 434 collected supernatant was filtered using a 0. Results from the first 467 two time points reflect the capacity of viral attachment or entry into the target cells, while 468 results from the latter four time points represent the viral replication dynamics. The primary R packages are mostly 489 maintained by the Bioconductor project. K-values were selected automatically at 33nt, 55nt and 77nt 514 for these samples. After assembling, contigs was blasted to nt database (20190301) to 515 confirm their origins, and only contigs belonging to coronavirus were retained for base 516 correction. Next, filtering reads of each sample were mapped back to retained assembled 517 contigs and bam-readcount was applied (-min-mapping-quality=5, other parameter was 518 set default) to calculate the base frequency of every post of each assemble contigs. Finally, bam files were inspected in igv 521 manually to verify each mutation based on the number of reads mapped, the balance 522 between reads mapped to plus and minus strands of the reference genome, and the 523 relative positions of the mutations on these reads. A summary of the sequencing statistics of the 11 viral isolates involved in the 547 study, Related to Figure 1. A summary of the nucleotide mutations that lead to the S247R mutations 550 observed in the 11 patient-derived isolates, Related to Figure 1. A summary of additional mutations in the S gene and the tri-nucleotide mutation, 553 Related to Figure 1. Note that all three major 557 clusters described in the study are labeled accordingly. P-values were calculated between consecutive time points using the t-test and 570 adjusted p-values are shown. Note that the 585 actual position of S247 was not determined in the original structure, hence a small red arc 586 was in place to represent to the potential flexible loop conformation for (C) and (D). Also 587 note that the protein complex is trimeric, but only one of the three mutations was labeled. Interactive Tree of Life v2: Online annotation and display of phylogenetic 651 trees made easy. Modeling the spread of Middle East respiratory 42 655 syndrome coronavirus in Saudi Arabia. On the Analysis of 674 Intrahost and Interhost Viral Populations: Human Cytomegalovirus as a Case Study of Pitfalls and 675 Expectations. Clinical presentation and virological assessment of hospitalized 696 cases of coronavirus disease 2019 in a travel-associated transmission cluster. Purcell2,3 Abstract | Significance testing was developed as an objective method for summarizing statistical evidence for a hypothesis. It has been widely adopted in genetic studies, including genome-wide association studies and, more recently, exome sequencing studies. However, significance testing in both genome-wide and exome-wide studies must adopt stringent significance thresholds to allow multiple testing, and it is useful only when studies have adequate statistical power, which depends on the characteristics of the phenotype and the putative genetic variant, as well as the study design. Here, we review the principles and applications of significance testing and power calculation, including recently proposed gene-based tests for rare variants. An important goal of human genetic studies is to detect appealing for fine-mapping a region with multiple Likelihoods 5 Probabilities (or probability genetic variations that have an influence on risk of significant signals to identify the true causal variants. The typical Inherent in the significance testing framework is the under an assumed statistical genetic study involves collecting a sample of subjects requirement that studies are designed to enable a realismodel as a function of model with phenotypic information, genotyping these subtic chance of rejecting the null hypothesis (H) when it is parameters.
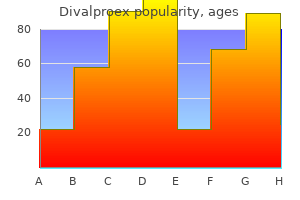
Disodium Hydrogen Orthophosphate (Phosphate Salts). Divalproex.
- Improving aerobic exercise performance.
- High blood calcium, when sodium and potassium phosphates are used.
- Low blood phosphate, when sodium and potassium phosphates are used.
- How does Phosphate Salts work?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Sensitive teeth, heartburn, cleaning out the bowels as a laxative preparation for intestinal tests such as colonoscopy when sodium phosphates are used, and other conditions.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Dosing considerations for Phosphate Salts.
- Preventing some types of kidney stones.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96719
This title takes effect on the date that is 18 months after the date of enactment of this Act medicine 802 divalproex 500mg otc. If any provision of this Act symptoms of mono purchase divalproex mastercard, an amendment made by this Act treatment 1 degree av block discount divalproex 500 mg fast delivery, or the application of such provision or amendment to any person or circumstance is held to be unconstitutional treatment for strep throat cheap divalproex american express, the remainder of this Act medications known to cause hair loss purchase cheap divalproex on line, the amendments made by this Act symptoms 7 weeks pregnancy generic 500 mg divalproex with amex, and the application of such provisions to any person or circumstance shall not be affected thereby. Civil penalties collected for violations of section 12 shall be deposited in the general fund of the Treasury. T h e differentgene th atmakesth e F actorV L eidenproteinisinh erited from one or both parents. T h e clottingactionof F actorV iscontrolled by anoth erproteincalled A ctivated ProteinC. A blood test(called ascreeningtest)cansh ow ifyouh ave A ctivated ProteinC resistance. Heterozygousparent Parentw ith norm algene Ifyouh ave th e h eteroz ygoustype,th ere isa50% ch ance th atyourch ild willinh erita F actorV L eidengene from you. Y ourdoctor cantellyouh ow much fluid isrigh tforyourage,h ealth and activity level. Y ourbroth ersand sistersmay h ave inh erited th e mutated gene forF actorV L eiden,justlike youdid. If you have never had a blood clot, you do not need treatment 800 with blood thinners. T h e risk increaseswith age: Some research suggests that women with the Factor V Leiden gene who have had pregnancy losses may have a greater risk of miscarriages. However, there are things that you can do to reduce your chances of developing a W ith FactorV Leiden the risk of a blood clotincreases dangerous blood clot. W h enyouare ready,talk with yourh ealth care providerforadvice and h elpto lose weigh t. Heterozygous Heterozygous Heterozygous Heterozygous Take care w hen traveling long distances. W h enyouneed h ealth care orgo to th e h ospital,tellyourh ealth outifF actorV L eidenisth e cause ofth e resistance and wh attype ofF actorV L eiden care team th atyouh ave F actorV L eiden,so th atth ey canplanth e care youneed. B efore becomingpregnant,talk with yourdoctorabouth ow yourrisk ofblood T h ere are 2 copiesforF actorV gene,wh ich are passed downfrom ourparents. Heterozyg ous FactorV Leiden Ifyouinh erited 1 F actorV L eidengene from one parent,youh ave th e h eteroz ygous How w illI know if I g etblood clotfi Y ourch ild willh ave eith erth e h eteroz ygousorh omoz ygoustype,dependingon Heterozygous Heterozygous Child w ith Child w ith wh eth erth e gene passed downfrom h isorh eroth erparentisnormal(F actorV) child child norm algene norm algene orabnormal(F actorV L eiden). W h enyouare injured,yourbody stopsbleedingby ch angingliquid blood into a plug(clot)th atblocksth e leaksindamaged blood vessels. F actorV L eidenresiststh e effectsofA ctivated ProteinC,so ittakeslongerto turnoff F actorV L eiden. T h isiswh y F actorV L eidenissometimescalled A ctivated ProteinC R esistance and wh y people with th is mutationclotmore th anth ose with outit. There is also another bleeding disorder known as acquired haemophilia, which is not inherited like the classical form of haemophilia. Acquired haemophilia usually develops when people are older and can affect both men and women. In Australia there are more than 2,800 people with haemophilia, who are nearly all male. However, some females who carry the genetic alteration that causes haemophilia can also have bleeding problems. The common belief that people with haemophilia could bleed to death from a cut is a myth. A person with haemophilia does not bleed any faster than anyone else, but the bleeding continues for longer if it is not treated and may lead to a delay in healing. Minor cuts and scratches are not a problem and need only 2 a Band-Aid and some pressure at the site of bleeding. With deeper cuts or injuries, bleeding continues for longer if blood does not form a tough, adherent clot where the blood vessels have been damaged. If internal bleeding is not stopped quickly with treatment, it will result in pain and swelling. Over a period of time, repeated bleeding into joints and muscles can cause permanent damage, such as arthritis in the joints, and chronic pain. Bleeds into the head, spine, neck, throat, chest, stomach or abdominal area are much less common but can be life-threatening. If this happens, the person with haemophilia should attend an emergency centre immediately and the Haemophilia Centre should also be contacted. There is at least one specialist Haemophilia Centre in every Australian state or territory, located in a major public hospital. The Haemophilia Centre has a team of health professionals, including doctors, nurses, physiotherapists, and social workers or counsellors, who specialise in the treatment and care of people with bleeding disorders. A person with haemophilia will have the same level of severity over their lifetime, eg a person with severe haemophilia will always have severe haemophilia. Within a family, males with haemophilia will also have the same level of severity, eg if a grandfather has severe haemophilia and his grandson has inherited haemophilia, his grandson will also have severe haemophilia. The laboratory tests will show whether he has mild, moderate or severe haemophilia. Haemophilia may be suspected if babies have internal bleeding or unusual swelling or bruising after delivery, continue to bleed after a heel prick or after circumcision, or have excessive bruising after immunisation. Testing should be repeated when the baby is six months of age to confrm the results. When all babies begin to crawl and walk, they can knock into hard objects as well as having twists, falls or sitting down with a bump. In a child with severe haemophilia, these might become serious and should be checked by a haemophilia specialist. Painful swelling or reluctance to use an arm or a leg can be a sign that a bleed has taken place. The specialist nurses and physiotherapists at the Haemophilia Centre can advise on haemophilia issues during these normal childhood stages. Informing the nurse or doctor giving the immunisation that the baby or toddler has haemophilia is important. Injections can be given subcutaneously, into the fatty tissue under the skin, rather than into the muscle, and pressure put on the skin where the child was injected. If you have a child with haemophilia, contact the Haemophilia Centre for advice on how your child should be immunised. If they have mild haemophilia, minor injuries may heal normally because there is enough clotting factor activity in the blood. The bleeding problem might not be noticed until the person has surgery, a tooth taken out or a major accident or injury. Growing up with haemophilia With treatment and support from their Haemophilia Centre, most people with haemophilia can live relatively normal healthy lives. Unless there are complications, young people can expect to grow up with fewer or no joint problems from their haemophilia. With sensible precautions, they can play most sports, exercise and look forward to a full and productive life. Men with haemophilia will pass the altered gene on to their daughters but not their sons. Males have one X chromosome, which they receive from their mother, and one Y chromosome, which they receive from their father. There are four possible combinations of sex chromosomes that children can receive from their parents. A woman who carries the altered gene can pass it on to both her sons and her daughters. With each pregnancy, there is a 50% chance her male baby will have haemophilia or a 50% chance her female baby will carry the altered gene. No family history of haemophilia In about one third of people born with haemophilia, there is no history of the disorder in the family. Once haemophilia appears in a family the altered gene is then passed on from parents to children following the usual pattern for haemophilia. Family members should seek genetic counselling and testing if there is someone in the family who has haemophilia. In very rare cases, some girls or women have particularly low factor levels causing them to have moderate or severe haemophilia. All females who carry the gene should have testing for their clotting factor levels. Unlike males with haemophilia, where the factor level is the same within the same family, the factor level in females who carry the gene is unpredictable and varies between family members. Women and girls with lower levels should have theirs checked periodically, as their factor levels may change with age, pregnancy and hormonal medications. If their factor level is low, they will need a treatment plan to prevent bleeding problems and manage any situations that occur. A common time for testing whether a girl or woman carries the gene is when she reaches childbearing age and can understand the process and implications fully and make the decision for herself. Finding out whether she carries the gene is a process which will take time, sometimes many months. The Haemophilia Centre can help with information and advice about genetic testing and can provide a referral to a genetic counsellor, if needed. Women, their partner, parents or family can talk to the Haemophilia Centre or genetic counsellor individually or together prior to testing and many fnd it helpful. If a person starts exploring genetic testing but decides against it, there is no obligation to complete the process.
Mutation [250] Zappella M medicinebg order generic divalproex on-line, Meloni I medications to treat bipolar generic 500 mg divalproex with amex, Longo I medications or therapy buy 250 mg divalproex free shipping, Canitano R treatment lupus purchase divalproex australia, Hayek G 9 medications that can cause heartburn quality 500mg divalproex, Rosaia L symptoms in children divalproex 250mg discount, et al. Macrocephaly as a clinical analysis in autistic boys with developmental regression. For healthy development, published medical chromosomes should contain just the expected amount of genetic literature. Like most other named author and chromosome disorders, having an extra part of chromosome 7 publication date are may affect the development and intellectual abilities of a child, given to allow you although there is considerable variability in these and other to look for the individual features that are observed. We have addition, this leaflet 23 pairs of chromosomes giving a total of 46 individual draws on chromosomes. Of these 46 chromosomes, two are the sex information from a chromosomes that determine whether we are male or female. The remaining 44 conducted in 2010, chromosomes are grouped in 22 pairs, numbered 1 to 22. February 2013, Unique had 21 Chromosome Duplications members with a A sperm cell from the father and an egg cell from the mother each pure 7q11. When they join together duplication (no they form a single cell that carries two copies of each other chromosome chromosome. These the chromosomes and genetic material) in order to make the members range in trillions of cells that form during human growth and development. We are still learning about the specific roles of the genes in known to have this region (see Ongoing Research into chromosome 7q11. In the diagram of chromosome 7 on the right you can see the bands are numbered outwards on each arm starting from where the two arms meet (this is known as the centromere). The extra piece of genetic material on q arm chromosome 7 is too small to be seen using a microscope. So a basic chromosome staining analysis (such as karyotyping) is unlikely to identify this duplication. Williams syndrome is caused by a deletion of the same piece of chromosome that is duplicated in 7q11. The duplication is very unlikely to have been inherited and has almost certainly occurred for the first time in this child arr cgh (7)(q11. This means base pair numbers are continually adjusted so it is important to note which build your genetic test results refer to . In the children who are affected, the features that are most notable and most common are: fi Speech and language delay or disorder fi Learning difficulties. A small number of babies may be born with a split in the roof of the mouth or lip (cleft palate or lip) fi Children are generally healthy although a minority have seizures fi Subtle facial features (a large head (macrocephaly) has been described in about half of people reported with 7q11. But there will still be differences, sometimes quite marked, between your child and others with an 6 years apparently similar chromosome diagnosis. It is important to see your child as an individual and not to make direct comparisons with others with the same diagnosis or syndrome name. However, careful examination for possible subtle language difficulties have shown that most, if not all carriers will have experienced some language difficulties at some point during their lives (Mervis 2015). Recent studies have identified about a quarter of parents as having passed on the duplication to their child (Morris 2015). However, far fewer people were initially reported in the medical literature (about 50 were reported in 2011). More people are still reported with the deletion, this is very likely to be due to the fact that the duplication is less severe and the features are highly variable (Velleman 2011; Morris 2015). However, a few women have reported problems during pregnancy and some infants have required intensive care following birth (Morris 2015). However, a few babies are small and underweight at birth, and a significant fraction are in the upper 5% of birth weights (Morris 2015). Birth weights recorded at Unique and in the published medical literature show a considerable variation with an average of 3. Overall, no consistent effect on growth has been found (Somerville 2005; Berg 2007; Depienne 2007; Van der Aa 2009; Unique). More recent publications in the medical literature have identified a number of children with a 7q11. Feeding Most babies and children do not have feeding problems and many are able to successfully breastfeed, although one or two need tube feeding at first (Somerville 2005). Unique data show that many babies (6 out of 7) have gastro-oesophageal reflux (where feeds and stomach contents return into the food passage and are often vomited or may be inhaled, causing chest infections, known as aspiration pneumonia) but this has generally been well controlled by giving feeds slowly, positioning a baby semi-upright for feeds and where necessary raising the head end of the bed for sleeping. If these measures are not enough, prescribed medications or anti-reflux milk are usually enough to keep feeds down. In only one case was reflux serious enough for hospital treatment (Berg 2007; Torniero 2007; Unique). A more recent research project (Morris 2015) described four young children as having significant problems with feeding requiring feeding via gastrostomy (one of whom was still tube fed at age 12 years). One Unique child had no feeding problems as a baby but struggled initially when she started eating solid food and would choke very easily. One child described in the medical literature had hyperphagia (increased appetite and consumption of food) (Depienne 2007; Unique). In six Unique children (out of eight), and also in 66% of a series of children in the published medical literature (Morris 2015), constipation was a significant problem. Dietary changes and/or medication can help to manage constipation (Berg 2007; Van der Aa 2009; Unique). Appearance Babies and children with this duplication look perfectly normal and would not stand out from a crowd of other children. Geneticists trained to note unusual features may find some but these do not add up to a typical, recognisable facial appearance. Three authors have commented on a slight asymmetry of the face and macrocephaly (a large head) has been reported in a few people (Somerville 2005; Berg 2007; Torniero 2007; Van der Aa 2009; Velleman 2011). Development: sitting, moving, walking (gross motor skills) Some people with a 7q11. All people described in the literature and known to Unique were fully mobile although some older children still had minor problems with balance and gait 9 years (Somerville 2005; Berg 2007; Depienne 2007; Torniero 2008; Van der Aa 2009; Unique). Individual babies start to sit between 6 months and 15 months (average 10 months). Independent walking was mastered between 12 months and 2 years 2 months (average 18 months). In some cases, there were difficulties with coordinating both sides of the body, and with balance, leading to difficulties standing on one leg, hopping, skipping and pedalling (Somerville 2005; Berg 2007; Depienne 2007; Unique). One of the causes of the delay in mobility is low muscle tone (hypotonia), reported in as many as 70 % of children. This makes a child or baby feel floppy to handle but generally improves as children mature and may disappear with physiotherapy and exercises (Van der Aa 2009; Unique). She is able to do most of the things she should, she is just not as strong/quick/independent/confident. In terms of self care, data from Unique and the medical literature suggests that children may be late to be toilet trained during the day (average age 4 years) and at night. In a child with a borderline or mild learning disability, it 10 years may not be appropriate for parents to expect toileting to occur at the same age as in other unaffected children (Depienne 2007; Unique). Children have early delays in learning to express themselves understandably in organised words and phrases. However, all older children and adults who have been fully described do speak and most of them eventually talk in phrases and sentences, many with no obvious difficulty. Despite this, it is clear that the range, severity and permanence of the effect on speech and language vary a lot between individuals. While some children have only spoken their first understandable words between the ages of 18 months and four years, their understanding has been 8 generally much more advanced than their ability to talk. Later stages of language development have also been delayed, with vocabulary increasing but not at the same rate you would expect in other children. Progression to two-word phrases and sentences has been noted after the age of six years. One report suggests that 15 % (4 children out of 26) have mild language delays; 35 % (9 children out of 26) have moderate delays and 50 % (13 children out of 26) have more severe delays. Another recent study of 42 adults and children (aged 18 months to 61 years) found that receptive language skills (understanding of language) were less affected than expressive language (what they are able to communicate). Most of the toddlers in this study had very limited speech and few identifiable, meaningful words. Among 25 children (aged 4-17 years) more than three quarters had verbal apraxia and dysarthria (see box below) more than half had articulation problems. Most had learned to compensate for their difficulties; the errors they made were primarily in challenging multisyllabic words (eg aluminium) or tongue twisters (Somerville 2005; Kriek 2006; Berg 2007; Depienne 2007; Torniero 2007; Van der Aa 2009; Velleman 2011; Unique). More recently, 52 of 61 children (82%) were diagnosed with Speech Sound Disorder, with older children being less likely to have a diagnosis. One child had speech delay but improved dramatically between the ages of 4fi years and 5 years, coincident with medication for severe anxiety (see Behaviour page 14) (Berg 2007). It includes speech planning symptoms such as speech that takes lots of effort; difficulty putting sounds and syllables together in the correct order to form words. Speech Sound Disorder is a communication disorder in which children have persistent difficulty saying words or sounds correctly. Speech sound production describes the clear articulation of individual sounds (phonemes) that make up spoken words. Speech sound production requires both the knowledge of how speech sounds and the ability to coordinate the jaw, tongue, and lips with breathing and vocalizing in order to produce it. In most cases, children with speech sound disorder respond well to treatment and speech difficulties improve over time. Pronunciation difficulties have been obvious, with children only articulating the first syllable of a word or not progressing beyond two-syllable words. When tested, hearing has been normal but specific difficulties making certain sounds of speech (such as l, r) have been described in both children and adults. These specific learning differences result in many children requiring special help in school. A recent study suggests that 61 % (39 children out of 63) have average or low average intelligence, 30 % (19 children out of 63) have borderline average intelligence or mild learning difficulties and only 8 % (5 children out of 63) have moderate or severe learning difficulties (Mervis 2015). Most children will attend mainstream school but some may need classroom assistance or special needs lessons; other children benefit from a special education school (Van der Aa 2009; Unique). The expressive language delay does not appear to lead on to a comparable delay in reading. It is believed that visuo-spatial reasoning (recognizing visual patterns and drawing inferences from them) is relatively protected in most children with a 7q11. Unique families report that their children draw relatively well and in an interesting way. However, writing skills and mathematics may be weak areas as may any learning area where children are expected to articulate their thoughts rapidly.
Lung cancer in never smokers: Clinical epidemiology and environmental risk factors treatment zoster ophthalmicus quality 250mg divalproex. The unexpected role for the aryl hydrocarbon receptor on susceptibility to experimental toxoplasmosis medicine 02 generic divalproex 250 mg free shipping. Genotoxic effects of chlorpyrifos medicine 4211 v cheap 250 mg divalproex, cypermethrin symptoms pneumonia proven divalproex 250 mg, endosulfan and 2 medicine 2015 order divalproex 250 mg,4-D on human peripheral lymphocytes cultured from smokers and nonsmokers treatment sinus infection discount 500 mg divalproex with mastercard. Health symptoms related to pesticide exposure and agricultural tasks among rice farmers from northern Thailand. Cancer mortality in workers exposed to chlorophenoxy herbicides and chlorophenols. Cellular toxicity of 2,4, 5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid: Formation of 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetylcholine. The fate of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) following oral administration to man. The cutaneous lesions of dioxin exposure: Lessons from the poisoning of Victor Yushchenko. Chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin and dibenzofuran levels in human adipose tissue and milk samples from the north and south of Vietnam. Dioxins and dioxinlike chemicals in blood and semen of American Vietnam veterans from the state of M ichigan. A follow-up: High level of dioxin contamination in Vietnamese from Agent Orange, three decades after the end of spraying [letter]. Polychlorinated biphenyls and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin induce intrachromosomal recombination in vitro and in vivo. Occupational exposures as risk factors for oral cancer evaluated in a Swedish case-control study. Polychlorinated biphenyls: the occurrence of the main congeners in follicular and sperm fuids. A prospective study of mortality and trauma-related risk factors among a nationally representative sample of Vietnam veterans. Spontaneous abortion, sex ratio, and paternal occupational exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Neurodegenerative diseases: Occupational occurrence and potential risk factors, 1982 through 1991. Residential and occupational exposure to pesticides may increase risk for cutaneous melanoma: A case-control study conducted in the south of Brazil. M ultiple myeloma mortality and agricultural practices in the prairie provinces of Canada. Gene expression profling of responses to dimethylarsinic acid in female F344 rat urothelium. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen production is dependent on the aromatic hydrocarbon receptor. Environmental and occupational exposure of metals and their role in male reproductive functions. Association of asthma with use of pesticides: Results of a cross-sectional survey of farmers. Early pregnancy agricultural pesticide exposures and risk of gastroschisis among offspring in the San Joaquin Valley of California. The role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in normal and malignant B cell development. M odulation of natural killer cell antitumor activity by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Higher urinary heavy metal, phthalate, and arsenic but not parabens concentrations in people with high blood pressure, U. Incidence and prevalence of multiple allergic disorders recorded in a national primary care database. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-null allele mice have hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells with abnormal characteristics and functions. Loss of aryl hydrocarbon receptor promotes gene changes associated with premature hematopoietic stem cell exhaustion and development of a myeloproliferative disorder in aging mice. Persistent organic pollutants and abnormal geometry of the left ventricle in the elderly. Epigenetic transgenerational actions of environmental factors in disease etiology. Rhinitis associated with pesticide exposure among commercial pesticide applicators in the Agricultural Health Study. Preliminary report of reproductive outcomes among pesticide applicators using 2,4,5-T. The New Zealand soft tissue sarcoma case-control study: Interview fndings concerning phenoxyacetic acid exposure. Soft tissue sarcoma and exposure to phenoxyherbicides and chlorophenols in New Zealand. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor directs hematopoietic progenitor cell expansion and differentiation. Phenoxy herbicides and chlorophenols: A case-control study on soft tissue sarcoma and malignant lymphoma. Ah receptor activation potentiates neutrophil chemoattractant (C-X-C motif) ligand 5 expression in keratinocytes and skin. Post-traumatic stress disorder among American Legionnaires in relation to combat experience in Vietnam: Associated and contributing factors. A soft tissue sarcoma case-control study in a large multi-chemical manufacturing facility. Effect of developmental dioxin exposure on methylation and expression of specifc imprinted genes in mice. Genome-wide profling of 5-formylcytosine reveals its roles in epigenetic priming. Ligand-dependent and independent modulation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor localization, degradation, and gene regulation. Attenuating effect of lycopene and ellagic acid on 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced spermiotoxicity and testicular apoptosis. Plasma polychlorinated biphenyl concentrations and immune function in postmenopausal women. Environmental factors in an Ontario community with disparities in colorectal cancer incidence. Ontogeny of swimming behavior and brain catecholamine turnover in rats prenatally exposed to a mixture of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic and 2,4, 5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acids. The role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in the development of cells with the molecular and functional characteristics of cancer stem-like cells. Pesticide use and incident diabetes among wives of farmers in the Agricultural Health Study. Arsenic and subclinical vascular damage in a sample of Italian young adults: A cross-sectional analysis. Cancer, heart disease, and diabetes in workers exposed to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. A pilot epidemiologic study of possible health effects associated with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin contaminations in Missouri. Individual differences in arsenic metabolism and lung cancer in a case-control study in Cordoba, Argentina. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor and aryl hydrocarbon nuclear translocator expression in human and rat placentas and transcription activity in human trophoblast cultures. Social and behavioral consequences of the Vietnam experience among American Legionnaires. A geographic information system for characterizing exposure to Agent Orange and other herbicides in Vietnam. Estimation of exposure to Agent Orange and other defoliants among American troops in Vietnam: A methodological approach. Exposure estimates in epidemiological studies of Korean veterans of the Vietnam W ar. Combat and herbicide exposures in Vietnam among a sample of American Legionnaires. Health and reproductive outcomes among American Legionnaires in relation to combat and herbicide exposure in Vietnam. External infuences on the immune system via activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Prenatal exposure to polychlorinated biphenyls and dioxins is associated with increased risk of wheeze and infections in infants. Growth and thyroid function in children with in utero exposure to dioxin: A 5-year follow-up study. The effect of in utero exposure to dioxins and polychlorinated biphenyls on reproductive development in eight yearold children. Thyroid and growth hormone concentrations in 8-year-old children exposed in utero to dioxins and polychlorinated biphenyls. In utero and lactational exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin modulates dysregulation of the lipid metabolism in mouse offspring fed a high-calorie diet. Effects of cytochrome p450 inducers on the gene expression of ocular xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes in rats. The relationship between Agent Orange and prostate specifc antigen: A comparison of a hotspot and a non-sprayed area in Vietnam. Infuence of dioxin exposure upon levels of prostate-specifc antigen and steroid hormones in Vietnamese men. The relationship between dioxins exposure and risk of prostate cancer with steroid hormone and age in Vietnamese men. Exposure to chemicals and metals and risk of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A systematic review. Effect-based hazard identifcation of house dust by in vitro assays detecting dioxin-like compounds, thyroid and reproductive toxicants. Distributions and chemical forms of arsenic after intravenous administration of dimethylarsinic and monomethylarsonic acids to rats. Dietary administration of sodium arsenite to rats: Relations between dose and urinary concentrations of methylated and thio-metabolites and effects on the rat urinary bladder epithelium. Parameters of immunological competence in subjects with high consumption of fsh contaminated with persistent organochlorine compounds. The 2016 revision of the W orld Health Organization classifcation of lymphoid neoplasms. Dioxins and cytogenetic status of villagers after 40 years of Agent Orange application in Vietnam. Human papilomavirus in head and neck cancer: M olecular biology and clinicopathological correlations. Sex ratio of the offspring of New Zealand phenoxy herbicide producers exposed to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Dioxin concentrations in breast milk of Vietnamese nursing mothers: A survey four decades after herbicide spraying. Effects of perinatal dioxin exposure on development of children during the frst 3 years of life. The enhancing effect of the antioxidant n-acetylcysteine on urinary bladder injury induced by dimethylarsinic acid. Dioxin silences gonadotropin expression in perinatal pups by inducing histone deacetylases: A new insight into the mechanism for the imprinting of sexual immaturity by dioxin. Toxic effects of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid on human sperm function in vitro. Risk of adverse reproductive outcomes associated with proximity to municipal solid waste incinerators with high dioxin emission levels in Japan. The disease intersection of susceptibility and exposure: Chemical exposures and neurodegenerative disease risk. The Agricultural Health Study: Factors affecting completion and return of self-administered questionnaires in a large prospective cohort study of pesticide applicators. Constitutive expression of aryl hydrocarbon receptor in keratinocytes causes infammatory skin lesions. Dioxin risk assessment: Mechanisms of action and possible toxicity in human health. Alteration of lipid status and lipid metabolism, induction of oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation by 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic herbicide in rat liver. Neurodevelopmental retardation, as assessed clinically and with magnetoencephalography and electroencephalography, associated with perinatal dioxin exposure.
Cheap divalproex 500mg. Atlas Genius- Symptoms (subtitulada al español).
References
- Sanders DB, Howard JF, Johns TR. Single fiber electromyography in myasthenia gravis. Neurology. 1979;29:68-76.
- Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. Ultrasound Screening for Fetal Abnormalities. Report of the RCOG Working Party. London: RCOG Press, 1997: 2-3.
- Deavers M, Guinee D, Koss MN, Travis WD. Granular cell tumors of the lung. Clinicopathologic study of 20 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19(6):627-35.
- Dire DJ. Emergency management of dog and cat bite wounds. Emerg Med Clin North Am 1992;10:719-736.
- Chen CR, Cheng TO, Chen JY, et al. Long-term results of percutaneous balloon mitral valvuloplasty for mitral stenosis: a follow-up study to 11 years in 202 patients. Cathet Cardiovasc Diagn. 1998;453:132-39.