John Ellwood
- Professor Emeritus

https://publichealth.berkeley.edu/people/john-ellwood/
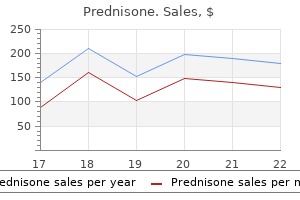
If in situ allergy shots fatigue buy prednisone with visa, the of anastomotic leak may be related to intraoperative manage epidural catheter should be appropriately dosed prior to emer ment variables allergy shots igg buy prednisone 5mg otc, particularly systemic blood pressure and cardiac gence allergy symptoms in infants buy discount prednisone on-line. Tracheal extubation is performed at emergence with output and may thus be modifiable by anesthetic management allergy shots immune system generic 20 mg prednisone. The head of the bed should be elevated tube blood flow allergy testing norman ok cheap prednisone 40 mg visa, though the limited available data do not sup between 30 and 45? to optimize respiratory mechanics and port this reasoning allergy otc purchase cheapest prednisone. The effect of vasoconstrictors on gastric to minimize the potential for reflux and aspiration. Postop tube blood flow has not been well studied, but a small clini erative therapy includes antibiotics and thromboprophylaxis. Towards this end it may be prudent to postpone dos ing the indwelling epidural catheter in a hypotensive patient and to consider the use of inotropic agents with or without Postoperative Care of the Esophagectomy Patient vasopressor activity. Early ambulation and chest in the operating room provided that they are normothermic, physiotherapy are used to reduce respiratory complications. Although absence of air leak is confirmed, though mediastinal drains an older randomized trial comparing early vs. The indwelling epidural catheter is gen extubation group, this difference was not statistically sig erally used and left in situ until pleural drains are removed, at nificant [237] and has not been observed subsequently. Early which time pain control can be adequately accomplished with extubation after esophagectomy has been well studied and parenteral or enteral medications. Feeding via jejunostomy is supported by a number of retrospective and observational tubes is initiated after 24 h postoperatively and advanced over analyses [108, 238, 239] as well as reports of standardized a period of several days. A contrast study of the esophagus is management approaches [109] and fast track clinical path usually performed on or about the fifth postoperative day and ways [108, 110, 240]. Factors which may predict failure or if normal, a clear diet by mouth is begun at that time. At dis complications associated with early extubation include a his charge, the patient will be eating solid food and the jejunos tory of smoking and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease tomy tube is clamped. At emergence, patients should be seated 30? above supine and extubated upon return of protective airway reflexes. Adverse Outcomes After Esophagectomy Supplemental oxygen may be delivered via face tent or nasal Adverse outcomes after esophagectomy surgery have histori cannulae. If postoperative ventilatory support is required or cally been divided into surgical and anesthetic complications. Preoperative, blockers for esophageal surgery has been discussed earlier operative, and postoperative factors that may predispose to the and applies here as well. Though high quality comparative stud evidence suggests that intraoperative management may have ies are few and randomized controlled trials are completely an impact on the incidence of this complication. Though the optimization of tissue oxygen ual or cluster of these complications can result in respira delivery through appropriate management of hemodynamics, tory insufficiency or respiratory failure, which may require fluid status, and oxygenation is a priority for all perioperative specific therapies including the continuation or reinstitution patients, this truism may be particularly critical for patients of mechanical ventilation. Factors predictive Cardiovascular Complications of pulmonary complications after esophagectomy include age [250, 251], proximal location of esophageal tumor, and dura Cardiovascular complications account for significant mor tion of surgery [250], as well as forced expiratory volume in bidity and mortality after esophagectomy. While generally considered plications associated with esophagectomy and their incidence benign after cardiac surgery, these diagnoses may be more in a large series was 23. Though injury can occur whom atrial fibrillation was a marker for increased morbidity from a variety of mechanisms, the final pathway appears to and mortality [246]. Atrial fibrillation after esophagectomy involve inflammatory mediators including cytokines and cel is also associated with a higher rate of pulmonary complica lular mediators. Still a very active area of investigation, it tions, anastomotic leakage, and sepsis [245]. The routine prophylactic use of digoxin, flecainide, and amiodarone is not supported by the available Improving Outcomes After Esophagectomy evidence [248]. Though lung injury in this context is multifactorial, there is a growing awareness that anesthetic and perioperative factors Surgery for Esophageal Rupture are involved. Strategies to protect the based on the severity of these presenting conditions and the lung and optimize outcomes after major thoracic surgery are nature of the planned procedure. To the extent possible, fluid most likely to be successful if they minimize these injurious deficits should be corrected preoperatively and may be guided stimuli. Guidance in the absence of definitive outcome data by standard and invasive monitoring as appropriate. Because in the perioperative thoracic surgery setting is based largely of the likelihood of further fluid losses and hemodynamic dec on results from studies of animal models, surrogate mark ompensation, an arterial catheter for continuous blood pres ers of lung injury, and patients with established lung injury. Nonetheless, several reasonable conclusions can be drawn at the principles of anesthetic management are based on cor this time. Thus, the choice and dose of induction and neuromuscular blocking ventilation should be as physiologic as possible in an effort agents tailored to the patient?s hemodynamic status. Since oxygen toxicity and oxidative esophageal obstruction at the sphincter level as well as for the stress may also contribute to the development of adverse out relief of pain from esophageal spasm. Arguably, the most important anesthetic consideration effects such as myocardial protection. Recent evidence suggests is the possibility of aspiration on induction of anesthesia with that sevoflurane may also affect lung tissue by modulating the loss of protective airway reflexes. Anesthesia for Esophageal Surgery 435 of retained food material in the esophagus is dramatically Transthoracic repair of esophageal diverticula is usually increased. It may also be desirable to restrict oral intake to only accomplished via a left thoracotomy incision. Approaches to minimize the risk of regurgita the anesthesiologist may assist by passing a large esophageal tion and aspiration have been discussed previously and are bougie with surgical guidance until it passes the diverticular especially important in these patients. The use of hageal integrity has been demonstrated by a contrast esopha thoracoscopy to perform a transthoracic myotomy undoubt gram several days postoperatively. Most patients can be extubated in the operating room Clinical Case Discussion (Fig. He denies ever having an elec aged to manually express and empty the diverticulum prior to trophysiologic study performed. Other efforts to avoid (enalapril), hypercholesterolemia (simvastatin), and asthma aspiration of diverticular contents include a head-up position (albuterol as needed and Claritin). His only surgery has been a (30?) during induction and a rapid sequence induction without C4?7 discectomy and fusion and a L4?S1 laminectomy. In the patient with difficult airway anatomy scheduled for an Ivor-Lewis esophagectomy. Caution should be exercised during placement of a gastric drain tube or esophageal bougie as these may enter the diverticulum and cause perforation. Thoracic Diverticula Patients presenting with thoracic esophageal diverticula may represent a subclass of patients at the highest risk for aspiration in the perioperative period. First, these diverticula may be large and potentially contain significant quantities of food material. Secondly, these diver ticula cannot be emptied by manual expression, though drain age may be possible with the careful placement of a large bore drain tube. Additionally, most thoracic diverticula are associ ated with an esophageal motility disorder such as achalasia which is itself, a high-risk condition with regard to aspiration. Thus, all reasonable precautions should be taken, including a head-up position, and either a rapid sequence induction or an Fig. Laparoscopic fundoplication: 5-year follow Focused Preoperative History, Physical, up. A 25-year gram to evaluate audible murmur and ventricular function experience with open primary transthoracic repair of parae (see Chap. Perforation of the Considerations Will Optimize esophagus: correlation of site and cause with plain film findings. Thoracic epidural to provide postoperative analgesia for management of esophageal perforation. Avoidance of beta-blockade because of a significant his tion in adults: aggressive, conservative treatment lowers morbid tory of reactive airway disease and chronic calcium chan ity and mortality. Calcium channel blockers indicated for treating forations with self-expandable covered metal stents. Use of self-expandable oxygen delivery, with particular attention to the high-risk plastic stents for the treatment of esophageal perforations and esophageal anastomosis. Use of large-diameter metallic stents to seal traumatic non seek to optimize cardiac output and oxygen delivery while malignant perforations of the esophagus. High postoperative risk of atrial arrhythmias, in particular, cal review of epidemiological studies. Achalasia: physiology and etiopatho preoperative use of a calcium channel blocker and history genesis. The spec if atrial fibrillation is sustained and resistant to rate control trum of esophageal motor disorders in Chagas? disease. Delayed presentation of tracheo Esophageal radiography and manometry: correlation in 172 patients oesophageal fistula following percutaneous dilatational tracheos with dysphagia. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Williams, tracheo-esophageal fistula associated with endotracheal intuba and Wilkins; 2007. Thoracoscopic versus laparoscopic modified Heller Myo sophageal fistula in the adolescent and adult. Thoracoscopic esophagomyotomy for achalasia: cheoesophageal fistula with co-existing laryngeal cleft. Thoracoscopic esophagomy fistulas presenting in adults: presentation of two cases and a synop otomy for achalasia: preoperative patterns of acid reflux and long sis of the literature. Temporary stenting of acquired Heller-Dor operation remains an effective treatment for esopha benign tracheoesophageal fistulas in critically ill ventilated geal achalasia at a minimum 6-year follow-up. Evaluation and outcome of different surgical techniques for between subjective and objective outcome measures after Hel postintubation tracheoesophageal fistulas. Surgical treatment of epiphrenic diverticula: a plus Dor fundoplication versus Nissen fundoplication for achala 30-year experience. Gastroin evaluation of esophageal reconstruction using the colon or the test Endosc. Multimodal treatment of oesophageal colon for free oesophageal reconstruction: an experimental radio cancer. Postoperative func Thoracic Surgeons practice guideline series: guidelines for the tion of free? jejunal transplants for replacement of the cervical management of Barrett?s esophagus with high-grade dysplasia. Transthoracic versus transhi guidelines on perioperative cardiovascular evaluation and care for atal esophagectomy: a prospective study of 945 patients. J Thorac noncardiac surgery: executive summary: a report of the American Cardiovasc Surg. Mini Practice Guidelines (writing committee to revise the 2002 guide mally invasive esophagectomy: outcomes in 222 patients. Quality of life after gists, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, colon interposition by necessity for esophageal cancer replace Society for Vascular Medicine and Biology, and Society for ment. A comparison of thoracic patients with gastric tube in place after esophageal resection: and lumbar epidural techniques for post-thoracoabdominal use of omeprazole to decrease gastric acidity and volume. Thoracic epidural erative intravenous pantoprazole in elective-surgery patients: a versus intercostal nerve catheter plus patient-controlled analge pilot study. Continuous epi improving preoperative gastric fluid property in adults undergo dural or intercostal analgesia following thoracotomy: a prospec ing elective surgery. Gastroesophageal reflux and aspiration of gas phine requirement after esophagectomy with thoracotomy: a tric contents in anesthetic practice. Postoperative analgesia reduces sic efficacy and side-effects of paravertebral vs epidural block mortality and morbidity after esophagectomy. Postthoracotomy paraver effects of postoperative analgesic therapies on pulmonary out tebral analgesia: will it replace epidural analgesia? Perioperative risk fac versus postoperative epidural analgesia: a randomised study. J Cardiothorac ysis of reduced death and complication rates after esophageal Vasc Anesth. Continuous positive airway pathways improve outcomes in patients with esophageal cancer. Significant airway tomy is decreased after introduction of a multimodal anesthetic compromise in a child with a posterior mediastinal mass due to regimen. Fracture of the cricoid cartilage unusual cause of intraoperative tracheal compression and expi after Sellick?s manoeuvre. High risk of aspiration and difficult intubation down position for patients with a full stomach. Curr Opin anaesthesia for operative obstetrics: with special reference Anaesthesiol. Aspiration risk after esophagec reflux and tracheal aspiration in the thoracotomy position: tomy. American Society of Anesthesiologist Task Force on Preopera tubes during thoracic surgery. Randomized use of pharmacologic agents to reduce the risk of pulmonary clinical trial to determine the effect of nasogastric drainage on aspiration: application to healthy patients undergoing elective tracheal acid aspiration following oesophagectomy. Arndt endobronchial blocker during oesophagec prevent perioperative complications. Cricoid bation device for a double-lumen tube during rapid-sequence pressure displaces the esophagus: an observational study using induction. Intraoperative intravascular intravenous fluid restriction on postoperative complications: com volume optimisation and length of hospital stay after repair of parison of two perioperative fluid regimens: a randomized asses proximal femoral fracture: randomised controlled trial. Randomised controlled trial assessing the impact of gastrointestinal function after elective colonic resection: a ran a nurse delivered, flow monitored protocol for optimisation of domised controlled trial. Effect of intraoperative fluid management on outcome oesophageal Doppler guided fluid management shortens post after intraabdominal surgery. Does central venous pressure or pulmonary erative colloid administration reduces postoperative nausea and capillary wedge pressure reflect the status of circulating blood vomiting and improves postoperative outcomes compared with volume in patients after extended transthoracic esophagectomy? Goal-directed intraopera loid administration improves the microcirculation of healthy and tive fluid administration reduces length of hospital stay after perianastomotic colon. Effect of fluid pressure variation monitoring during high-risk surgery: a pilot loading with saline or colloids on pulmonary permeability, randomized controlled trial.
Children with present with incontinence allergy luxe buy discount prednisone 40mg on-line, urinary tract infections and dysfunctional voiding have a higher rate of recurrent constipation and demonstrate fluctuating or intermittent urinary tract infections than children with no voiding patterns during repeated uroflowmetry allergy medicine hair loss buy cheap prednisone 5 mg line. They may include small bladder No clear data are available on the possible causes of capacity allergy symptoms green phlegm trusted prednisone 20mg, increased detrusor thickness allergy treatment relief buy prednisone 10 mg visa, decreased dysfunctional voiding allergy under armpits buy prednisone with mastercard. It may be that an detrusor detrusor contractility allergy symptoms sleepy purchase prednisone 10 mg with mastercard, impaired relaxation of the external overactivity eventually leads to overactivity of the urinary sphincter/ pelvic floor during voiding, weak or pelvic floor muscles, with subsequent insufficient interrupted urinary stream and large post-void residual relaxation during voiding [61]. There may also be ultrasound relaxation of the pelvic floor muscles during voiding abnormalities, secondary vesicoureteric reflux, fecal may be a learned condition during the toilet training soiling or constipation [54, 71, 72]. The child?s environment, in particular toilet conditions Symptoms are often refractory to standard therapy of 731 hydration, bowel management, timed voiding and Treatment basic relaxed voiding education. Effective intervention Treatment is aimed at optimizing bladder emptying requires combination therapy, generally with a sizeable after each void. Treatment is is the procedure of choice to promote complete bladder aimed at optimizing bladder emptying and inducing full emptying, in combination with treatment of infections relaxation of the urinary sphincter or pelvic floor prior and constipation [which may be extreme in these to and during voiding. Intravesical electrostimulation has been Specific goals are: described, but at this time it is still not recommended as a routine procedure for children. If the bladder neck is implicated the children with voiding postponement only 20% in increased resistance to voiding, alpha-blocker drugs exhibiting a fluctuating voiding pattern. Recurrent urinary infections and be determined whether or not voiding postponement constipation should be treated and prevented during can develop in the setting of a perfectly normal urinary the treatment period. As with detrusor overactivity, In some children giggling can trigger partial to complete the natural history of untreated dysfunctional voiding bladder emptying well into their teenage years, and is not well delineated and optimum duration of therapy intermittently into adulthood [75]. Voiding is of long duration, low pressure, intermittent It is postulated that laughter induces a generalized and often augmented with abdominal straining. It has also been suggested that bladder has a larger than normal capacity, a normal giggle incontinence is due to laughter triggering the compliance and reduced or no detrusor contraction micturition reflex and overriding central inhibitory during voiding. The previously used term lazy bladder? with cataplexy (a state of excessive daytime is incorrect and should no longer be used. Long-standing overactivity it is difficult to determine the appropriate form of of the pelvic floor may in some children be responsible treatment. Positive results have been reported with for decompensation of the detrusor, leading to a non conditioning training, methylphenidate and imipramine contractile detrusor. There is no acceptable 732 evidence that any form of treatment is superior to no Abnormal recruitment of the external anal sphincter intervention. Grade of recommendation D causative, in that it elicits concomitant urethral sphincter and pelvic floor co-contractions. In the case of the urinary system, high Urinary leakage that occurs in girls a short time after pressures generated by the detrusor muscle to voiding to completion, that is not associated with any overcome a decrease in urethral diameter can strong desire to void, may be the result of vesicovaginal stimulate detrusor hypertrophy, detrusor overactivity, reflux and lead to incompetence of the vesicoureteric [81]. In the early stages of defecation disorders, during voiding due to labial adhesions, a funnel shaped bowel emptying is incomplete, infrequent and poorly hymen, or an inappropriate position on the toilet. As the dysfunction progresses stool quality classic presentation is that of a girl who does not becomes abnormal, the child develops distension of spread her legs apart during voiding and who is not the rectum and descending colon, seems to lose sitting all the way back on the toilet seat, but who is normal sensation and develops fecal retentive soiling. Changes in voiding position and treatment of labial Children with elimination syndrome commonly adhesions will lead usually to resolution of the urine complain of urinary incontinence, non-monosym leakage. The incidence of detrusor over activity, constipation and infrequent of children with elimination syndrome and sub-clinical voiding. The genitourinary tract and the gastrointestinal system Assessment follows the same process as for other are interdependent, sharing the same embryologic aspects of pediatric bladder dysfunction, with the origin, pelvic region and sacral innervation. Although addition of a 2 week bowel diary and relevant symptom children with voiding disturbances often present with score. The inclusion of an ultrasound rectal diameter bowel dysfunction, until recently this co-existence measure, either via the perineum or when assessing was considered coincidental. However, it is now the bladder, has been shown to be discriminative for accepted that dysfunction of emptying of both systems, children with elimination syndrome. The common when considered in isolation, are not conclusive for neural pathways, or the mutual passage through the the diagnosis of elimination syndrome. There is no pelvic floor musculature, may provide a theoretical evidence to suggest that anorectal manometry is basis for this relationship, as may the acquisition of warranted as a first line investigation in these children. Treatment There is also evidence to suggest that in severe cases Treatment aims at assisting a child to become clean symptoms may have a neurological basis. Infections do not ameliorate with disimpaction [if needed], prevention of stool antibacterial prophylaxis. Pelvic Bladder training? is used widely, but the evidence floor awareness training and biofeedback therapy are that it works is variable [50, 88]. More active conventional management involves constipation management on bladder symptoms, a combination of cognitive, behavioral, physical and however until last year the baseline characteristics pharmacological therapy methods. Common modes of subjects were not described adequately enough of treatment include parent and child reassurance, to allow clear diagnosis of elimination syndromes [57, bladder retraining (including timed toileting), 87]. Grade of recommendation C pressure associated with urinary incontinence [25, 89-91]. Despite its use for many years caregiver(s) are educated about normal bladder there is no set format to urotherapy and many clinical function and responses to urgency. The aim of urotherapy is to normalize the cotherapy, pelvic floor muscle relaxation techniques micturition pattern and to prevent further functional and biofeedback, either alone or in combination. This is achieved through a combination Although there are many studies reported in the of patient education, cognitive, behavioral and physical literature assessing the effects of various forms of therapy methods. The paucity of in 240 children with daytime incontinence noted studies evaluating basic standard therapy initiatives achievement of dryness in 126 children (55%). Alarm has precluded double-blinded trials of novel and therapy has traditionally been used for the treatment multimodal interventions. Whilst clinically important of nocturnal enuresis and but was recently used in benefits are commonly described, patient numbers, management of daytime wetting. When a time watch objective outcome measures and length of follow-up was utilized as a reminder to void at regular intervals are sub-optimal. An earlier study of a contingent alarm [which sounded when the child wets] the main objectives of treatment are to normalise versus a noncontingent alarm system (which sounded the micturition pattern, normalise bladder and pelvic at intermittent intervals to remind the child to void) floor overactivity and cure the incontinence, infections over 3 months in 45 children [92] was equally and constipation. Children learn Predictors for dryness included a low voiding to recognize the desire to void and to suppress this frequency, larger volumes voided in relation to age by normal central inhibition instead of resorting to expected storage and fewer incontinent episodes per holding manoeuvers [i. Children with dysfunctional voiding learn to initiate Following a 3 month training programme, 42. Antibiotic prophylaxis may improve their continence than those with poor 734 compliance. It has recently been highlighted however, biofeedback group compared to the standard therapy that there is frequently conflict between school rules, only group. Adaptive coping techniques results of intervention in children who are continually added to urotherapy training may enhanced gains in growing and maturing. Physiotherapy is concerned with re-training with dysfunctional voiding and 73% of those with a of specific muscle groups. Adjunctive physiotherapeutic combined disturbance had a normal micturition pattern. This requires careful guidance for due to pelvic floor muscle overactivity) abnormalities. This is invasive and a time consuming process with limited use as a routine Neuromodulation has been used in adults for a variety treatment. Transcutaneous and percu display, and attempts to empty completely in one taneous neuromodulation delivered over either the relaxed void. Ultrasound may be used to determine sacral outflow or peroneal region of the ankle at a the post void residual and demonstrate complete frequency between 10-25 Hz, has proven a useful emptying. Interactive computer games are commonly adjunctive treatment in children with an detrusor used to make biofeedback training more attractive to overactivity [22, 24, 25]. Intravesically stimulation can children [100, 101], however care should be taken impact function of an underactive detrusor and that posture and muscle recruitment approximates potentially improve detrusor contractility and enhance that of the voiding position. Results are generally system by artificially activating neural structures; positive but overall may not be superior to high quality facilitating both neural plasticity and normative afferent standard urotherapy. For biofeedback in the Vasconcelos study [94] did not children with structural abnormalities, for example achieve greater continence rates at the study end imperforate anus, electrostimulation is one method point, although a greater proportion of subjects of facilitating strength gains in the skeletal muscle achieved earlier dryness. Treatment is particularly residual volumes were significantly reduced in the useful in patients with very little pelvic floor awareness 735 to stimulate muscle recruitment. Once neural efficiency of the risk of persistent wetting with the noncontingent has improved, training is augmented by active pelvic alarm, the difference in the reduction in wetting floor contractions. In a more recent retrospective A literature search revealed 10 reports of the use of review by Van Laecke et al, a cure rate of 35% after neuromodulation in children with non-neurogenic the use of a daytime alarm was described[109]. Only one of these studies was to the retrospective design of the study the level of randomized and controlled, whilst the rest were case evidence is low. There is minimal standardization of therapies rather than single interventions, which populations, application parameters or outcome makes it difficult to evaluate the results. Thus evidence is largely drawn from low therapy and biofeedback both focus on the pelvic quality studies. Relaxation of the pelvic floor during voiding warrants larger, controlled and randomized studies. In most papers the inclusion and exclusion stimulation with implantable electrodes have been criteria are not clearly documented, and it may very published. In a group of 20 patients between 8 and well be that the more difficult patients with both 17 years old followed prospectively, urinary storage and voiding dysfunction were included in incontinence, urgency and frequency, nocturnal the study population. Furthermore, different series enuresis and constipation were improved or resolved may describe different groups of patients due to in 88% (14 of 16), 69% (9 of 13), 89% (8 of 9), 69% poor definitions and an inadequate classification (11 of 16) and 71% (12 of 17) of subjects, respectively. In children with a suspected bladder outlet Complications were seen in 20% of patients. Most often the anatomic abnormality Due to the uncontrolled design the level of evidence causing abstruction can be treated at the same is low. In girls, a meatal web may cause a deflection modality suggests future positive development in of the stream upwards [causing stimulation of the children to be likely. Grade of recommendation D may cure this problem, though no information on the long-term effects is available [64]. Only one randomised clinical trial has been published to establish the efficacy of this Antimuscarinic therapy remains one of the common form of treatment. Halliday et al compared a contingent forms of therapy for the detrusor overactivity. Its use alarm which sounded when the child wets] with a is predicated on the concept that parasympathetic noncontingent alarm system (which sounded at mediated stimulation of muscarinic receptors in the intermittent intervals to remind the child to void) [92]. Antimuscarinic agents have been demonstrated to Success was measured as 6 consecutive increase bladder capacity, increase bladder weeks without daytime wetting. Nine children in the compliance and decrease detrusor contractions in non-contingent group and 6 children in the contingent neurogenic detrusor overactivity. Although the risk of is believed to play a role in many children with persistent wetting with the contingent alarm was 67% functional incontinence, vesicoureteral reflux and 736 Table 2. It is the first antimuscarinic agent designed pharmacotherapy is instituted when behavioral therapy specifically for use in detrusor overactivity and is felt has failed to achieve a satisfactory outcome. It?s affinity for the bladder clinicians use pharmacologic therapy as a first line compared to other organ systems leads to an improved therapy in children with moderate to severe daytime tolerability profile. The delivery Despite the frequent use of anticholinergic therapy, system of the long acting preparation is such that the often in conjunction with a behavioral therapy regimen, capsule may be cracked and sprinkled? on food. Currently the Hjalmas reported the results of an open label, dose pharmacologic therapy most widely used in children escalation study using immediate release tolterodine with detrusor overactivity is oxybutynin [111]. Bolduc et al reported on a prospective crossover dose-related, both for oral and intravesical admi study of 34 children followed for > 1 year who were nistration [113]. Efficacy amount of active metabolite [produced in the liver]: was assessed by a questionnaire and was comparable resulting in a more favorable tolerability profile. Sixty-eight percent delivery system requires an intact tablet and thus it noted a > 90% reduction in wetting episodes at 1 year cannot be cut or crushed to facilitate swallowing. This method of delivery also avoids the first effects with tolterodine and 18% reported the same pass effect and leads to increased amounts of side effect as with oxybutynin, but felt it was less oxybutynin available compared to immediate release severe. Its use in the neurologically intact patient Munding et al reported on the use of tolderodine in is limited by the need for catheterization [114]. There double blinded, assessing the efficacy of oxybutynin was no documentation of uroflow studies to make the in detrusor overactivity in children. Curran et al, in a diagnosis of dysfunctional voiding? and from the retrospective review assessed the efficacy of several symptoms these children appeared to have detrusor agents, primarily oxybutynin in children with non overactivitys. Children were started on behavioral neurogenic detrusor overactivity, confirmed by modification for 4-6 weeks and pharmacologic therapy urodynamics who were refractory to behavioral was instituted if they failed or had only slight therapy. Eighty percent had complete resolution or a 1 month?s follow-up was needed for inclusion, but the significant improvement in their urinary symptoms. Grade of recommendation C retrospective study of the efficacy and safety of Tolterodine, a nonselective antimuscarinic is currently immediate release and long acting tolterodine and being used for the treatment of detrusor overactivity extended release oxybutynin [121]. Children started 738 out with the lowest possible dose, 2 mg tolterodine and incontinence episodes (-0. Final dose and evidence 1 that shows beneficial effect of anti duration of treatment were not noted. Initial and that extended release oxybutynin was more results seem promising, but more studies need to be effective than extended release tolterodine in resolving done. The trigone should not be injected, tolterodine extended release in a large pediatric as there is an increased risk of reflux developing. Botulinum toxin is not registered for injection in the detrusor or the sphincter Level of evidence: 3. It is off label used and further prospective One of the drugs which has been investigated in a studies are needed before general recommendation. Because of serious cardiac side effects shows beneficial effects of botulinum toxin in 70% of terodiline has been withdrawn from the market. Injection of botulinum toxin is also possible into used in small series in children.
Diagnostic guidelines A definite diagnosis of dependence should usually be made only if three or more of the following have been present together at some time during the previous year: (a)a strong desire or sense of compulsion to take the substance; (b)difficulties in controlling substance-taking behaviour in terms of its onset spring allergy symptoms 2013 purchase 10mg prednisone, termination allergy forecast hawaii buy genuine prednisone, or levels of use; (c)a physiological withdrawal state (see F1x allergy kansas city discount prednisone 20 mg with visa. Narrowing of the personal repertoire of patterns of psychoactive substance use has also been described as a characteristic feature (e allergy medicine not strong enough buy prednisone with mastercard. It is an essential characteristic of the dependence syndrome that either psychoactive substance taking or a desire to take a particular substance should be present; the subjective awareness of compulsion to use drugs is most commonly seen during attempts to stop or control substance use allergy shots problems cheap 10 mg prednisone with mastercard. This diagnostic requirement would exclude allergy testing diet generic prednisone 20mg with amex, for instance, surgical patients given opioid drugs for the relief of pain, who may show signs of an opioid withdrawal state when drugs are not given but who have no desire to continue taking drugs. Includes: chronic alcoholism dipsomania drug addiction the diagnosis of the dependence syndrome may be further specified by the following five-character codes: F1x. Onset and course of the withdrawal state are time-limited and are related to the type of substance and the dose being used immediately before abstinence. Diagnostic guidelines Withdrawal state is one of the indicators of dependence syndrome (see F1x. Withdrawal state should be coded as the main diagnosis if it is the reason for referral and sufficiently severe to require medical attention in its own right. Typically, the patient is likely to report that withdrawal symptoms are relieved by further substance use. It should be remembered that withdrawal symptoms can be induced by conditioned/learned stimuli in the absence of immediately preceding substance use. In such cases a diagnosis of withdrawal state should be made only if it is warranted in terms of severity. Many symptoms present in drug withdrawal state may also be caused by other psychiatric conditions. Simple "hangover" or tremor due to other conditions should not be confused with the symptoms of a withdrawal state. The diagnosis of withdrawal state may be further specified by using the following five-character codes: F1x. Delirium tremens is a short-lived, but occasionally life-threatening, toxic-confusional state with accompanying somatic disturbances. It is usually a consequence of absolute or relative withdrawal of alcohol in severely dependent users with a long history of use. In some cases the disorder appears during an episode of heavy drinking, in which case it should be coded here. The classical triad of symptoms includes clouding of consciousness and confusion, vivid hallucinations and illusions affecting any sensory modality, and marked tremor. Delusions, agitation, insomnia or sleep-cycle reversal, and autonomic overactivity are usually also present. The sensorium is usually clear but some degree of clouding of consciousness, though not severe confusion, may be present. The disorder typically resolves at least partially within 1 month and fully within 6 months. Diagnostic guidelines A psychotic disorder occurring during or immediately after drug use (usually within 48 hours) should be recorded here provided that it is not a manifestation of drug withdrawal state with delirium (see F1x. Late-onset psychotic disorders (with onset more than 2 weeks after substance use) may occur, but should be coded as F1x. Psychoactive substance-induced psychotic disorders may present with varying patterns of symptoms. These variations will be influenced by the type of substance involved and the personality of the user. For stimulant drugs such as cocaine and amfetamines, drug-induced psychotic disorders are generally closely related to high dose levels and/or prolonged use of the substance. A diagnosis of a psychotic disorder should not be made merely on the basis of perceptual distortions or hallucinatory experiences when substances having primary hallucinogenic effects (e. In such cases, and also for confusional states, a possible diagnosis of acute intoxication (F1x. Particular care should also be taken to avoid mistakenly diagnosing a more serious condition (e. Many psychoactive substance-induced psychotic states are of short duration provided that no further amounts of the drug are taken (as in the case of amfetamine and cocaine psychoses). False diagnosis in such cases may have distressing and costly implications for the patient and for the health services. Consider the possibility of another mental disorder being aggravated or precipitated by psychoactive substance use (e. In such cases, a diagnosis of psychoactive substance-induced psychotic state may be inappropriate. Disturbances of time sense and ordering of events are usually evident, as are difficulties in learning new material. Other cognitive functions are usually relatively well preserved and amnesic defects are out of proportion to other disturbances. Diagnostic guidelines Amnesic syndrome induced by alcohol or other psychoactive substances coded here should meet the general criteria for organic amnesic syndrome (see F04). The primary requirements for this diagnosis are: (a)memory impairment as shown in impairment of recent memory (learning of new material); disturbances of time sense (rearrangements of chronological sequence, telescoping of repeated events into one, etc. Personality changes, often with apparent apathy and loss of initiative, and a tendency towards self-neglect may also be present, but should not be regarded as necessary conditions for diagnosis. Although confabulation may be marked it should not be regarded as a necessary prerequisite for diagnosis. Consider: organic amnesic syndrome (nonalcoholic) (see F04); other organic syndromes involving marked impairment of memory (e. Diagnostic guidelines Onset of the disorder should be directly related to the use of alcohol or a psychoactive substance. Cases in which initial onset occurs later than episode(s) of substance use should be coded here only where clear and strong evidence is available to attribute the state to the residual effect of the substance. The disorder should represent a change from or marked exaggeration of prior and normal state of functioning. The disorder should persist beyond any period of time during which direct effects of the psychoactive substance might be assumed to be operative (see F1x. Alcohol or psychoactive substance-induced dementia is not always irreversible; after an extended period of total abstinence, intellectual functions and memory may improve. The disorder should be carefully distinguished from withdrawal-related conditions (see F1x. It should be remembered that, under certain conditions and for certain substances, withdrawal state phenomena may be present for a period of many days or weeks after discontinuation of the substance. Conditions induced by a psychoactive substance, persisting after its use, and meeting the criteria for diagnosis of psychotic disorder should not be diagnosed here (use F1x. Consider: pre-existing mental disorder masked by substance use and re-emerging as psychoactive substance-related effects fade (for example, phobic anxiety, a depressive disorder, schizophrenia, or schizotypal disorder). Consider also organic injury and mild or moderate mental retardation (F70-F71), which may coexist with psychoactive substance misuse. This diagnostic rubric may be further subdivided by using the following five-character codes: -75 F1x. Schizotypal disorder possesses many of the characteristic features of schizophrenic disorders and is probably genetically related to them; however, the hallucinations, delusions, and gross behavioural disturbances of schizophrenia itself are absent and so this disorder does not always come to medical attention. Most of the delusional disorders are probably unrelated to schizophrenia, although they may be difficult to distinguish clinically, particularly in their early stages. They form a heterogeneous and poorly understood collection of disorders, which can conveniently be divided according to their typical duration into a group of persistent delusional disorders and a larger group of acute and transient psychotic disorders. Schizoaffective disorders have been retained in this section in spite of their controversial nature. F20 Schizophrenia the schizophrenic disorders are characterized in general by fundamental and characteristic distortions of thinking and perception, and by inappropriate or blunted affect. Clear consciousness and intellectual capacity are usually maintained, although certain cognitive deficits may evolve in the course of time. The disturbance involves the most basic functions that give the normal person a feeling of individuality, uniqueness, and self-direction. Perception is frequently disturbed in other ways: colours or sounds may seem unduly vivid or altered in quality, and irrelevant features of ordinary things may appear more important than the whole object or situation. Perplexity is also common early on and frequently leads to a belief that everyday situations possess a special, usually sinister, meaning intended uniquely for the individual. In the characteristic schizo phrenic disturbance of thinking, peripheral and irrelevant features of a total concept, which are inhibited in normal directed mental activity, are brought to the fore and utilized in place of those that are relevant and appropriate to the situation. Thus thinking becomes vague, elliptical, and obscure, and its expression in speech sometimes incomprehensible. Breaks and interpolations in the train of thought are frequent, and thoughts may seem to be withdrawn by some outside agency. Ambivalence and disturbance of volition may appear as inertia, negativism, or stupor. The onset may be acute, with seriously disturbed behaviour, or insidious, with a gradual development of odd ideas and conduct. The course of the disorder shows equally great variation and is by no means inevitably chronic or deteriorating (the course is specified by five-character categories). In a proportion of cases, which may vary in different cultures and populations, the outcome is complete, or nearly complete, recovery. The sexes are approximately equally affected but the onset tends to be later in women. Diagnostic guidelines the normal requirement for a diagnosis of schizophrenia is that a minimum of one very clear symptom (and usually two or more if less clear-cut) belonging to any one of the groups listed as (a) to (d) above, or symptoms from at least two of the groups referred to as (e) to (h), should have been clearly present for most of the time during a period of 1 month or more. Conditions meeting such symptomatic requirements but of duration less than 1 month (whether treated or not) should be diagnosed in the first instance as acute schizophrenia-like psychotic disorder (F23. Symptom (i) in the above list applies only to the diagnosis of Simple Schizophrenia (F20. Viewed retrospectively, it may be clear that a prodromal phase in which symptoms and behaviour, such as loss of interest in work, social activities, and personal appearance and hygiene, together with generalized anxiety and mild degrees of depression and preoccupation, preceded the onset of psychotic symptoms by weeks or even months. Because of the difficulty in timing onset, the 1-month duration criterion applies only to the specific symptoms listed above and not to any prodromal nonpsychotic phase. The diagnosis of schizophrenia should not be made in the presence of extensive depressive or manic symptoms unless it is clear that schizophrenic symptoms antedated the affective disturbance. If both schizophrenic and affective symptoms develop together and are evenly balanced, the diagnosis of schizoaffective disorder (F25. Schizophrenia should not be diagnosed in the presence of overt brain disease or during states of drug intoxication or withdrawal. Similar disorders developing in the presence of epilepsy or other brain disease should be coded under F06. Pattern of course the course of schizophrenic disorders can be classified by using the following five-character codes: F20. The clinical picture is dominated by relatively stable, often paranoid, delusions, usually accompanied by hallucinations, particularly of the auditory variety, and perceptual disturbances. Disturbances of affect, volition, and speech, and catatonic symptoms, are not prominent. Examples of the most common paranoid symptoms are: (a)delusions of persecution, reference, exalted birth, special mission, bodily change, or jealousy; (b)hallucinatory voices that threaten the patient or give commands, or auditory hallucinations without verbal form, such as whistling, humming, or laughing; (c)hallucinations of smell or taste, or of sexual or other bodily sensations; visual hallucinations may occur but are rarely predominant. Thought disorder may be obvious in acute states, but if so it does not prevent the typical delusions or hallucinations from being described clearly. Affect is usually less blunted than in other varieties of schizophrenia, but a minor degree of incongruity is common, as are mood disturbances such as irritability, sudden anger, fearfulness, and suspicion. The course of paranoid schizophrenia may be episodic, with partial or complete remissions, or chronic. In chronic cases, the florid symptoms persist over years and it is difficult to distinguish discrete episodes. Diagnostic guidelines the general criteria for a diagnosis of schizophrenia (see introduction to F20 above) must be satisfied. In addition, hallucinations and/or delusions must be prominent, and disturbances of affect, volition and speech, and catatonic symptoms must be relatively inconspicuous. Delusions can be of almost any kind but delusions of control, influence, or passivity, and persecutory beliefs of various kinds are the most characteristic. It is important to exclude epileptic and drug-induced psychoses, and to remember that persecutory delusions might carry little diagnostic weight in people from certain countries or cultures. The mood is shallow and inappropriate and often accompanied by giggling or self-satisfied, self-absorbed smiling, or by a lofty manner, grimaces, mannerisms, pranks, hypochondriacal complaints, and reiterated phrases. There is a tendency to remain solitary, and behaviour seems empty of purpose and feeling. This form of schizophrenia usually starts between the ages of 15 and 25 years and tends to have a poor prognosis because of the rapid development of "negative" symptoms, particularly flattening of affect and loss of volition. Hebephrenia should normally be diagnosed for the first time only in adolescents or young adults. The premorbid personality is characteristically, but not necessarily, rather shy and solitary. For a confident diagnosis of hebephrenia, a period of 2 or 3 months of continuous observation is usually necessary, in order to ensure that the characteristic behaviours described above are sustained. For reasons that are poorly understood, catatonic schizophrenia is now rarely seen in industrial countries, though it remains common elsewhere. These catatonic phenomena may be combined with a dream-like (oneiroid) state with vivid scenic hallucinations. Transitory and isolated catatonic symptoms may occur in the context of any other subtype of schizophrenia, but for a diagnosis of catatonic schizophrenia one or more of the following behaviours should dominate the clinical picture: (a)stupor (marked decrease in reactivity to the environment and in spontaneous movements and activity) or mutism; (b)excitement (apparently purposeless motor activity, not influenced by external stimuli); (c)posturing (voluntary assumption and maintenance of inappropriate or bizarre postures); (d)negativism (an apparently motiveless resistance to all instructions or attempts to be moved, or movement in the opposite direction); (e)rigidity (maintenance of a rigid posture against efforts to be moved); (f)waxy flexibility (maintenance of limbs and body in externally imposed positions); and (g)other symptoms such as command automatism (automatic compliance with instructions), and perseveration of words and phrases. In uncommunicative patients with behavioural manifestations of catatonic disorder, the diagnosis of schizophrenia may have to be provisional until adequate evidence of the presence of other symptoms is obtained.
For 2 separate days procedure: (allow 2 hours on day 1 for stress test allergy symptoms dark circles under eyes cheap prednisone 10mg free shipping, 1 hour on day 2 to complete the exam) Nothing to eat or drink for 6 hours prior to exam on both days allergy shots toddlers cheap prednisone. Often allergy and immunology salary order prednisone online now, contrast materials allow the radiologist to distinguish normal from abnormal conditions allergy testing chattanooga purchase prednisone no prescription. They are substances that temporarily change the way x-rays or other imaging tools interact with the body allergy forecast grapevine order prednisone 5 mg on-line. When introduced into the body prior to an imaging exam allergy treatment training discount prednisone 40mg fast delivery, contrast materials make certain structures or tissues in the body appear different on the images than they would if no contrast material had been administered. Contrast materials help distinguish or "contrast" selected areas of the body from surrounding tissue. By improving the visibility of specific organs, blood vessels or tissues, contrast materials help physicians diagnose medical conditions. They can be: swallowed (taken by mouth or orally) administered by enema (given rectally) injected into a blood vessel (vein or artery; also called given intravenously or intra-arterially) Following an imaging exam with contrast material, the material is absorbed by the body or eliminated through urine or bowel movements. Contrast materials can have a chemical structure that includes iodine, a naturally occurring chemical element. These contrast materials can be injected into veins or arteries, within the disks or the fluid spaces of the spine, and into other body cavities. It is also used rectally and is available in several forms, including: powder, which is mixed with water before administration liquid paste tablet When iodine-based and barium-sulfate contrast materials are present in a specific area of the body, they block or limit the ability of x-rays to pass through. Saline (salt water) and gas (such as air) are also used as contrast materials in imaging exams. Microbubbles and microspheres have been administered for ultrasound imaging exams, particularly exams of the heart. In some situations, iodine-based contrast materials are substituted for barium-sulfate contrast materials for rectal administration. Typically they are used to enhance the: internal organs, including the heart, lungs, liver, adrenal glands, kidneys, pancreas, gallbladder, spleen, uterus, and bladder gastrointestinal tract, including the stomach, small intestine and large intestine arteries and veins of the body, including vessels in the brain, neck, chest, abdomen, pelvis and legs soft tissues of the body, including the muscles, fat and skin brain breast Microbubble Contrast Materials Microbubble contrast materials are tiny bubbles of an injectable gas held in a supporting shell. They are extremely small?smaller than a red blood cell?and have a high degree of "echogenicity", or ability to reflect ultrasound waves. Once the microbubbles are in the bloodstream, ultrasound technology is able capture differences in echogenicity between the gas in the microbubbles and the surrounding tissues of the body, producing an ultrasound image with increased contrast. The microbubbles dissolve, usually within 10 to 15 minutes, and the gas within them is removed from the body through exhalation. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound with microbubbles is a convenient, relatively inexpensive way to improve visualization of blood flow that does not use radiation. Untargeted contrast-enhanced ultrasound the more common method? helps diagnose certain diseases by providing evaluation of blood flow in the heart and other organs. In targeted contrast-enhanced ultrasound, specific molecules are bound to the surface of the microbubbles. After injection, the microbubbles attach at tissue sites expressing the molecular target, leading to a local increase in the ultrasonic signal. Contrast materials are safe drugs; adverse reactions ranging from mild to severe do occur but severe reactions are very uncommon. While serious allergic or other reactions to contrast materials are rare, radiology departments are well-equipped to deal with them. Because contrast materials carry a slight risk of causing an allergic reaction or adverse reaction, you should tell your doctor about: allergies to contrast materials, food, drugs, dyes, preservatives, or animals medications you are taking, including herbal supplements recent illnesses, surgeries, or other medical conditions history of asthma and hay fever history of heart disease, diabetes, kidney disease, thyroid problems or sickle cell anemia You will be given specific instructions on how to prepare for your exam. Side effects and adverse and allergic reactions Barium Sulfate Contrast Materials You should tell your doctor if these mild side effects of barium-sulfate contrast materials become severe or do not go away: stomach cramps Contrast Materials Page 4 of 9 Copyright? 2019, RadiologyInfo. Iodine-based Contrast Materials Mild reactions include: nausea and vomiting headache itching flushing mild skin rash or hives Contrast Materials Page 5 of 9 Copyright? 2019, RadiologyInfo. Most are mild, but severe rashes may require medication after discussion with your physician. Contrast-Induced Nephropathy Patients with impaired kidney (renal) function should be given special consideration before receiving iodine-based contrast materials by vein or artery. At-Risk Patients Some conditions increase the risk of an allergic or adverse reaction to iodine-based contrast materials. These include: previous adverse reactions to iodine-based contrast materials history of asthma history of allergy heart disease Contrast Materials Page 6 of 9 Copyright? 2019, RadiologyInfo. Medications are sometimes given before the contrast material is administered to lessen the risk of an allergic reaction in susceptible patients. Very rarely, patients are allergic to gadolinium-based contrast materials and experience hives and itchy eyes. Gadolinium-based contrast material may be withheld in some patients with severe kidney disease. While there are no known negative effects from this, your doctor may take gadolinium retention into account when selecting a contrast agent. There are a number of different gadolinium-based contrast agents available, each with its own safety profile. Decisions on which material to use may be affected by the part of the body being imaged, the cost of the material and other factors. Barium-Sulfate Oral and Rectal Contrast Material If a barium-sulfate contrast material (given orally or rectally) will be used during your exam, you will be asked not to eat for several hours before your exam begins. If the contrast material will be given rectally, you may also be asked to cleanse your colon with a special diet and medication (possibly including an enema) before your exam. If you swallow the contrast material, you may find the taste mildly unpleasant; however, most patients can easily tolerate it. If your contrast material is given by enema, you can expect to experience a sense of abdominal fullness and an increasing need to expel the liquid. Some patients may experience changes in their normal bowel movement patterns for the first 12 to 24 hours. Iodine-based Contrast Material When an iodine-based contrast material is injected into your bloodstream, you may have a warm, flushed sensation and a metallic taste in your mouth that lasts for a few minutes. It is a good idea to increase your fluid intake after an imaging exam involving an iodine-based contrast material to help remove the contrast material from your body. Gadolinium-based Contrast Material When the gadolinium is injected, it is normal to feel coolness at the site of injection, usually the arm for a minute or two. For all of the above administrations of contrast material (barium sulfate, iodine-based, and gadolinium-based): If you have not been sedated, no recovery period is necessary. Pregnancy and contrast materials Prior to any imaging exam, women should always inform their physician or x-ray technologist if there is any possibility that they are pregnant. Many imaging tests and contrast material administrations are avoided during pregnancy to minimize risk to the baby. Intravenous Contrast Material (Iodine and Gadolinium) and Breast-feeding: Contrast Materials Page 8 of 9 Copyright? 2019, RadiologyInfo. We believe, therefore, that the available data suggest that it is safe for the mother and infant to continue breast-feeding after receiving such an agent. If the mother remains concerned about any potential ill effects, she should be given the opportunity to make an informed decision as to whether to continue or temporarily abstain from breast-feeding after receiving a gadolinium contrast medium. If the mother so desires, she may abstain from breast-feeding for 24 hours with active expression and discarding of breast milk from both breasts during that period. In anticipation of this, she may wish to use a breast pump to obtain milk before the contrast study to feed the infant during the 24-hour period following the examination. Disclaimer this information is copied from the RadiologyInfo Web site. To ensure that, each section is reviewed by a physician with expertise in the area presented. Crohn?s disease and ulcerative colitis are disorders of unknown cause, involving genetic and immunological influence on the gastrointestinal tract?s ability to distinguish foreign from self-antigens. They share many overlapping epidemiological, clinical, and therapeutic characteristics. In some patients it is not possible to distinguish which form of inflammatory bowel disease is present (Figure 2). There are, however, important pathological and clinical differences that distinguish these inflammatory disease processes. Cobblestoning mucosa and aphthous or linear ulcers characterize the endoscopic appearance of Crohn?s disease. Radiographic studies of patients with Crohn?s disease characteristically show fistulae, asymmetry, and ileal involvement. In contrast, radiographic studies of patients with ulcerative colitis show continuous disease without fistulizing or ileal disease. Figure 3 compares the anatomic distribution of Crohn?s disease and ulcerative colitis. Although the terminal ileum and the right colon are the most commonly involved sites, a similar pathological and clinical disorder can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth to the perianal area. The broad term Crohn?s disease does not imply any one cause, site, or pathological response. Crohn?s is a chronic illness that requires expensive medications, often hospitalization and/or surgery, and results in a heavy social and economic toll. Comparison of the appearance of normal, Crohn?s, and ulcerative colitis mucosa; gross (top); histological (center); endoscopic (bottom). Urban areas have a higher incidence of disease than rural populations, and ethnic minorities (south Asians in the United Kingdom, blacks in South Africa, Bedouin Arabs in Israel) are at lower risk. Jews originating from middle Europe (Ashkenazi Jews) and those individuals of Scandinavian descent are at increased risk (Figure 5). Inflammation extends all the way through the intestinal wall from mucosa to serosa. Initially only a small segment of the gastrointestinal tract may be involved, but Crohn?s disease has the potential to progress extensively. Although surgical resection of inflamed segments may temporarily arrest symptoms, subsequent inflammation is likely to recur. Resection is not curative in Crohn?s disease, which is in contrast to ulcerative colitis, where colectomy eliminates the illness. This illness usually appears early in life; about one-sixth of patients present before the age of 15 and often with severe disease. The cause of Crohn?s disease is unknown, although strong genetic influences are suggested by the occurrence of this disease in families, with a higher incidence in Jews than in the general population. Genetic influences are more prominent in the younger onset subgroup of patients than those who present after the age of 40. In one-third of patients with Crohn?s disease, the gross pathologic changes are limited to the terminal part of the ileum. About 40% of patients have ileocolitis, involvement of the distal ileum and proximal colon. About 5% have ileojejunitis, in which there is either continuous involvement throughout the small bowel, or more commonly, several sharply demarcated skip areas separated by normal bowel, sparing the terminal ileum. The colonic lesions are often segmental and sometimes spare the rectum; this helps to distinguish them from ulcerative colitis, which always involves the rectum and is continuous rather than segmental. Despite these differences, in about 10% of patients with chronic inflammatory bowel disease confined to the colon both macroscopically and microscopically, the diagnosis must be classified as indeterminate. Ulcerative colitis can be cured by total colectomy, and disease does not recur in an ileoanal pouch. Alternatively, segmental resections of the colon can be helpful in patients with Crohn?s disease. The widespread microscopic disease may partially account for the high rate of recurrence (50% at 5?I0 years) after surgical resection of all gross disease. In contrast, ulcerative colitis usually remains within the mucosa; in only a few patients does colitis go on to perforate. These are usually considered diagnostic, since granulomas are rare in ulcerative colitis. The inflammatory type affects 30% of patients, remains localized to the mucosa and submucosa, and causes diarrhea and pain from acute partial obstruction. Aggressive transmural inflammation leads to intra-abdominal fistulae from the diseased bowel wall to another bowel loop, or to a nearby organ like the urinary bladder. Types of Crohn?s disease; A, stenosing; B, inflammatory; C, fistulizing; D, radiographic image of fistula. After about 7?8 years of ileal disease, patients develop a fixed, scarred obstruction that causes painful cramping and requires surgical management. Most patients go to surgery 8?10 years after the onset of disease or after a previous resection for obstruction. This obstructive process seems to be caused by inflammatory cytokines that are not inhibited by corticosteroids, anti-inflammatory salicylates, or immunomodulator drugs. In the bowels? effort to decompress the obstructed segment, fistula can develop through fissures in the thickened bowel wall in the proximal part of a stenotic area, causing secondary fistula or even perforation. Symptoms Crohn?s disease usually begins in the teens and twenties; however, ones-sixth of patients present before age 15. Patients most often present with abdominal cramps, diarrhea, delayed growth (in prepubescent patients), weight loss, fever, anemia, a right lower quadrant abdominal mass (if a complication has developed in the ileal area), or perianal fistula. Typically, patients with ileitis or ileocolitis have an insidious onset and a long course before they receive a specific diagnosis. Crohn?s disease can have several patterns of involvement: jejunoileitis, ileitis, ileocolitis and colitis. Patients with inflammation of the jejunum and ileum often present with cramping abdominal pain after meals and eventually develop diarrhea. These patients, many of whom are teenagers or young adults, may have prominent extraintestinal manifestations including arthritis, fever, skin lesions, and delayed growth.
The risk of rubella embryopathy increases when the initial infection occurs in the early stages of pregnancy (weeks 1 12: 70 90%; weeks 13 20: under 18%; after week 21: under 2%) allergy skin test results buy prednisone 5 mg. Moreover allergy shots denver purchase prednisone 40mg on-line, 168 congenital rubella has been identified in isolated cases after reinfection with the wild virus in the first trimester allergy shots with a cold order prednisone online from canada. The transmission rate of the virus from mother to fetus is > 90% in the first weeks of pregnancy (weeks 1 to 11) allergy testing tulsa order generic prednisone line. This falls to around 55% in weeks 12 17 and then increases continuously until it reaches 90% at the end of pregnancy allergy symptoms yeast foods cost of prednisone. The frequency and severity of rubella embryopathy depends on the point in time of the infection allergy symptoms cigarette smoke purchase generic prednisone pills. The test is time consuming (19 hours), easily reproducible (however subjective in terms of reading the hemolysis zones) and specific in relation to the defined threshold value (hemolysis diameter in mm). The IgG avidity test and immunoblot are additional tests for confirming an acute infection and for establishing the point of infection. An immunoblot detects the IgG antibodies against the envelope proteins E1 and E2 and against the C protein of the nucleocapsid. The detection of anti-E2 IgG antibodies means that the infection is usually more than 3 months in the past. An acute rubella infection (initial infection or primary infection) can be diagnosed in a laboratory using pathogen detection or using serological methods (rubella IgG seroconversion at an interval of at least 7 days, significant increase in rubella IgG at an interval of 2 4 weeks, detection of IgM antibodies). Titers peak after 8 20 days, persist for 1 3 years at moderate levels (64 512) and can be detected for decades (possibly for the rest of the individual?s lifetime) at decreasing levels. The IgM antibody detection test is positive starting on st th the 1 to 4 day after the onset of the rash depending on the sensitivity of the test. IgM antibodies peak after around 1 2 weeks and usually persist for 4 12 weeks. Another possible cause of positive IgM findings are long-persisting IgM antibodies after an earlier infection or vaccination. The longest proven persistence was > 15 years (after a wild virus infection) (personal communication by M. Therefore, positive rubella virus IgM results during pregnancy must be clarified by a second IgM test and by additional tests (IgG avidity and immunoblot) with regard to possible damage to the fetus. No anti-E2 IgG antibodies can be detected in the immunoblot in the first 6 8 weeks after a primary infection; the IgG avidity is low. A high avidity and the detection of E2-specific IgG antibodies are an indication of an initial infection or vaccination that occurred at least three to four months in the past. Compared to a primary infection, whole antibodies and IgG antibodies appear later after a vaccination. A vaccination cannot be serologically differentiated from a wild virus infection with any certainty. Whole antibodies and IgG antibodies persist in decreasing titers for at least 16 20 years. Unlike with a primary infection, IgG antibodies against E2 antigens form in only 50 60% of vaccinated individuals several years after the vaccination. Usually moderately to highly avid IgG antibodies and anti-E2 IgG antibodies can be detected a few weeks after reinfection. Depending on the manufacturer and point in time when the blood sample is taken, no rubella virus IgM antibodies can be detected in around 30% of reinfected patients. Pathogen detection plays a subordinate role in diagnosing a post-natal rubella infection. The following methods are used to differentiate between a primary infection (only detecting IgM antibodies is not proof) and a past infection before pregnancy:. If a prenatal infection is suspected, pathogen detection (from chorionic villi, amniotic fluid, fetal blood) is used in addition to detecting IgM antibodies in umbilical blood (after the 18th 21st week). IgM antibody determination is primarily conducted when a congenital rubella virus infection is suspected in newborns (> 90% of congenitally infected children test positive for anti-rubella virus IgM at birth). This is followed by pathogen detection in blood, throat secretion, urine, and possibly aspirated lens material in the case of cataracts. Specific IgG antibodies persist for many years with congenital infections; however, a positive IgG result no longer proves a congenital infection after the first rubella vaccination. The lab conducting the test must literary indicate whether immunity is assumed or not based on the findings. In the commentary to the guidelines it is noted that the threshold values that are defined by the manufacturer should be 171 considered when conducting the antibody test. This means that labs can draw different conclusions regarding the immune status of the pregnant individual based on the determined rubella antibody value. Rubella antibody detection is only used to determine immune status when the documentation on the two vaccinations is missing or when the rubella serostatus before the pregnancy is unknown. If there is th th no immunity, a control test should be conducted in the 16 17 week of pregnancy. When the results for IgM are positive, an IgG avidity test and an anti-E2 immunoblot should also be conducted to establish the point of infection. Reinfections are characterized by a rapid increase in IgG titers, moderately to highly avid IgG antibodies and anti-E2 IgG antibodies. If a prenatal infection is suspected, pathogen detection is performed in addition to IgM detection as part of invasive prenatal diagnostic testing. Bunyaviruses are enveloped, spherical-pleomorphic viruses measuring around 80 120 nm in diameter. Phleboviruses have been isolated in the Americas from phlebotomine sandflies of the genus Lutzomyia, and in Africa, southern Europe and central Asia from sandflies of the genus Phlebotomus and the genus Sergentomyia. For several years outbreaks of acute meningitis and meningoencephalitis have been observed in several European countries adjacent to the Mediterranean Sea (Italy, Portugal, Spain, France, Greece, Cyprus and Turkey). Severe neurological diseases have also been observed in returning European travelers. Progression of the disease can be severe, however there have only been isolated cases of death. In cases of doubt, a quadrupling or more of the antibody titers in a second serum sample is clear proof. It should be noted that there is antigen cross reactivity between various phleboviruses. The more specific neutralization test is considered the method of choice when a confirmation of the phlebovirus serotypes is required. However, this method is laborious and time-consuming, and is only conducted in special laboratories. Based on the patient?s travel history, it should be differentially diagnosed from dengue fever, West-Nile fever and Rift Valley fever. The European Bat lyssaviruses 1 and 3 (genotypes 5 and 6) are significant human pathogenic lyssaviruses [345]. Rabies is a zoonosis that is found around the world with the exception of several islands. Both the urban and sylvatic forms of rabies have been pushed back for the most part in Europe through systematic control measures. The immunization of dogs and foxes in Germany has led to the elimination of domestic, terrestrial rabies. In addition to Germany, other European countries are officially considered rabies free due to the oral immunization of foxes and the corresponding monitoring of wild animals. Rabies is of great importance to travel medicine 173 since there is an elevated risk of infection (e. The time it takes for the disease to break out depends on the amount of inoculated virus that is introduced into the body and the location of the bite wound (the shorter the distance between the wound and the central nervous system, the shorter the incubation period). In humans, the infection appears in the form of an acute case of encephalomyelitis that almost always leads to coma and death within one week after the first clinical symptoms appear. Rabies progresses in three stages: 1) prodromal stage with initial, unspecific complaints. If rabies is suspected, active and passive immunization must be introduced immediately. Thus only a positive detection of a rabies infection has any explanatory power while the patient is alive. Serological methods for detecting viral antibodies are not used to diagnose rabies since the patients usually die before virus-specific antibodies form. The diagnosis of a rabies virus infection is mostly done post mortem through virological diagnostic testing. The vaccinia virus has a wide host spectrum (infections are known in humans, buffalo, cattle, elephants, pigs, rabbits etc. The vaccinia virus is mainly used today as an expression vector in cellular and molecular biology and to develop recombinant vaccinations. Complications from classic vaccinia vaccinations include rare to very rare cases of eczema vaccinatum, generalized vaccinia, and post vaccinal encephalitis. The differential diagnosis includes: infections from herpes simplex viruses or the varicella-zoster virus, other zoonotic orthopox viruses (above all cow pox which also occurs in Germany), mycoses, erythema multiforme and other skin diseases. Three genotype groups can currently be differentiated: E, J and M (E [European genotype], J [Japanese genotype], M [mosaic genotype]). Afterwards the virus persists in the neurons of the dorsal root ganglia and cranial nerve ganglia. The varicella are primarily transmitted through droplets and aerosols; transmission through contact with the contents of the vesicles or crust is also possible. The virus can be transmitted to the embryo or st st fetus throughout the entire pregnancy. Only isolated cases st th have been reported during the 21 to 24 week of pregnancy. Reinfections after exogenic re-exposure are very rare and progress mildly or asymptomatically. These are in direct relation to the number of vaccinations and the time after the vaccination. Reported data show a clear decrease in the number of cases and complications after introduction of the vaccination in 2004. These were related to the first indications of herd immunity and a decrease in wild virus circulation. The patient is already infectious in the prodromal phase (1 2 days before the exanthem appears); it ends when the last efflorescence has healed. Complications include bacterial super infections, varicella-pneumonia which occurs more frequently in adults than in children, and neurological complications (e. Varicella up to the 21 week of pregnancy can lead to the rare (frequency rate of 1. In only one of these cases was the diagnosis confirmed in the newborn through pathogen detection. In this case, the rd mother became ill with varicella in the 23 week of pregnancy. There is an elevated risk of severe neonatal varicella 7 days before and 7 days after birth. Severe neonatal varicella with disseminate hemorrhagic exanthem, skin lesions and pneumonia occur around the due date in around 8% of cases. The symptoms of herpes zoster include pain in up to three adjacent dermatomes (mostly T3 to L3), often related to an erythema and subsequent clusters of blisters. Complications include zoster ophtalmicus, zoster oticus, zoster generalisatus and post-zoster neuralgia. Exceptions are when there are specific situations and circumstances that would warrant this. However, the test is very laborious and requires a lot of experience so that it is not routinely used. Depending on the sensitivity of the test systems used, IgG antibodies can be detected before IgM antibodies. IgM and IgA antibodies appear in 40 60% of patients with herpes zoster in the course of the disease. During the acute phase, patients frequently do no develop any IgA antibodies [279]. When the IgG finding is borderline or negative despite two vaccinations, no statement can currently be made on immune protection. Serological tests can be used to confirm the diagnosis if there is an unclear clinical picture for immunocompetent patients, and molecular-biological detection methods are not available or the efflorescence is already healed. However, it should be noted that, from a serological perspective, tests 178 using samples taken during the acute and convalescence phases have the highest level of diagnostic significance. It is related to the Japanese encephalitis virus, the Murray Valley encephalitis virus and the St. West Nile virus is one of the most widely distributed arboviruses (arthropod-borne viruses). It is transmitted to birds (which serve as a pathogen reservoir) and to humans and other mammals (e. The geographic distribution of the virus includes Africa, Asia, the Middle East, North and South America, the Caribbean, Australia (Kunjin virus), India and in scattered areas across southern and central Europe (including Russia). The first incidence of the virus (line 1) occurred in an outbreak in New York in 1999 and within a few years the virus had spread throughout North America. The frequency, distribution and intensity of the outbreaks (with an increase in neuroinvasive diseases) has changed considerably since the mid-1990s due to more favorable environmental factors. For example, line 2 has been identified in Hungary, Greece and Italy alongside line 1. Even though previous studies in Germany, including serosurveys of bird ringers and birds, have been unable to verify any autochthonous infections, the importation of the virus cannot be ruled out in the future [82; 250; 377]. A neuroinvasive disease can develop in < 1% of cases as part of the second phase of illness. This includes meningitis, encephalitis or acute flaccid paralysis or poliomyelitis-like syndrome.
Discount 10mg prednisone with amex. Allergy Symptoms & Treatments : How to Treat Pet Allergies.
References
- Schramm WM, Strasser K, Bartunek A, Gilly H, Spiss CK. Effects of rocuronium and vecuronium on intracranial pressure, mean arterial pressure and heart rate in neurosurgical patients. Br J Anaesth. 1996;77:607-611.
- Martin SE, Mathur R, Marshall I, Douglas NJ. The effect of age, sex, obesity and posture on upper airway size. Eur Respir J 1997;10(9):2087-90.
- Katz JS, Saperstein DS, Gronseth G, Amato AA, Barohn RJ. Distal acquired demyelinating symmetric (DADS) neuropathy. Neurology. 2000;54:615-620.
- Tan KT, Lip GY. Fondaparinux. Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11(4):415-419.
- Landymore R, Isom W, Barlam B: Management of patients with cold agglutinins who require open-heart surgery, Can J Surg 26:79, 1983.
- Satoh J, Miyasaka N, Yamada T, et al. Extensive cerebral infarction due to involvement of both anterior cerebral arteries by Wegener's granulomatosis. Ann Rheum Dis 1988;47:606.