Francis D. Ferdinand MD, FRCSEd, FACS, FACC
- Assistant Professor of Surgery, Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia,
- Pennsylvania
- Associate Investigator, Lankenau Institute for Medical Research
- Division of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Lankenau Hospital, Wynnewood,
- Pennsylvania
Defects of Segmentation and Cleavage Cause Loss of Key Structures Holoprosencephaly this represents a series of defects in which the interhemispheric fissure is absent or partly formed owing to a failure of the telencephalon to divide into the two hemispheres erectile dysfunction quiz buy dapoxetine from india. Holoprosencephaly is a continuum: complete cleavage failure gives rise to alobar holoprosencephaly erectile dysfunction va rating generic 30mg dapoxetine with mastercard, partial failure leads to lobar holoprosencephaly and the subtlest form is failure of olfactory nerves to form erectile dysfunction caused by radical prostatectomy purchase dapoxetine 60 mg without prescription, causing arrhinencephaly erectile dysfunction 37 years old order 30 mg dapoxetine overnight delivery. In alobar holoprosencephaly erectile dysfunction treatment centers buy dapoxetine 60 mg with visa, there is a bulbous horseshoe-shaped cortical dome consisting of fused frontal poles, across which the gyri show an irregular horizontal orientation. A common ventricular chamber is created by lateral displacement of the posterior portions of the telencephalon. It has spawned much speculation, but no one theory covers all features of the condition. One theory posits that a meningomyelocele anchors the lower end of the spinal cord, causing downward growth of the vertebral column, and creating traction on the medulla. This theory does not explain other facets of the malformation (curvature of the medulla, beaking of the quadrigeminal plate). Other proposals include increased intracranial pressure plus hydrocephalus or limited size of the posterior fossa. The brain exhibits a lack of separation of the hemispheres and a single large ventricle when viewed from an anterior perspective. No interhemispheric fissure is present; therefore, this is alobar holoprosencephaly. Arrhinencephaly is the least severe form of holoprosencephaly and consists grossly solely of absence of the olfactory bulbs and nerves, hence the name ("a," without, and "rhinencephaly," nose brain). There are usually more subtle microscopic abnormalities, and most of these individuals have some degree of mental retardation. Holoprosencephaly is rarely compatible with life beyond a few weeks or months, and survival is associated with severe mental retardation and seizures. Monogenic holoprosencephaly is sometimes associated with mutations in sonic hedgehog, an important signaling molecule. Arrhinencephaly the absence of the olfactory tracts and bulbs (rhinencephalon) is the least severe of the holoprosencephaly defects. It is clinically manifested by lack of a sense of smell (anosmia) and may be associated with mental retardation. Lack of a corpus callosum does not entail significant loss of interhemispheric functional coordination, but it is associated with seizures. The corpus callosum physically tethers and functionally interconnects the hemispheres, so its absence permits the lateral ventricles to drift outward and upward, a radiographically diagnostic finding of "bat-wing" ventricles. Congenital Atresia of the Aqueduct of Sylvius this is the most common cause of congenital obstructive hydrocephalus. It may result from deranged mesencephalic (midbrain) development and occurs in 1 in 1000 live births. The brain is enlarged owing to grotesque ventricular enlargement, with thinning of the cerebral cortex and stretching of white matter tracts. A coronal section of the brain at the level of the thalamus reveals absence of the corpus callosum and "bat-wing" shape of the lateral ventricles. Primitive neurons and glia move centrifugally from the periventricular germinal matrix to populate the cortex. The number and positions of neurons in the cortex determine the cortical infolding that creates sulci and gyri. These disorders of cortical development thus reflect the nature and severity of disruption of gyral patterning. Portions of the germinal matrix induce formation of specific overlying portions of the cerebral cortex; that is, there is a spatial destiny of neuroglial cells in a given region of germinal matrix. If a focal region of germinal matrix is destroyed or damaged, the cortical destination of the cells spawned in that region will reflect this damage. Schizencephaly is an example of such a failure of focal cortical development due to damage to the germinal matrix. More global, often genetically determined defects of neuroglial proliferation and migration result in a more widespread and severe cortical defect, called lissencephaly, meaning "smooth brain. The cortical surface of the cerebral hemispheres is smooth or has imperfectly formed gyri. Heterotopias are focal disturbances in neuronal migration that lead to nodules of ectopic neurons and glia, usually in white matter. They are often associated with mental retardation and seizures and may be caused by maternal alcoholism. Pachygyria is a condition in which the gyri are reduced in number and unusually broad. Broad textured gyri are seen here in the superior frontal region, indicating a defect in cortical formation. If the brain is deprived of blood or oxygen, the cerebral hemispheres may liquify, leaving a fluid-filled cranial cavity, a state called hydranencephaly. The head circumference reflects the largest size that the brain attained before the insult, and the head can be transilluminated as no tissue remains to block the passage of light through the cranial vault. Less severe, but still devastating, hypoxia/ischemia may lead to late-term and perinatal cerebral infarcts. In adults, the gray matter receives 3 times the blood and consumes 3 times the oxygen as the white matter. In developing brains, the periventricular germinal matrix and streams of migrating neuroglia equalize bioenergetic demand, so that deep structures and cerebral cortex have similar huge energy and substrate requirements. The deep periventricular white matter is a watershed perfusion zone and is at highest risk for infarction. Thus, intrauterine or perinatal hypoxia ischemia may cause chalky white, sometimes calcific periventricular leukomalacia. Infarcted areas may undergo resorption, leading to multicystic leukoencephalopathy, with numerous interconnected cystic cavities deep in the white matter near the ventricles. The germinal matrix is active during later phases of gestation but gradually involutes as term approaches. If a baby is born prematurely, its metabolically active germinal matrix is perfused by delicate capillaries floating in a frenzied sea of stem cells and newly spawned neuroglia. These delicate vessels may be exposed to dramatic swings in perfusion pressure, leading to germinal matrix hemorrhage. Hemorrhage may remain confined to a small region of the germinal matrix or it may spread catastrophically as intraventricular hemorrhage. Germinal matrix hemorrhage is a major challenge in clinical management of premature newborns. The surface of the brain exhibits an excessive number of small, irregularly sized, randomly distributed gyral folds. Structural and functional abnormalities may be attributed to gross chromosomal derangements of the smaller autosomes. The congenital deformities involve the brain, facial features and extremities: holoprosencephaly, arrhinencephaly, microphthalmia, cyclopia, low-set ears, harelip and cleft palate. While most brain tumors arise in adults, some are more common in childhood, the most prominent being medulloblastoma, pilocytic astrocytoma and diffuse pontine astrocytoma. Together, primary brain tumors are second only to leukemia as the most common childhood malignancy, and are the most common pediatric solid tumors. The two most common brain tumors of childhood are medulloblastoma and pilocytic astrocytoma. Other, rarer tumors also tend to occur in children, such as diffuse pontine glioma, atypical teratoid/ rhabdoid tumor and choroid plexus carcinoma. Similarly, metastatic carcinomas from the lung, breast and colon mainly affect older adults. Still others have a peak incidence in young adulthood, such as ganglioglioma and central neurocytoma. Some tumors may be most common in adults but spare no age group: glioblastomas are the most common and most malignant gliomas and may occur at any time in life. Brain metastases of primary tumors elsewhere follow the gender patterns of incidence of those tumor types. Thus, intradural, extra-axial spinal cord masses would be meningioma and peripheral nerve sheath tumors; masses within a cerebral lateral ventricle are more likely to be choroid plexus papillomas, ependymomas or other tumors that frequent those haunts. The nature of the interface between the lesion and the surrounding brain is also important. For example, the borders of highly infiltrative tumors, such as fibrillary astrocytomas and lymphomas, are subtle and diffuse, but interfaces with the surrounding brain are much better circumscribed for metastases or minimally infiltrative primary tumors, such as pilocytic astrocytoma or ganglioglioma. Nontumor diseases, many of which mimic tumor radiologically, also often have characteristic enhancement patterns; for example, demyelinating pseudotumor frequently presents as a mass lesion with "open ring" or "C-shaped" enhancement, while cerebral abscesses typically show a very smooth-walled enhancing ring. Contemporary neuroimaging techniques provide the first look at the "gross pathology" of a central nervous system lesion and constitute a rich source of information that can be utilized by the pathologist to formulate a refined differential diagnosis prior to surgical biopsy and tissue examination. Shown here are representative examples of magnetic resonance images that illustrate the highly informative features of six different brain lesions. A contrast-enhancing, circumscribed mass located within the lateral ventricle (choroid plexus meningioma). Diffuse hyperintensity involving both frontal lobes and the left temporal lobe (infiltrating glioma). C-shaped open ring-enhancing lesion in the white matter of the right parietal lobe (demyelinating pseudotumor). Hyperintense midline mass of the cerebellar vermis and fourth ventricle (medulloblastoma). Contrast-enhancing midline mass of the sellar and suprasellar region (pituitary adenoma). However, there are those that grow en plaque (flat and plaque-like) along the skull base and surround cranial nerves and blood vessels as they enter and exit the cranial cavity. These can be very difficult to treat surgically and often do not respond well to radiation or chemotherapy. Iatrogenic: Induction of meningiomas by radiation therapy generally involves a latent period of a decade or more and is directly related to radiation dosage. The average interval between treatment and detection of a meningioma for such patients was 35 years. With higher radiation doses, such as are used for head and neck cancers, the interval may be as short as 5 years. The classic histologic hallmark of meningiomas is a whorled pattern, often in association with psammoma bodies (laminated, spherical calcospherites). They have many intercellular junctions, owing to their origin from the cohesive arachnoid barrier cell layer. Patients often have seizures, particularly with tumors at parasagittal sites over the convexity of the hemispheres. Thus, tumors of the olfactory groove produce anosmia; those in the suprasellar region cause visual deficits by compressing the optic chiasm; meningiomas in the cerebellopontine angle cause cranial nerve dysfunction; and those along the spinal cord compromise spinal nerve root and spinal cord function. Tumors that are not completely excised tend to recur, and some may undergo anaplastic progression over time. Magnetic resonance imaging showing a superficial dura-based circumscribed mass, with tapering enhancement of the dura adjacent to the site of tumor attachment ("dural tail"); the chief entity in the differential diagnosis for this magnetic resonance appearance is meningioma. Meningiomas are immunopositive for epithelial membrane antigen, which is used as a diagnostic adjunct in difficult cases (inset). The ultrastructural hallmark of meningiomas is numerous intercellular junctions (desmosomes), which tightly bind adjacent meningioma cell processes together. Infiltrating astrocytomas exhibit a diffuse, fuzzy interface with the adjacent brain tissue that is being invaded on magnetic resonance imaging. Diffuse astrocytomas infiltrate the brain widely and include lowgrade fibrillary astrocytoma, anaplastic astrocytoma and the most malignant astrocytic tumor, glioblastoma. These include pilocytic astrocytoma, pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma and subependymal giant cell astrocytomas. Diffuse tumor infiltration of brain and spinal cord is a major reason there is little effective therapy for these tumors. Gemistocytic astrocytoma is a distinctive subtype of low-grade astrocytoma in which the main population of cells has prominent globular cytoplasm filled with glial intermediate filaments. This tendency for anaplastic progression is even more pronounced with the gemistocytic variant. Diffuse astrocytomas of childhood, diffuse pontine astrocytomas infiltrate and expand the brainstem pons, often to the point of encircling the basilar artery. Although usually solitary, they may rarely present as two separate epicenters of enhancement within the brain. Such cases may closely mimic metastases radiologically, with biopsy providing a definitive diagnosis. Similarly, molecular insight into the basis for resistance to treatment is also beginning to be understood. Common locations include the cerebellum, brainstem, optic nerves and third ventricular region. Pilocytic astrocytomas are very low-grade circumscribed contrast-enhancing gliomas. The compact areas frequently have prominent Rosenthal fibers, a histologic hallmark of pilocytic astrocytoma. Mitotic activity, vascular proliferation and foci of necrosis in pilocytic areas do not have the same kind of negative prognostic significance as in diffuse astrocytomas. In favorable anatomic locations, such as the cerebellum, surgical resection may be curative. There is usually a several-year history of poorly controlled seizure activity; the temporal lobe is the most common location.
Diseases
- Bone fragility craniosynostosis proptosis hydrocephalus
- Klippel Feil syndrome dominant type
- Popliteal pterygium syndrome lethal type
- Absence of tibia with polydactyly
- Factor II deficiency
- Marchiafava Micheli disease
- Spinal bulbar motor neuropathy
- Nyctophobia
- Esophageal neoplasm
Financially erectile dysfunction doctor montreal order generic dapoxetine on-line, these improvements also corresponded to significant cost savings erectile dysfunction systems 90mg dapoxetine free shipping, despite over half of the patient population receiving antibiotics thyroid erectile dysfunction treatment purchase dapoxetine 90 mg online. Before implementation of a clinical decision-support system erectile dysfunction treatment in mumbai buy 30mg dapoxetine overnight delivery, the antimicrobial susceptibility of P low testosterone causes erectile dysfunction dapoxetine 30mg generic. After the implementation of a clinical decision-support program to curtail the consumption of broad-spectrum antibiotics, P. Here, the computer decision-support program has identified that a patient is receiving an antibiotic to which the pathogen is not susceptible. As a result, providers significantly reduced their use of broad-spectrum antibiotics, particularly third-generation cephalosporins and carbapenems, even after adjustments were made for severity of illness and the presence of positive microbiology results. Although education is a large component of antimicrobial stewardship efforts, its impact is oftentimes short lived, as Buising et al. Based on the studies outlined above, the benefits associated with clinical surveillance programs are highlighted in Table 27. Increased appropriateness of antimicrobial therapy (drug, dose, and duration) (Thursky et al. Typically, such programs contain large amounts of individual patient and institutional data, which can be used for data mining, trending, or reporting purposes. Likewise, clinical surveillance software programs can also systematically and rapidly process large amounts of data from existing information systems. Clinical decision-support programs offer a variety reporting features, depending on the specific program concerned, which have been effective in benchmarking antimicrobial usage for stewardship programs. Both internal and external benchmarking have been employed to track antimicrobial stewardship interventions and highlight where future interventions may be necessary. Currently, clinical decision-support programs lack the means to track antimicrobial stewardshipinitiated interventions that are made on behalf of a patient. This feature may be integrated with clinical decision-support programs in the future; however, at present, separate programs for intervention tracking are still required. These commitments can be substantial barriers to an institution with limited resources. In addition, some tasks, such as benchmarking antimicrobial use, can be accomplished using other data information systems. Nonetheless, the interventions identified by clinical decision-support programs have demonstrated significant cost savings above those that an antimicrobial stewardship program can accomplish alone. In some cases, the cost savings may cover or offset the cost of purchasing and maintaining a clinical decision-support program. Information Technologies Mobile devices Mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets are increasingly being used by healthcare providers. The Wolters Kluwer Health 2013 Physician Outlook Survey conducted with over 300 physicians in April 2013 showed that 80% used smartphones in daily practice and that 60% used a tablet. The most common use for the smartphones was to access drug information, and for the tablet, medical research was the most common reason cited. Interestingly, search engines such as Yahoo and Google were the most frequently used to access medical information that could directly impact the diagnosis, treatment, and care of patients (Wolters Kluwer Health, 2013). According to a different survey conducted with 1063 physicians and mid-level providers in 2013, 86% of the healthcare professionals used a smartphone in their professional activities. Similarly, there was an increase in tablet use in daily practice among the clinicians from 34% in 2012 to 53% in 2013 (Epocrates, 2013; Terry, 2013; Wicklund, 2013). Overall, the tablet has been responsible for the significant increase in mobile devices in the healthcare field in the last few years. Tablets are being used by clinicians to interact with electronic health records, write notes and e-prescribe (Epocrates, 2013; Wicklund, 2013). The Apple iPad has the greatest share of the tablet market owing to the quality of the graphics and the choice of apps available. Technologic Support for Antimicrobial Stewardship 307 Pharmacists have also adopted mobile technologies as a way of accessing clinical references and as point-of-care tools (Fox et al. The availability of these support systems on digital assistants has led to an increase in clinical interventions being documented and significant healthcare cost savings (Calloway et al. Means to accomplish such tasks are not easily disseminated across a hospital or healthcare system. The utilization of medical apps has allowed broader access to medical information related to antimicrobial agents, microbiology, diagnosis and the treatment of infectious diseases, thereby alleviating some of the educational barriers observed. Hospitals that use the evidence-based clinical decision-support resource UpToDate. For example, patients had shorter inpatient length of stay and lower risk-adjusted 30 day mortality rates, with improved quality performance measures compared with hospitals without access to UpToDate (Isaac et al. Advantages the utilization of mobile technologies by healthcare professionals as time-saving tools to access clinical references at the point of care has been shown to optimize medical research ability, expand access, and increase productivity (Isaac et al. These technologies also have the potential to improve the quality of care, as it has been estimated that their use is linked to the avoidance of more than 27 million potentially dangerous drug interactions each year (Wicklund, 2013). Furthermore, mobile technologies have the potential to inform, educate, and empower patients. Another benefit of tablets is the ability to provide bedside education to patients. A computer on wheels is already utilized to provide anticoagulation education to patients who are new to oral or injectable anticoagulants. It would be feasible to also provide this type of education to patients receiving long-term antimicrobial therapy. Smith School of Business, stated that mobile technologies should help to address one of the persistent problems in healthcare to date-patient activation and engagement. With greater access to healthcare through electronic medical records, medical literature, mobile apps and social networking, healthcare consumers are more likely to be informed and actively participate in their own healthcare decisions (Beyers, 2014). Other important advantages of tablets include features that help to organize all patient monitoring forms in one place. This helps to cut down on paper that healthcare professionals, including house staff, print off on a daily basis. Another possible use of tablets may be the sharing of handoff reports between providers. This allows for real-time, up to date patient information to be communicated between all medical teams without having to make phone calls or tracking personnel down to pass along the information verbally. Drawbacks Perhaps some of the mobile technologies may save time for providers, but there is also a fear that access to digital communications may create an 308 R. Walraven increase in workload and become a time burden for providers (Harmon, 2010). Much of the work done currently related to the use of mobile devices for patient care has to do with ensuring securely protected health information. Another concern about the use of mobile devices is the potential for spread of bacterial infections due to colonization of these devices. The results showed that phones belonging to patients and visitors were more likely to be colonized with pathogenic bacteria than phones belonging to healthcare workers (39. These results are encouraging and support the use of mobile devices by healthcare workers within healthcare settings. However, close monitoring and infection control measures must be in place to avoid mobile devices serving as reservoir of bacteria and promoting the further spread of bacterial infections. Successful decontamination of mobile devices is not easily accomplished as most are affected by exposure to liquids and high temperature. Ultraviolet irradiation has also been proposed as a mode of disinfection of these devices (Tekerekog et al. Several apps are available as drug references ranging from the more basic to those with enhanced features that have been of great value for most medical providers, including pharmacists. Care must be taken when searching for medical apps, as so many are poorly categorized, and others have not been reviewed and their data content may be questionable. It is important to look at the developer of the app as well as at the last review date to make sure that the app provides updates. Several apps also have free content which is limited, with payment required for broad access and more valuable information. Other apps also have an infectious disease focus such as "Bugs and Drugs" from Epocrates (which has recently been removed from the Epocrates app store), "Antibiograms" from Portable Databases, and the "Antibiotic Guide" produced by Dr Farookh Jishi, although the information provided by these apps has not been formally reviewed (for instance, data accessed on "Bugs and Drugs" for specific areas such as New Mexico could not be validated). Social media the utilization of social media to enhance healthcare outcomes has not been researched thoroughly despite the increasing popularity and accessibility of these means of communication. As most providers are now employing mobile devices in their professional activities, it is reasonable to postulate that communications could be increased within health systems and between providers and their patients if social media avenues were exploited by the healthcare field. Hospital portals are not always easy to navigate, and information often gets lost during dissemination. In the future, for example, health systems or single institutions could use Twitter to transmit small messages to the house staff reminding them to wash their hands, or alerting them of flu cases being seen within the institution/community. Alerts through social media could also help to remind staff about upcoming lectures, newly approved antibiograms, and drug shortages, just to name a few items. The University of South Technologic Support for Antimicrobial Stewardship 309 Table 27. Several other podcasts related to infectious diseases and bacterial resistance are also readily available for mobile devices. Such easy and open access allows for busy healthcare providers to stay connected at all times without too much effort. A healthcare system constitutes an interprofessional milieu with diverse professionals coming together to care for patients. Reaching out to this diverse community has great challenges that used to be ignored. Social networking has been used to effectively educate students from different professional curricula. Of course, this model of education should not be the sole mode used, but it could complement already existing methods. Furthermore, a recently published study demonstrated that in order to be effective, education through social networks needs to be performed within a facilitated environment and curriculum (Pittenger, 2013). The unsecure nature of current social media does not allow its use as a professional means for communication in the healthcare field, but it has the potential to quickly transform healthcare communications. However, this would require a commitment from healthcare systems to develop secure and private networks, and from researchers to investigate the utility and merit of such a method of communication. Data on national antimicrobial resistance trends are analyzed and reported on a regular basis and can be compared by local, regional, and state antibiotic use. Frequently, national efforts to curtail inappropriate antibiotic prescribing habits backed by financial incentives to compliant healthcare facilities may be implemented to effect a positive change. Telehealth To date, antimicrobial stewardship has been primarily accomplished at the local hospital or health system level and little has been done on a larger scale. The impact of inappropriate antimicrobial use and the burden of resistance should be addressed on a more global level. The challenges associated with such a project would include reaching out to providers within the community and in rural areas, as well as removing boundaries between healthcare delivery systems and countries, for example. National health surveillance systems, the electronic data capture of antimicrobial consumption, and digital medical records may help in the establishment of such global programs. In addition, telehealth has become a novel way to practice medicine and provide care on a global level. Conventional medical care approaches have been incapable of delivering care to all those patients who need it, and telehealth has allowed an increased access to healthcare. This platform has also been used as a way to disseminate education on the appropriate use of antimicrobial agents. Because antimicrobial drug resistance is considered a public health threat, there needs to be better surveillance of antimicrobial prescribing and resistance trends to address outbreaks as they occur, rather than implementing damage control after the fact. Through their national stewardship programs, they have been able to use existing regulatory frameworks to influence prescribing practices aimed at improving patient outcomes Technologic Support for Antimicrobial Stewardship 311 misuse of antibiotics, promote safer and more effective ways to treat infectious diseases, and globalize antimicrobial stewardship. As many of the aforementioned studies have shown, these applications provide greater efficiencies as well as cost savings, both in patient care and in meeting regulatory compliance. Mobile technologies have drastically improved access to drug information and clinical reference sources. They have facilitated communications and interactions amongst healthcare providers and between the providers and their patients. Epocrates (2013) Epocrates 2013 Mobile Trends Report: Maximizing Multi-Screen Engagement among Clinicians. Walraven 28 Role of Guidelines and Statistical Milestones for Antimicrobial Stewardship Damary C. Some measures have not been proven to be effective and are not recommended, such as antimicrobial cycling, scheduled antimicrobial switches, and using redundant combination therapy to prevent resistance. The guidelines do recommend the use of established guidelines, or the use of evidence from the literature to develop institution-specific pathways or guidelines for antimicrobial use. These advantages are seen without an increased risk of mortality, complications, or readmission (Dellit et al. Interventions can be broad, pharmacy driven, and/or infection and syndrome specific. The checklist allows hospitals and healthcare systems to "assess key elements and actions to ensure optimal antibiotic prescribing and limit overuse and misuse of antibiotics in hospitals. This study highlights the discordance between clinical practice and published guidelines, and highlights for the institution what areas to target to improve patient care. Guideline development can begin with nationally published guidelines and incorporate local expertise, local trends of antimicrobial resistance, and hospital targets for decreased and appropriate antibiotic use to create hospital-specific or healthcare network-specific guidelines. Studies evaluating the implementation of ventilator-associated pneumonia treatment guidelines have shown improved rates of appropriate initial therapy. The development and implementation of guidelines can also include non-infectious disease specialists, such as emergency department clinicians, who are often on the front line of antibiotic prescribing.
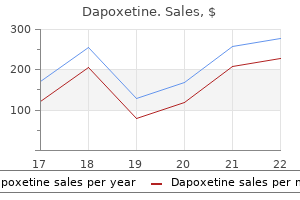
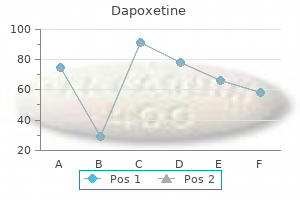
60 mg dapoxetine with visa. Erectile Dysfunction- Finally a treatment that works without a prescription. Guaranteed Erections.
If the lysogenic cycle is adopted erectile dysfunction my age is 24 order dapoxetine australia, the phage chromosome is integrated into the bacterial chromosome erectile dysfunction operations cheap 30mg dapoxetine with mastercard, where it can remain dormant for many years erectile dysfunction at 30 buy dapoxetine 30mg on-line. It occurs most commonly in bacteria and in some species occurs naturally but it can be affected by artificial means impotence caused by diabetes discount dapoxetine 30 mg overnight delivery. Mechanisms of acquired antibiotic resistance Mechanisms of acquired antibiotic resistance can mainly occur as a result of: Destruction or inactivation of antibiotics erectile dysfunction doctors in ny buy generic dapoxetine 90mg on-line. An alteration of antibiotic target site to reduce/eliminate binding of the antibiotic to the target. Impaired uptake of the antibiotic either due to reduction in the cell permeability or blockage of the mechanism by which the antibiotic enters the cell. Role of drugs and therapeutics committee the drugs and therapeutics committee of the hospital plays a key role in the promotion of rational antibiotic prescribing. They should meet on a regular basis with following objectives: Formulate antibiotic guidelines based on the local antimicrobial resistance pattern and review guidelines on a regular basis. Approve use of newer agents based on the clinical efficacy, cost, and side effect profile. Once approved, the use of new antimicrobial agents should be restricted to agreed clinical conditions and be prescribed only on the advice of a clinical microbiologist or infectious diseases physician. Monitor compliance with the guidelines and feedback data to the senior medical staff on a regular basis to influence prescribing habits. It is important to note that compliance data with the guidelines are generally collected by pharmacists will not provide information on the appropriateness of prescribing as they do not have the qualifications and expertise to assess whether patients had an infection or not. If the resources are available, conduct antibiotic ward rounds at least once a week involving microbiologist, antimicrobial pharmacist, and a nominated clinical member (McCorry et al. The information from the antibiotic ward round must be fed back to the senior clinicians and senior management in a timely manner. During the antibiotic ward rounds, consider to review the following data: Does the patient really need antibiotic(s) Is the reason for prescribing documented in the medical notes and supported by the clinical and other relevant information Have the appropriate specimens been collected prior to starting antibiotic therapy If the microbiology reports are available, was the antibiotic switched to a narrowspectrum agent(s) Is the selection of an antibiotic based on the previous/recent bacteriological reports Control of multidrug-resistant microorganisms is essential, as it has following impacts: the patient is less likely to respond to the first-line empirical antibiotic therapy. Limited choice in selection of older `tried and tested `agents which are cheaper and their efficacy and side effect profiles are well known. In addition, newer agents have restricted licensing conditions due to limited availability of clinical data on their efficacy and side effect profiles. Increased costs of isolation precautions and cost of additional investigations due to extra length of stay. The management approach depends on two factors: 1) endemicity of the resistant microorganisms in the health care facility, and 2) vulnerability of the patients in the wards/unit where they occur. Patients who have intra-abdominal, cardiothoracic, orthopaedic, vascular, and urological procedures/surgery. Therefore antibiotic stewardship programmes should be implemented both in hospitals and the community Use narrow-spectrum antibiotics, if possible. The patients should be kept in isolation until the swab results are available On confirmation, application of contact precautions must be instituted immediately Hand hygiene is crucial to prevent cross-infection and this must be rigorously enforced. If transfer is essential then receiving ward/department/hospital must be informed in advance so that patients are isolated in a side room with appropriate infection control precautions implemented on admission. Pathogenicity Human reservoirs of organisms Antibiotic selective pressure High/moderate Nose and moist and hairy areas of the body area. Skin lesions, wounds, incisions, ulcers and exit sites of indwelling devices, if present. Umbilicus swab from newborn infants Colonize wounds,ulcers and medical device sites Not effective Faeces or deep rectal swab or colostomy. Umbilicus swab from newborn infants Colonize wounds,ulcers and medical device sites Not effective Skin lesions, wounds, incisions, ulcers and exit sites of indwelling devices, if present. Umbilicus swab from newborn infants Colonize wounds, ulcers and medical device sites esp. The bacterium was discovered in 1881 by Sir Alexander Ogston who was a professor at the University of Aberdeen. It is one of the most common pathogens, well known for causing skin and soft tissue infection. They are resistant to all of the beta-lactam classes of antibiotics (such as penicillins), penicillinase-resistant penicillins. However in recent years, this infection can be successfully treated with newer but more expensive agents. Overcrowding of wards with higher concentrations of long-term patients with multiple comorbidity. Higher throughput of patients which can lead to inadequate decontamination of equipment and environment. The benefit of universal screening of all patients on a routine basis is less clear, and costs can be considerable. If the isolation facilities are not available the patients should be risk assessed and can be cohorted into bay/area. S/he should be advised that there is no risk to healthy relatives or others outside the hospital and should be given a fact sheet. As a general rule, infected/colonized patients should be seen towards the end of a ward round, if practical. Number of visitors should be kept to a minimum and those who are susceptible are probably best advised not to visit a patient. Hand hygiene: physically clean hands must be disinfected using an alcoholic hand rub. Alternatively, wash hands with soap (or antiseptic chlorhexidine/ detergent) and water before and after contact with the patient or their immediate environment. Personal protective equipment: single-use disposable gloves must be worn when handling contaminated tissue, dressings, or linen. Single-use disposable plastic aprons must be worn for activities involving contact with the patient or his/her environment and should be discarded into a clinical waste bag before leaving the room. Non-permeable disposable gowns are required only for extensive physical contact with the patient. Any reusable disposal items must be disinfected/sterilized according to local policy. All linen must be put into the appropriate bag, sealed at the bedside, and removed directly to the dirty utility area or to the collection point. On discharge of patient, the room must be terminally cleaned and disinfected using appropriate disinfectant. Colonized patients who are undergoing surgical procedures should receive decolonization therapy prior to surgery (see Box 10. In elective cases, the decolonization therapy should start 5 days prior to surgery and on the day of operation the patients should be dressed in a theatre gown as close to the time of operation as is practical. Vancomycin should be given as a surgical prophylaxis as per local protocol (see Chapter 15, Table 15. Patients should be operated on at the end of the operation list where possible to allow time for decontamination procedures. Where this is not possible, as in cases of emergency surgery, theatre surfaces in close contact with the patient, such as the operating table, equipment, and trolley, should be thoroughly cleaned and decontaminated before being used for the next patient. Any infected or colonized lesions must be covered with an impermeable dressing during the operation and the adjacent areas treated with an appropriate antiseptic. Patients should be allowed to recover after surgery in the operating theatre or an area not occupied by other patients to avoid possible contamination of the usual recovery area. Nose: apply 2% nasal mupirocin (Bactroban Nasal) ointment three times a day for 5 days. A small amount of ointment (about the size of a matchstick head) should be placed on a cotton bud and applied to the anterior part of the inside of each nostril. The nostrils are closed by gently pressing the sides of the nose together; this will spread the ointment throughout the nares. A prolonged course (>7 days) or repeated courses (>two courses per hospital admission) should be avoided to prevent the emergence of mupirocin resistance. Success with low-level resistance strains is about 80% but with highlevel resistance strains is only about 27%. Naseptin contains peanut oil and is contraindicated in persons with peanut allergy. Throat: chlorhexidine gluconate spray or gargle for pharyngeal carriage may be added but its efficacy is not known. Topical nasal applications are not effective in clearing throat or sputum colonization. Eradication of throat colonization by use of systematic antimicrobial therapy is not part of routine decolonization therapy but if considered essential, then this can be given on the advice of a medical practitioner on an individual patient basis. A combination of any two oral antibiotics from fusidic acid, rifampicin, trimethoprim, and doxycycline or co-trimoxazole can be prescribed for 7 days based on the antibiotic sensitivity testing. Body bathing: Shower: the antiseptic body wash should be applied directly to the skin, paying particular attention to the hair, around the nostrils, under the arms, between the legs (groin, perineum, and buttock area), feet, and working downwards. For an antiseptic to be effective, recommended contact time on skin must be followed. All antiseptic should be used with care in patients with dermatitis and broken skin and must be discontinued if skin irritation develops. Body bathing or bed bathing: patients confined to bed can be washed with an antiseptic solution. Wet the skin and apply the antiseptic preparation directly onto the skin using a disposable clean cloth; alternatively use pre-soaked antiseptic disposable towel. Mupirocin ointment should be applied three times a day to small lesions for 5 days in selected cases only. Antiseptic powder: 1% chlorhexidine dusting powder can be used to treat carrier sites and should be applied to intact skin such as the perineum, buttocks, flexures, and axillae three times daily for 5 days. The screening swabs should be taken from the nose, perineum/groin, operative and wound sites, abnormal or damaged skin, invasive devices, catheter urine samples, and sputum, if expectorating. Direct culture methods: swab can be plated directly on to selective chromogenic agar. Broth enrichment culture: swabs are placed in enrichment broth and subsequently plated on to selective chromogenic agar. This method is more sensitive then the direct culture method but it can take up to 48 hours to get the confirmation. The result is usually available within 3 hours but it has has not been widely adopted. This is because the test is very expensive and has reduced sensitivity for samples other than nasal swabs. It addition, the swab has to be inoculated on culture medium for final confirmation and antibiotic sensitivity testing, which is required for treatment of patients and typing which is essential for epidemiology purpose. Of the factors examined, throat colonization, mupirocin resistance and age greater than 80 years were significantly associated with failure of decolonization (Gilpin et al. Those who are no longer colonized or infected and those in whom the site/s of colonization or infection does not pose a risk of infection to others, may be transported without the need for any additional infection control precautions. The following infection control measures should be taken for patients who are colonized or infected in one or more sites which cannot be covered with an occlusive dressing are liable to present a risk of cross-infection to other patients: the patient should be given clean clothing before transport. Physically clean hands can be disinfected with an alcoholic hand rub after contact with the patient or the environment. Blankets and pillow cases should be placed in an appropriate bag for laundering according to local protocol. The vehicle should be thoroughly cleaned with detergent and disinfected with freshly prepared hypochlorite solution (1000 ppm av Cl2). Because of its resistance patterns, they are more difficult to treat if infection occurs and they also have a high propensity to become endemic due to better survival in the environment. It is commonly found in patients who had been treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics and have received vancomycin. Based on the local surveillance, selective screening should be considered for high-risk patients in identifying colonized individuals. In an outbreak situation, screening swabs for culture from multiple body sites, i. Since the most frequent site of colonization is the large bowel, a faecal sample is the most useful screening specimen. It is important to emphasize that stool carriage may persist for months or years and oral antibiotic therapy to eradicate the carriage is not successful. Patients can remain colonized for a long time after discharge from hospital therefore an alert system for re-admission of these patients is required so that these patients can be promptly identified and placed in a single room with en suite toilet and isolation precautions. It also poses problems to health care facilities as numerous outbreaks have been reported worldwide. These organisms can develop resistance during treatment against third-generation cephalosporins (cefotaxime, ceftriaxone, and ceftazidime) due to the induction of chromosomal AmpC beta-lactamases. Non-fermenters: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumannii, Stenotrophomonas maltophia, etc. Although newer agents are available, they are not as effective as older agents and their side effects and clinical efficacy for treatment of various infections is not fully evaluated. Most of the patients from the community are colonized in the urinary tract and wound sites. Early identification by taking screening swabs and prompt isolation is essential, especially if the patients are being admitted to a high-risk unit. Since Gram-negative bacteria mainly survive in wet environments, it is essential that the environment be kept clean and dry. Make sure that bedpan washer disinfector, or macerators are in good condition and in working order. If a bedpan washer disinfector breaks down, it should be repaired as an emergency. Bedpans and urinals should be disinfected using heat treatment, if possible, or disposable bedpans and urinals can be used, if available.
Bergamota (Bergamot Oil). Dapoxetine.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Treating mycosis fungoides (a tumor under the skin due to a fungal infection) when combined with ultra-violet (UV) light, protecting the body against lice and other parasites, psoriasis, vitiligo (loss of the color pigment on the skin), anxiety during radiotherapy, and other conditions.
- What is Bergamot Oil?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Dosing considerations for Bergamot Oil.
- How does Bergamot Oil work?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96182
References
- Honda T, Tamura G, Waki T, et al. Demethylation of MAGE promoters during gastric cancer progression. Br J Cancer 2004;90:838.
- Noiri E, et al. Oxidative and nitrosative stress in acute renal ischemia. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2001;281:F948.
- Connolly SJ, Ezekowitz MD, Yusuf S, et al. Dabigatran versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 2009; 361:1139.
- Kilickan L, Toker K. The effect of preemptive intravenous morphine on postoperative analgesia and surgical stress response. Panminerva Med 2001;43:171-175.
- Petersen FB, Buckner CD, Clift RA, et al. Infectious complications in patients undergoing marrow transplantation: a prospective randomized study of the additional effect of decontamination and laminar air flow isolation among patients receiving prophylactic systemic antibiotics. Scand J Infect Dis. 1987;19:559-567.
- Mochida K, Shinomiya K, Andou M: Urodynamics and electrophysiologic study of the urinary disturbances caused by cervical myelopathy, J Spinal Disord 2:141n145, 1996.