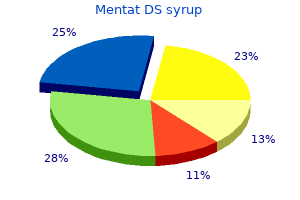
"Order 100 ml mentat ds syrup fast delivery, medicine used to treat chlamydia".
A. Josh, M.A., M.D., Ph.D.
Associate Professor, Lincoln Memorial University DeBusk College of Osteopathic Medicine
Treatment of elderly subjects with mild thyroid hormone deficiency was not associated with benefit in the study by Razvi et al (193) treatment jammed finger quality mentat ds syrup 100ml. Incident ischemic heart disease events symptoms diabetes order mentat ds syrup 100 ml, all-cause mortality treatment urinary tract infection order mentat ds syrup 100ml with mastercard, cause-specific mortality nioxin scalp treatment proven 100 ml mentat ds syrup, and incident cerebrovascular events were comparable in older untreated and L-T4treated groups (193). As in younger patients, overtreatment with L-T4 should be avoided because of the adverse cardiovascular and skeletal consequences of iatrogenic hyperthyroidism in elderly people. L-T4 formulations for CoH L-T4 tablets are approved for treatment of CoH in the United States; administration is facilitated by crushing the tablets, mixing with water, and giving with a spoon. In Europe, a liquid L-T4 formulation is available with administration of the desired dosage by a dropper. In one study, a liquid formulation of L-T4 was administered to 28 consecutive newborns with primary CoH (469) in a median starting dose of 12. These results demonstrated comparable efficacy of the liquid formulation to that of L-T4 tablets but in a formulation that is easier to administer. Some studies have reported an increased risk of craniosynostosis, hyperactivity, delinquency, aggressiveness, and poor attention in children with CoH who were overtreated with L-T4 (475). Higher performance scores for behavior, reading, spelling, and math were reported in newborns who received 50 g/d L-T4 (1217 g/kg/d) vs 37. In one study, 83 infants were assigned to receive 3 different starting doses of thyroid hormone at birth (6. Evaluation at 4 years of age indicated that infants with severe CoH who had started L-T4 treatment at the highest dose had the highest intellectual assessment scores (472). Some studies tailored the starting L-T4 dose according to the severity of hypothyroidism. An L-T4 dose of 15 g/kg/d was started in infants with athyreosis, whereas 12 g/kg/d was administered to infants with an ectopic gland and 10 g/kg/d in infants with dyshormonogenesis. Routine thyroid function tests should be repeated 4 weeks after a change in L-T4 dosage (21). No specific guidelines have been developed for monitoring genetic conditions associated with hypothyroidism. The L-T4 dosage requirement in CoH progressively declines from 10 to 15 /kg/d in infants to 4 to 5 g/kg/d by the age of 5 years due to a progressive decrease in the rate of T4 turnover (20, 21). Full replacement doses of L-T4 should be administered when the diagnosis of hypothyroidism is formulated in children and adolescents. Transient psychosis and intracranial hypertension have been reported during the early phase of L-T4 therapy as well as in subjects undergoing progressive increase of L-T4 doses (483). In prepubertal children, bone maturation and pubertal development should be monitored. Among these selected studies, only 6 were longitudinal trials and only 4 L-T4 were multicenter studies. On the contrary, no predictive factors for progression were identified in patients with isolated hyperthyrotropinemia after a 3-year follow-up (486). Two longitudinal studies evaluated the effects of replacement doses of L-T4 on growth velocity (487, 488). They observed a significant improvement in growth velocity after 6 months and 1 year of treatment with L-T4; this improvement was more significant in the pubertal group (487). Similarly, no effects of L-T4 on neuropsychological functions were reported in children with Downloaded from academic. Conflicting results have been reported in 2 studies that assessed the effect on L-T4 on thyroid volume in children (493, 494). Acute and chronic kidney disease Thyroid hormones affect renal development and physiology, with significant changes in renal function, electrolytes, and water homeostasis noted in patients with thyroid dysfunction (496 498). Hypothyroidism induces a decrease in glomerular filtration, hyponatremia, and reduced facilitation of water excretion (496). Therefore, the normalization of thyroid function with L-T4 replacement therapy in hypothyroid patients may improve kidney function (502507). Kaplan-Meier analysis indicated that renal event-free survival was significantly lower in the nontreatment group (P.
The myelopathy sometimes stabilizes symptoms zollinger ellison syndrome 100 ml mentat ds syrup overnight delivery, leaving the patient with only a moderate paraparesis symptoms ms cheap 100ml mentat ds syrup free shipping. Pathologically medications zetia buy 100ml mentat ds syrup otc, the lesions are characterized by confluent areas of necrosis with a predilection for the white matter symptoms 9 weeks pregnancy cheap mentat ds syrup 100ml with visa. There is no effective treatment, although corticosteroids sometimes delay progression of the lesion. A second form of late-delayed radiation myelopathy involves anterior horn cells and occurs mainly after pelvic irradiation. Months to years following irradiation, patients develop a subacute flaccid, often asymmetrical paraparesis that affects both distal and proximal muscles, accompanied by atrophy, fasciculations, and areflexia. The deficit usually stabilizes after a few months, often while the patient is still able to walk [47, 68]. Pathological reports describe degeneration of cauda equina roots with anterior horn cell central chromatolysis. Delayed complications of peripheral nerve irradiation An early-delayed brachial plexus reaction is characterized by paraesthesias in the hand and forearm, sometimes associated with pain and accompanied by weakness and atrophy in a C6T1 distribution. Nerve conduction studies reveal segmental slowing, and the course is characterized by recovery over a few weeks or months. This disorder is particularly common when carcinoma of the breast is being treated [70]. Late-delayed radiation plexopathy has been reported after irradiation of either the brachial or lumbosacral plexus [44, 59]. The disorder usually occurs a year or more after radiation therapy with doses of 60 Gy or more when conventional fractions are used. Brachial plexopathy is characterized by paraesthesias, loss of sensation and weakness of muscles in the upper or lower plexus. This disorder is frequently accompanied by lymphoedema and palpable induration in the supraclavicular fossa. Clinical or electrical myokymic discharges in the territory of affected nerves is a useful criterion for differentiating radiation damage from tumour infiltration of the plexus [35]. The disorder may stabilize after many months to years of slow deterioration or progress rapidly to a panplexopathy, rendering the entire arm useless, although usually without severe pain. The important differential diagnosis is between radiation damage and recurrent tumour affecting the plexus. Severe pain is almost invariably present if tumour is the culprit and is rare with radiation fibrosis. The need for diagnostic certainty rarely requires surgical exploration of the plexus. Clinical pictures Acute encephalopathy Neurological complications of chemotherapy Neurotoxicity of antineoplastic drugs is frequent (Table 2). As for radiation-induced complications, a low therapeutic index is an important dose-limiting factor for these agents. Chemotherapy neurotoxicity produces a limited number of nonspecific clinical pictures [58]. Neuropathy lowed by a state of confusion that may be associated either with stupor or, more often, with agitation. They are typically characterized by the acute onset of encephalopathy with fluctuating motor deficit that resolves spontaneously. Chronic encephalopathy the most characteristic is a "subcortical dementia" of variable severity developing progressively, months to years after treatment that often but not always included a combination of cranial radiotherapy and chemotherapy. The syndrome is characterized by apathy, intellectual and memory loss, frontal syndrome, sleep disorders and often incontinence and gait disorders. Spontaneous improvement may occur but, in many cases, progressive deterioration is the rule. Cerebellar syndrome A cerebellar syndrome, ranging from a simple gait ataxia to a pancerebellar syndrome, has been reported in patients Table 4 Cisplatin neurotoxicity Chemotherapy may induce different types of peripheral nervous system disorders: (1) An acute or subacute Guillain-Barrй-like syndrome, probably owing to selective demyelination. This syndrome is seen with suramin, an agent used for prostate cancer [20], and sometimes after Ara-C. Loss of position sense and ataxia are frequent in cisplatin-induced neuropathy, whereas taxane-induced neuropathy affects preferentially pinprick and tact.
Differential Diagnosis Common migraine symptoms 3 days past ovulation mentat ds syrup 100 ml overnight delivery, hemicrania continua medicine expiration generic mentat ds syrup 100 ml with visa, spondylosis of the cervical spine treatment eating disorders buy mentat ds syrup 100 ml overnight delivery. Other unilateral headaches useless id symptoms mentat ds syrup 100 ml low cost, such as cluster headache, are less important in this respect. Age of Onset: usually in the decades corresponding with the occurrence of carcinoma of the lung. Pain Quality: the pain is continuous, involving the root of the neck and ulnar side of the upper limb. It is usually progressive, requiring narcotics for relief, and becomes excruciating unless properly managed. The pain is a severe aching and burning associated with sharp lancinating exacerbations. There is paralysis and atrophy of the small muscles of the hand and a sensory loss corresponding to the pain distribution. The diagnosis is made on chest X-ray by the appearance of a tumor in the superior sulcus. Social and Physical Disability Those related to the neurological loss, unemployment, and family stress. Pathology or Other Contributory Factors Virtually always carcinoma of the lung, though any tumor metastatic to the area may give identical findings. Summary of Essential Features and Diagnostic Criteria the essential features are unremitting, aching pain of increasing severity, in time expanding to the ulnar side of the arm with exacerbations of sharp lancinating pain in the distribution of the lower brachial plexus. Continuous aching pain in the paraspinal region, shoulder, or elbow, in time expanding to the whole ulnar side of the arm. Exacerbations of sharp lancinating pain in Page 96 and occasional neurological loss; the diagnosis is made by chest X-ray demonstrating tumor at the apex of the lung, and the biopsy is made by tumor. Rarely, peripheral vascular insufficiency syndromes are found, and occasionally, the subclavian axillary vein complex can be compressed, and the patient presents with swelling and blueness consistent with symptoms of venous obstruction. Three physical findings are frequent: pain on pressure over the brachial plexus, just lateral to the scalenus anticus muscle; pain mimicked by abduction and external rotation of the arm; and pain when the brachial plexus is stretched by tipping the head to the opposite side. This is performed by maximal extension of the chin and deep inspiration with the shoulders relaxed forward and the head turned towards the suspected side of abnormality. Angiograms are indicated when there is an arterial or venous obstruction but are very poor diagnostic maneuvers, the milder forms of the thoracic outlet syndrome only affecting neurological symptoms. Electromyography may demonstrate evidence of nerve root compression across the thoracic outlet and denervation distally in the arm, but often fails to do so. Physiotherapy may strengthen the shoulder girdle and relieve symptoms, and this should be tried at first, but ordinarily symptoms will persist until the entrapment of the plexus is relieved. Complications Complications include arterial compression with thrombosis and an ischemic arm. Pathology A variety of anatomical abnormalities will compress the neurovascular bundle at the thoracic outlet and may cause this syndrome. It may be precipitated in predisposed individuals by flexion-extension injuries of the cervical spine with consequent postural or other change. Social and Physical Disabilities the patients are often unable to work because of dysfunction of the extremity involved. Due to compression of the brachial plexus by hypertrophied muscle, congenital bands, post-traumatic fibrosis, cervical rib or band, or malformed first thoracic rib. Age of Onset: the thoracic outlet syndrome is characteristically found in young to middle-aged adults but may affect older adults also. Pain Quality: typically, pain begins in the root of the neck, or shoulder, and radiates down the arm, but it may also affect the head. The ulnar aspect of the arm is the most commonly involved, but the pain may affect the entire arm. The pain in the hand or the arm is not usually intense, but the associated headache may be severe. The distribution of the paresthesias or pain in the shoulder or arm is varied and can be associated with a particular nerve root, or with many nerve roots. Often it is rather baffling in that it cannot readily be related to specific nerves or nerve roots. Hemiplegia from stroke secondary to vascular thrombosis and propagation of the clot may occur.


Although considered components of the normal microflora medications you cant drink alcohol with buy discount mentat ds syrup 100ml on-line, organisms such as Staphylococcus aureus symptoms nausea headache discount 100ml mentat ds syrup fast delivery, Haemophilus influenzae medications not covered by medicare cheap 100 ml mentat ds syrup mastercard, and Streptococcus pneumoniae will be identified by most laboratories treatment integrity checklist generic 100ml mentat ds syrup overnight delivery, if requested. When Neisseria gonorrhoeae or Corynebacterium diphtheriae is suspected, a special culture request is recommended. Contamination of specimens with normal microflora from the skin, rectum, vaginal vault, or another body site should be avoided. Feces should be collected in a clean cardboard container, with the time of collection recorded. Fecal samples should be collected before the ingestion of barium or other contrast agents and before treatment with antidiarrheal agents or antacids; these substances alter fecal consistency and interfere with microscopic detection of parasites. The collection of three samples on alternate days is recommended because of the cyclic shedding of most parasites in the feces. Microscopic examination is not complete until direct wet mounts have been evaluated and concentration techniques as well as permanent stains applied. Sampling of duodenal contents may be needed to detect Giardia lamblia, Cryptosporidium, and Strongyloides larvae. The laboratory procedures for detection of parasites in other body fluids are similar to those used in the examination of feces. The parasites most commonly detected in Giemsa-stained blood smears are the plasmodia, microfilariae, and African trypanosomes; however, wet mounts may be more sensitive for microfilariae and African trypanosomes. Diagnosis of malaria and distinctions among Plasmodium species are made by microscopic examination of thick and thin blood films. Bacterial autolysins (cell-wall recycling enzymes) contribute to cell lysis in the presence of these agents. Aminoglycosides Macrolides (erythromycin, clarithromycin, azithromycin), ketolides (telithromycin), and lincosamides (clindamycin) Streptogramins [quinupristin/dalfopristin (Synercid)] Oxazolidinone (linezolid) Tetracyclines (tetracycline, doxycycline, minocycline) and glycylcyclines (tigecycline) · Inhibition of bacterial metabolism: Drugs interfere with bacterial folic acid synthesis. The major mechanisms of resistance used by bacteria are drug inactivation, alteration or overproduction of the antibacterial target, acquisition of a new drug-insensitive target, decreased permeability to the agent, failure to convert an inactive prodrug to its active derivative, and active efflux of the agent. The mode of excretion is important in adjusting dosage if elimination is impaired. Although combination chemotherapy usually is not indicated, it is used for certain purposes: To prevent emergence of resistance For synergistic or additive activity For therapy directed against multiple potential pathogens · Choose a therapeutic agent on the basis of: Pharmacologic data Adverse reaction profile Site of infection. Evidence-based practice guidelines for most infections are available from the Infectious Diseases Society of America ( The most clinically relevant adverse reactions to common antibacterial drugs are listed below. Nonallergic skin reactions: Ampicillin "rash" is common among pts with Epstein-Barr virus infection. The rates are consistent with those reported by the National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance System (Am J Infect Control 32:470, 2004). Efforts to lower infection risks have been challenged by the growing numbers of immunocompromised pts, antibiotic-resistant bacteria, fungal and viral superinfections, and invasive procedures and devices. Hospital infection-control programs focus primarily on infections associated with the greatest morbidity or the highest costs. Other measures include identifying and eradicating reservoirs of infection and minimizing use of invasive procedures and catheters. Standard precautions are used for all pts when there is a potential for contact with blood, other body fluids, nonintact skin, or mucous membranes. Hand hygiene and use of gloves are central components of standard precautions; in certain cases, masks, eye protection, and gowns are used as well. Transmission-based guidelines: Airborne precautions, droplet precautions, and contact precautions are used to prevent transmission of disease from infected pts. More than one precaution can be combined for diseases that have more than one mode of transmission. Because antibiotic-resistant bacteria can be present on intact skin of infected pts, any contact with sick pts who may be harboring those bacteria should involve hand hygiene and use of gloves. Gowns are frequently used as well, although their importance in preventing cross-infection is less clear. Intensive education and "bundling" of evidence-based interventions reduce infection rates (see Table 85-1). The 310% risk of infection for each day a catheter remains in place is due to the ascent of bacteria from the periurethral area or via intraluminal contamination of the catheter. The pt should be assessed for symptoms of upper tract disease, such as flank pain, fever, and leukocytosis.