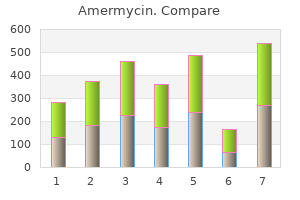
"Cheap 100 mg amermycin with visa, antibiotic resistance video".
L. Curtis, M.A., M.D., Ph.D.
Associate Professor, Meharry Medical College School of Medicine
Back pain Mechanical back pain Typically this comes on suddenly and the precipitating episode is readily identified antibiotic metronidazole buy discount amermycin 200mg on line. It may also arise more gradually particularly in relation to repetitively adopting a fixed posture antibiotic japanese buy amermycin 200mg online. On examination there is localised tenderness and restricted movement but neurological examination is normal medicine for uti male 100 mg amermycin sale. Advice regarding posture and lifting techniques antibiotic kill good bacteria buy discount amermycin 200 mg line, avoidance of bending, adjustments to work/ leisure activities, etc. Simple analgesics and heat therapy may help during the acute phase; some patients advocate manipulation or acupuncture by an experienced practitioner. Prognosis Early recognition and treatment are critical to preventing joint damage and destruction. Osteomyelitis and septicaemia may complicate cases in which the diagnosis is delayed. Vertebral disc prolapse Bulging of the gelatinous central nucleus pulposus through the annulus fibrosus of the intervertebral disc most commonly occurs in a posterolateral direction, and may lead to impingement of the nerve roots as they emerge from the spinal cord. Sudden cervical or lumbar disc protrusion is associated with pain in the neck or lower back, which is referred down the upper or lower limbs. In addition to simple measures (advice regarding posture, lifting techniques, avoidance of bending, adjustments to work/leisure activities, etc. Surgical decompression should be considered in those with persistent symptoms or if there is cord impingement. For reasons that are unclear, the joint capsule becomes adherent to the overlying rotator cuff muscles. It is typically unilateral and characterised by progressive pain and reduced mobility. Untreated, improvement with time is generally the rule but may take up to 2 years. Intra-articular injection of corticosteroid may help ease the pain and should be combined with regular exercises to restore movement. Rotator cuff tendonitis Repetitive or unaccustomed movements of the shoulder may result in inflammation of one or more of the rotator cuff muscle tendons. Pain during abduction, flexion or rotation of the shoulder is often accompanied by point tenderness. Vertebral crush fracture this is most commonly seen in middle-aged to elderly females in the context of osteoporosis of the thoracic spine. Sudden vertebral collapse results in abrupt Rheumatology 295 onset of severe pain. Achieving adequate pain control can be challenging and may require opioid analgesia. In the absence of a specific disease marker, the diagnosis is based on clinical features: the presence of five or more criteria, including at least two major, has a diagnostic sensitivity of > 95% and specificity of > 90%. Marked elevation of serum ferritin is a key finding in most patients and correlates with disease activity. Acute rheumatic fever this acute febrile systemic disorder affects mainly the heart and joints following a streptococcal infection (group A, b-haemolytic) and usually occurs between the ages of 5 and 15 years. The diagnosis is made when there is evidence of previous streptococcal infection plus one major and two minor or two major (Jones) criteria. In the section below, double asterisks denote major criteria, single asterisks minor criteria. Adult-onset An acute systemic inflammatory disorder of unknown aetiology, onset is typically between 16 and 35 years of age, with both sexes affected approximately equally. Mitral systolic and aortic murmurs also occur percarditis: friction rub or small effusion. Corticosteroids may be required, especially if there is evidence of cardiac involvement. Antistreptococcal therapy: intravenous benzylpenicillin during the acute phase and oral phenoxymethylpenicillin continued in those with cardiac involvement for at least 5 years and preferably until 20 years of age to prevent recurrence. Postinfectious arthralgia Low-grade (poly)arthralgia frequently follows some infections.
The amino acid cysteine is always added at 30 mg/g amino acids bacteria zapper for face buy generic amermycin 200 mg line, which improves Ca and P solubility virus usa buy amermycin 200 mg low price. Since solubility of Ca and P is a concern antibiotic resistance and farm animals discount 200mg amermycin otc, never reduce the amino acids to less than 2 antibiotic resistant salmonella generic 100 mg amermycin visa. Sodium phosphate can replace potassium phosphate in the same molar concentrations when potassium intake needs to be limited or potassium phosphate is not available. It is not necessary to decrease prophylactically the Intralipid infusion rate in the absence of any evidence of cholestasis. Growing infants, however, have a requirement for copper and will ultimately develop copper deficiency in the absence of adequate copper supplementation. In the presence of cholestasis without either jejunostomy or ileostomy, trace minerals (including copper and manganese) should be provided 3 times per week (Monday, Wednesday and Friday), and parenteral zinc should be provided at maintenance levels daily. In the presence of cholestasis with either jejunostomy or ileostomy, apart from the above supplementation, extra zinc should be provided to compensate for gastrointestinal losses. Lab monitoring of copper and zinc levels may indicate the need for further adjustments to supplementation. In those instances, copper and zinc should be supplemented despite cholestasis, but levels should be checked when medically feasible. In infants with cholestasis or renal failure, continue zinc daily per guidelines (Table 12-5c). Use of volume to provide protein is of greater importance in this setting than providing more than 1 g/kg/d of lipids or high concentrations of calcium and phosphorus. It is important to maintain both total blood phosphorous and magnesium within physiological ranges. Recommended goal parenteral nutrition composition for cooling given in Table 12-6b. Generally, the unbalanced addition of carbohydrate is not recommended to increase total calorie intake. Evaluate infant if residuals exceed 50% of the feeding volume or the infant has other symptoms of feeding intolerance. Stable> 2500 Cardiac babies: 20 mL/kg per day 1 Cardiac babies may need 20 mL/kg/for a 25-40 mL/kg per day longer period of time. Feedings for infants < 1500grams are usually best given on a pump for 30-60 minutes. The use of donor milk may be considered for all infants but infant formula is also an appropriate backup for infants > 1500 g birthweight. Low dose pressors, including dopamine (usually 5 mcg/kg/min or less) are compatible with initial trophic feeds. Trophic feeds are typically continued for 3 days for infants 751-1250 g and may continue for 5 days for infants 750 grams birthweight. Trophic feedings may be prolonged if the infant requires high dose pressor support. Consider bolus feeds every 3 hours given on a pump over 30 minutes in presence of feeding intolerance. Due to fat loss in tubing, it is preferred not to give continuous feeds unless severe feeding intolerance. Studies have found that providing oral care with expressed colostrum or breast milk is safe and may impart protection from these factors in an infant that may not be ready to feed. Nutrient components of human milk & fortified human milk are listed in Table 12-10a. Energy intakes of 100 to 130 kcal/kg per day will meet the needs for term and premature infants. Illness or surgery increases protein needs to 2-3 g/kg per day for the term infant. Thus, the caloric distribution and nutrient content of infant formulas are based on that of human milk.
Falls also occur more frequently in hospitals and immediate posthospital settings antibiotic use in animals cheap amermycin 200mg with amex. Vitamin D replacement for those who are deficient (shown to falls and improve body sway) antibiotics for sinus infection in india proven 100 mg amermycin. Environmental modifications such as installation of handrails antibiotic resistance join the fight order amermycin 100 mg free shipping, removal of rugs antibiotics good or bad generic amermycin 100 mg mastercard, use of shower rails and seats, use of ramps, and first-floor setup (placement of the bed, commode, and bath on the same floor-preferably the main level of the residence). A prolonged amount of time spent on the floor (as occurs in roughly 3% of all falls) can lead to rhabdomyolysis, dehydration, and hypothermia. Operative management may not always be consistent with a frail patient with preexisting immobility and shortened life expectancy. Generally, a hip fracture is also diagnostic of osteoporosis, necessitating treatment. Most surgeons now recognize the importance of expediting operative repair (should occur within 24 hours of the fracture). Postoperative rehabilitation: Should begin immediately or as soon as allowed by surgical recommendations. Includes mobilization, pain management, prevention of complications, and functional adaptation. Debridement of dead or infected tissue: Sharp, mechanical, or enzymatic debridement may be used. Selection of topical dressing: the goal is maintenance of a moist wound bed to promote healing. There is no need for systemic antibiotics unless there are signs of cellulitis (erythema, pain, warmth, or increasing drainage/odor). Note that the criss-cross marks in the necrotic area are from attempts to mechanically debride necrotic tissue. Surgical debridement of necrotic tissue under anesthesia revealed involvement of fascia and bone. Such changes may affect sleep pattern (the amount and timing of sleep), sleep structure (stages), or both. Typical complaints from patients > 65 years of age may thus include the following: Difficulty falling asleep. However, the following issues should be addressed by the primary physician: Sleep apnea should be diagnosed and treated. The following sleep hygiene measures should be recommended: Adherence to a regular morning rise time. Limiting of nighttime fluid intake to diminish the urge to urinate during sleeping hours. Medications: If all other measures fail and medications must be used, they should always be administered in the lowest effective dose and should be given as intermittent or short-term dosing only. Whereas no medications are recommended in the treatment of insomnia for the older patient, the use of the following medications should be actively discouraged: Benzodiazepines: the likelihood of falls, leading to hip fracture and motor vehicle accidents. Melatonin: Deficiency is difficult to measure, and effects on sleep disorders have not been proven. This may be because elderly patients are more likely to present with somatic complaints or experience delusions, and are less likely than younger patients to report a depressed mood. Epidemiologic data indicate that depression affects 1% of elderly individuals in the general community, 10% of those seeking primary care or in the hospital, and 40% of those who are permanently institutionalized. Fatigue and weight loss resulting from diabetes, thyroid disease, malignancy, vitamin B12 deficiency, or anemia. Sleep disturbance with daytime fatigue and depressed mood as a result of pain, nocturia, and sleep apnea. Pharmacotherapy: General principles for pharmacotherapy in older patients are as follows: Medications are chosen largely on the basis of their side effect profiles. Side effects typically last < 4 weeks, but weight gain and sexual dysfunction may last longer. Psychotherapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy, problem-solving therapy, and interpersonal psychotherapy are effective either alone or in combination with pharmacotherapy. Side effects of confusion and anterograde memory impairment may persist for up to six months.
M/E the bullae are suprabasal in location so that the basal layer remains attached to dermis like a row of tombstones virus quotes cheap 100 mg amermycin visa. Intraepidermal abscesses composed almost entirely of eosinophils are diagnostic of pemphigus vegetans antimicrobial vinyl fabric order amermycin 100 mg without prescription. M/E Superficial subcorneal bullae are found which contain acantholytic epidermal cells bacterial cell discount amermycin 200mg on line. The distribution of clinical lesions is similar to lupus erythematosus involving face antibiotics for acne boils purchase amermycin 200mg with visa. Three variants have been described-localised form occurring on the lower extremities; vesicular form consisting of small tense blisters; and vegetating form having verrucous vegetations found mainly in the axillae and groins. M/E the characteristic distinguishing feature from pemphigus is the subepidermal location of the non-acantholytic bullae. With passage of time, there is some epidermal regeneration from the periphery at the floor of the bulla. The bullous cavity contains fibrin network and many mononuclear inflammatory cells and many eosinophils. Dermal changes seen in inflammatory bullae consist of infiltrate of mononuclear cells, a few eosinophils and neutrophils. The disease has an association with gluten-sensitive enteropathy (coeliac disease). Both dermatitis herpetiformis and gluten-sensitive enteropathy respond to a gluten-free diet. M/E the early lesions of dermatitis herpetiformis consist of neutrophilic micro-abscesses at the tips of papillae, producing separation or blister between the papillary dermis and the epidermis. The older blisters contain fair number of eosinophils causing confusion with bullous pemphigoid. Direct immunofluorescence shows granular deposits of IgA at the papillary tips in dermatitis herpetiformis. The condition occurs due to hypersensitivity to certain infections and drugs, and in many cases, it is idiopathic. As the name suggests, the lesions are multiform such as macular, papular, vesicular and bullous. StevensJohnson syndrome is a severe, at times fatal, form of involvement of skin and mucous membranes of the mouth, conjunctivae, genital and perianal area. M/E the features are as under: i) Early lesions show oedema and lymphocytic infiltrate at the dermo epidermal junction. As the scales are removed by gentle scrapping, fine bleeding points appear termed Auspitz sign. Commonly involved sites are the scalp, upper back, sacral region and extensor surfaces of the extremities, especially the knees and elbows. M/E Fully-developed lesions show: i) Acanthosis with regular downgrowth of rete ridges to almost the same dermal level with thickening of their lower portion. The lesions are distributed symmetrically with sites of predilection being flexor surfaces of the wrists, forearms, legs and external genitalia. A special manifestation of idiopathic calcinosis cutis is tumoral calcinosis in which there are large subcutaneous calcified masses, often accompanied by foreign body giant cell reaction. Idiopathic calcinosis of the scrotum consists of multiple asymptomatic nodules of the scrotal skin. Tumours and tumour-like lesions may arise from different components of the skin such as surface epidermis, epidermal appendages and dermal tissues. Another group of tumours have their origin from elsewhere in the body but are cellular migrants to the skin. Though considered by many authors to include common viral warts (verrucae) and condyloma acuminata, true squamous papillomas differ from these viral lesions. M/E Squamous papillomas are characterised by hyperkeratosis, acanthosis with elongation of rete ridges and papillomatosis. M/E the pathognomonic feature is a sharply-demarcated exophytic tumour overlying a straight line from the normal epidermis at one end of the tumour to the normal epidermis at the other end. The other features are papillomatosis, hyperkeratosis and acanthosis as seen in squamous cell papillomas. They are often multiple, soft, small (a few mm in size), bag-like tumours commonly seen on the neck, trunk and axillae. M/E the tumours are composed of looselyarranged fibrovascular cores with overlying hyperplastic epidermis.
Multifactorial Threshold Model Unlike liability for a disease antibiotic definition order 200mg amermycin otc, the multifactorial diseases themselves are not continuous traits antibiotic resistance gene in plasmid buy amermycin 100 mg visa. Expression of the disease phenotype occurs only when a certain threshold of liability is reached antibiotic 272 buy amermycin 200 mg otc. As a simple example antibiotic resistance why does it happen buy amermycin 100 mg with visa, obesity is a complex, multifactorial condition in which excess body fat may put a person at risk for a variety of other conditions, including type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease (see below). In contrast, the genes and environmental factors underlying multifactorial traits have not been identified specifically. For example, if we wish to know the recurrence risk for siblings of individuals with cleft lip and/or palate, we ascertain a large cohort of individuals with cleft lip and/or palate and then measure the proportion of their siblings who are also affected with cleft lip and/or palate (in this case, the sibling recurrence risk is approximately 3%, which is considerably higher than the general population prevalence of 0. Recurrence risks for singlegene traits remain the same regardless of the number of affected individuals in the family. This does not mean that the true risk has changed; rather, it reflects the fact that additional affected individuals provide more information about the true risk. The presence of multiple affected individuals indicates that thefamily is located higher on the liability distribution. For example, one study showed that sibling recurrence risk for a neural tube defect (spina bifida or anencephaly; see Clinical Correlate) was 3% if one sibling was affected, 12% if two were affected, and 25% if three were affected. Again, this reflects the fact that the individual and his or her relatives are located higher on the liability distribution. For example, the prevalence of pyloric stenosis (congenital constriction of the pylorus) is approximately 111,000 for females and 1/200 for males. Thus, the average affected female is likely to be located higher on the liability distribution than is an affected male. In contrast, the risk of carrying a single-gene mutation decreases by only 1/2 with each successive degree of relationship. Although the recurrence risk for a single-gene disorder remains the same regardless of the prevalence of the disease in a population, the empirical risk for multifactorial diseases increases as the population prevalence increases. This is because populations with higher prevalence rates have a higher preponderance of genetic and errvironmental risk factors. Anencephaly (partial or complete absence of the brain) usually leads to a stillbirth, and anencephalies that survive to term do not live for more than a few days. Spina bifida, a protrusion of spinal tissue through the vertebral column, produces secondary hydrocephalus in 75% of cases and often produces some degree of paralysis. Improved intervention strategies have increased survival rates substantially 1 for this condition, with more than two thirds of patients now surviving beyond 10 years of age. Folic acid deficiency 1 is likely to be present in successive pregnancies, providing a nongenetic explanation for some of the familial clustering of this disease. However, there is also evidence for genetic variation in the abilily to metabolize folic acid. If we wish to gauge the relative effect of genetic inheritance on a trait, we can compare the concordance of the trait in monozygotic versus dizygotic twins (two individuals are concordant if they share the same trait; if they do not share the trait, they are discordant). As this table demonstrates, twin studies indicate that genes playa role in the causation of most common diseases. I Affective disorder i Club foot (unipolar) I Diabetes mellitus I I I Diabetes mellitus Epilepsy (idiopathic) I I! There is a formal equation that can be used to calculate heritability by using the data from twin studies. Adoption studies Another way of assessing the relative effects of genes and environment is to measure the prevalence of a trait in individuals who had one biologic parent with the trait b~t who were adopted by parents ~ho do not have the trait. Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes Oncogenes generally encode proteins that stimulate the cell cycle. The abnormal alleles either produce no protein prod ud (these types of alleles are called "null alleles") or encode proteins with significantly reduced activity. Typically, mutation of both copies (two hits) is necessary to promote tumor growth. In this study population, when one parent has schizophrenia, the risk of schizophrenia in an offspring is about 8 to 10 times higher than the risk in the general population.