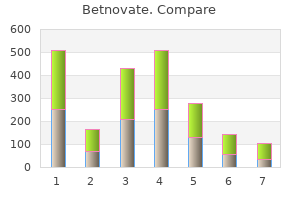
"Order betnovate 20gm with amex, acne kits".
D. Stan, M.B.A., M.B.B.S., M.H.S.
Vice Chair, Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University
The roles of antidiuretic hormone and atrial natriuretic peptide are not clearly established despite extensive study zone stop acne - 20 gm betnovate with amex. All patients with new-onset ascites or those requiring hospitalization should undergo diagnostic paracentesis with cell count acne 10 dpo order 20gm betnovate overnight delivery, ascites albumin determination acne 5 days past ovulation cheap betnovate 20gm without prescription, Gram stain acne leather jacket buy betnovate 20 gm line, and culture. Optional: amylase, bilirubin, triglycerides, cytology, myobacterial culture Abdominal Ultrasonography With Doppler 1. Most patients with cirrhotic ascites respond to dietary sodium restriction (40 to 60 mEq/day) and a diuretic. Spironolactone should be started at 50 to 100 mg/day and can be advanced up to 400 mg to achieve a daily weight loss of 0. Furosemide can be used instead of or in combination with spironolactone, beginning at a dose of 40 mg/day, although there is a greater incidence of azotemia than with spironolactone. Patients treated with two diuretics must be monitored carefully because weight loss may be rapid, even when one diuretic alone has been ineffective. In patients with alcoholic liver disease, abstinence may be effective therapy if cirrhosis has not yet developed. Ten per cent of patients with ascites fail to respond to standard therapy, either because fluid cannot be mobilized or there is associated prerenal azotemia. In these patients, therapeutic paracentesis is safe and can remove 4 to 6 L or more per visit in those with peripheral edema. In non-edematous patients, safe paracentesis requires infusing 6 to 8 g of albumin per liter of ascites removed. This option is quite costly; cost may be reduced by substituting for albumin with other plasma expanders such as dextran 70, although experience with non-albumin expanders is less extensive. Peritoneovenous shunting, performed by surgically placing a subcutaneous catheter between the superior vena cava and peritoneum, is as effective as therapeutic paracentesis in treating refractory ascites. However, low-grade disseminated intravascular coagulopathy, catheter infection, and shunt occlusion are frequent complications that reduce long-term efficacy substantially. Like other therapy for complications of portal hypertension, neither paracentesis nor peritoneovenous shunts prolong survival. Preliminary results are encouraging in small numbers of patients, but long-term follow-up in larger study groups is required. Liver transplantation remains the most definitive therapy for liver disease underlying ascites and should be considered first when ascites develops. The urgency for transplantation is increased if complications of ascites appear, particularly spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. The pathogenesis is uncertain but is believed to reflect altered gut wall permeability to bacteria, impaired capacity of hepatic and splenic macrophages to clear portal bacteremias, and/or the presence of a large volume of peritoneal fluid conducive to bacterial growth. The clinical presentation is subtle, and frank peritoneal pain or tenderness is uncommon. Typical findings include fever, signs of sepsis, or decompensation of previously stable liver function manifested by new encephalopathy or azotemia. Common causative organisms include Escherichia coli, Pneumococcus, Klebsiella, and anaerobes. Because ascites Gram stain is rarely positive, if ascites polymorphonuclear leukocyte count is greater than 250/mm3, a presumptive diagnosis should be made and empirical antibiotic therapy. Other complications of ascites include hepatic hydrothorax, abdominal wall hernias with rupture, and tense ascites with leakage (especially after paracentesis). Conservative management consists of appropriate initial therapy for most of these except hernia rupture, which requires surgical reduction. Hepatorenal syndrome, also known as functional renal failure, is defined as renal failure associated with severe liver disease without an intrinsic abnormality of the kidney. The cause is unknown, but reductions in renal blood flow, cortical perfusion, and glomerular filtration rate are consistent features. Elevated circulating levels of endothelin-1, a potent vasoconstrictor, may play an important role.
Macrophages acne vitamin deficiency cheap betnovate 20gm overnight delivery, the predominant cells in granulomas skin care 2 in 1 cheap 20 gm betnovate visa, often fuse to form characteristic multinucleated giant cells skin care obagi buy betnovate 20 gm otc. Granulomas have been found in 2 to 10% of all liver biopsy specimens delex acne discount betnovate 20gm with visa, and often no specific cause is identified. Major disorders in which hepatic granulomas are frequent include sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, histoplasmosis, and schistosomiasis (Table 151-2). For example, coccidioidomycosis is a well-established cause of granulomas in the western United States. A variety of therapeutic drugs, including phenylbutazone, allopurinol, and carbamazepine, are well documented to cause granulomas. In addition, granulomas are characteristically found in the early stages of primary biliary cirrhosis and in sarcoidosis. In most patients, the presence of granulomas does not adversely affect the liver and may be detected when a liver biopsy is being performed for some other reason, especially during evaluation of an increase in serum alkaline phosphatase. Many patients with even extensive granulomatous inflammation in the liver are asymptomatic. Sometimes a chronic hepatitis-apparently related to the granuloma-can progress to cirrhosis with portal hypertension. Only occasionally are the histologic features of the granulomas specific enough to help in the search for a cause. A rather characteristic type of inflammation with a fibrinoid ring is characteristic of Q fever. Granulomas in the liver often direct diagnostic attention toward a generalized disease process. Because granulomas represent a reaction pattern rather than a disease, the treatment depends on the diagnosis established. A few patients develop a chronic cholestatic disease from bile duct obstruction that may progress to cirrhosis. There is no established treatment for sarcoidosis affecting the liver; corticosteroids do not reliably improve the liver disease. Other infections include cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex, Cryptococcus neoformans, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, and Epstein-Barr virus. Maher A variety of inherited, infiltrative, and metabolic diseases affect the liver and also involve multiple organs. In some cases the hepatic component dominates the clinical picture, and in other cases it plays a contributory or even relatively minor role. This 52-kd protein, which comprises the alpha1 globulin fraction of serum, is synthesized primarily by hepatocytes. Patients who develop liver disease have an unusually high incidence of liver cancer. In later stages, copper is released into the circulation, permitting deposition in the brain, cornea, and kidneys. Symptoms of liver disease are the presenting complaint in roughly half of affected individuals. The most common syndrome is that of postnecrotic cirrhosis with hepatic dysfunction and portal hypertension. Rarely, the disease manifests as fulminant hepatic failure; in patients with massive liver necrosis, coincident hemolysis may provide an important clue to the diagnosis. Even Kayser-Fleischer rings are not pathognomonic, because they can occur in chronic cholestatic liver disease. Disease suspects identified by non-invasive testing should undergo liver biopsy to confirm and quantify hepatic copper accumulation. More than 250 mug of copper per gram of dry liver tissue is required to make the diagnosis. Copper chelation (see Chapter 220) improves survival but does not reverse cirrhosis.
Although there are no absolute contraindications to a diagnostic thoracentesis stop acne order betnovate 20gm free shipping, relative contraindications include a bleeding diathesis acne makeup betnovate 20 gm otc, anticoagulation acne zones meaning generic 20 gm betnovate otc, a small volume za skincare betnovate 20gm, mechanical ventilation, and low benefit-to-risk ratio. Therapeutic thoracentesis involves removing larger amounts of fluid (no more than 1000 to 1500 mL at one time because edema may occur in the re-expanded underlying lung, especially in cases of tension effusions). Although the classification of "transudate" or "exudate" is not absolute, the distinction is helpful in suggesting further evaluation and possible diagnoses. Transudates are due to imbalances in hydrostatic and oncotic pressures such as seen in heart failure or hypoalbuminemia; they may result from movement of fluid from the peritoneum to the pleural space. Exudates (Table 86-5) are defined by the presence of at least one of the following criteria: (1) pleural fluid/serum protein ratio greater than 0. Because many diagnoses produce overlapping values, acid-fast and Gram stains, aerobic and anaerobic cultures, cell count and differential, and cytologic analysis should be included in the study of these effusions. A bloody effusion not due to trauma is most likely due to malignancy or pulmonary infarction. A putrid odor is diagnostic of anaerobic empyema, whereas an ammonia odor suggests urinothorax. The value of other diagnostic markers such as adenosine deaminase, beta2 -microglobulin, pleural/serum cholinesterase, and lysozyme remain to be determined. The complications of thoracentesis include pain, bleeding (local, pleural, or abdominal), pneumothorax, infection, and spleen or liver puncture. With therapeutic thoracentesis, up to 50% of patients experience a temporary fall in Pa O2 of as much as 20 mm Hg. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia using a hook-type needle (Cope or Abrams). The contraindications are a small or loculated pleural effusion, an uncooperative patient, and anticoagulation or bleeding diathesis including azotemia with abnormal bleeding time. In most of the 5 to 10% of patients with undiagnosed effusion, the effusion itself disappears spontaneously or the cause becomes evident. When it is considered necessary to make a diagnosis, a biopsy can be obtained through thoracoscopy (introducing a rigid scope with a cold light source). Thoracoscopy may be performed under local anesthesia and has a high yield (> 85%). In some cases, it is necessary to perform an open pleural biopsy under general anesthesia. The main advantage is the possibility of obtaining larger specimens and concomitant lung tissue. Heart failure that results in biventricular failure with venous hypertension, is the most common cause of a transudative effusion. Effusions are often bilateral, usually larger on the right, and on the chest radiograph are associated with vascular congestion and cardiomegaly. Thoracentesis is indicated if the patient is febrile, the effusion is large and unilateral, or there is pain or unexplained hypoxemia. Transudates occur in 5 to 10% of patients with liver cirrhosis, secondary to movement of ascitic fluid through diaphragmatic defects or lymphatic channels; the effusion is more frequent on the right (70%). If in doubt, radioactive tracer injected in the ascitic fluid appears in the chest. Occasionally, chemical pleurodesis has effectively relieved symptomatic, recurrent effusions. A transudate is seen in up to 20% of patients with nephrotic syndrome due to decreased oncotic pressure (hypoalbuminemia) and increased hydrostatic forces; frequently bilateral, it improves by correcting the protein-losing nephropathy. Urinothorax is a rare ipsilateral pleural transudate that occurs with urinary system obstruction. The effusion has the characteristic odor of urine, and relief of the obstruction promptly resolves the effusion. Parapneumonic effusion (pleural fluid associated with pneumonia or lung abscess) is the most common cause of exudates. They may be uncomplicated and resolve spontaneously with antibiotics or may be complicated and require drainage.
Restoring perfusion may promptly restore function of myocardium that exhibits decreased function because of decreased perfusion ("hibernating" myocardium) acne 9 months after baby purchase 20 gm betnovate visa. Often acne 2004 generic 20 gm betnovate free shipping, however skin care hospitals in bangalore trusted 20gm betnovate, impaired function persists for some period of time after blood flow is restored and before the myocardium recovers ("stunning") acne 9 month old order betnovate 20 gm line. In general, hypokinesis and akinesis reflect the locus and extent of myocardial injury. Clinically, aneurysms may be recognized only later, manifested by heart failure, recurrent ventricular arrhythmia, or recurrent emboli. As left ventricular end-diastolic volume and pressure increase because of impaired regional contractility and relaxation, intramural diastolic ventricular pressure increases and myocardial perfusion declines. Peripheral arterial vasoconstriction and systemic venous constriction can no longer offset declining stroke volume, and blood pressure falls. Normally perfused zones initially may exhibit compensatory hyperkinesis with excessive wall thickening in systole. However, as the heart dilates over a period of 24 to 48 hours, hyperkinesis regresses. As the infarct thins and shrinks, and if infarct expansion does not predominate, ventricular dilatation may regress, and diastolic cardiac and pulmonary pressures may return toward normal. Acute right ventricular dysfunction diminishes cardiac output disproportionally to left ventricular injury. High-grade bradyarrhythmias are common, including those resulting from third-degree heart block. Occasionally, profound arterial oxygen desaturation can develop because of augmented right atrial pressure and right-toleft shunting through a patent foramen ovale. The hemodynamic changes resemble many of those seen with pericardial constriction or tamponade (see Chapter 65). Initially, compromised cardiac output is maintained by the combination of increased heart rate and ventricular dilatation with recruitment of the Frank-Starling mechanism. As healing progresses and the right ventricle becomes less compliant, its conduit function is restored, permitting maintenance of cardiac output at the expense of augmentation of right ventricular filling pressure. Augmentation of pulmonary venous pressure may cause diminished pulmonary compliance, dyspnea, pulmonary vascular redistribution (detectable radiographically), interstitial and alveolar pulmonary edema, respiratory decompensation, and hypoxemia. Coupled with dyspnea in the elderly, it may be manifested only as confusion and combativeness. Increased sympathoadrenal tone reflected by markedly elevated plasma catecholamine levels and adrenocortical stimulation may be prominent as well. Plasma concentrations of atrial natriuretic peptide decrease initially but then increase, perhaps because of heart failure and atrial stretch. Elevated plasma concentrations of vasopressin, angiotensin (with beta-adrenergic stimulation of renin release), and aldosterone contribute to fluid retention and hyponatremia. Impaired fibrinolysis and augmented platelet activation by circulating catecholamines may predispose to continuing coronary and ventricular mural thrombosis. Use of routine prophylactic lidocaine appears to be associated with increased mortality, and pharmacologic suppression of ventricular ectopy per se does not necessarily increase survival. Late mortality is also related to diminished left ventricular ejection fraction and elevated left ventricular end-systolic and end-diastolic volumes. Complex ventricular ectopy after hospital discharge correlates with subsequent mortality. In addition, however, a more modest prognostic benefit of an open infarct-related artery may be evident even when recanalization can be induced only 6 hours or more after onset of symptoms, when salvaging substantial amounts of jeopardized ischemic myocardium is no longer likely. An open infarct-related artery may improve ventricular function, improve collateral blood flow, decrease infarct expansion, decrease ventricular aneurysm formation, improve ventricular remodeling, diminish left ventricular dilatation, decrease late arrhythmia associated with ventricular aneurysms, and decrease mortality. Typical pain is intense, severe, unremitting for 30 to 60 minutes, and retrosternal, often radiating down the ulnar aspect of the left arm and into the neck, to the left shoulder, jaw, or teeth. The pain is classically described as crushing or squeezing, but it also may be described as an ache, burning pain, indigestion, or a feeling of fullness or "gas. Decreased systolic ventricular performance accounts for impaired perfusion of vital organs and reflex-mediated compensatory responses to hypotension, such as restlessness and impaired mentation, pallor, cutaneous vasoconstriction and sweating, tachycardia, and prerenal failure. Impaired left ventricular diastolic function leads to pulmonary vascular congestion with shortness of breath and tachypnea and may lead to pulmonary edema with orthopnea. Impaired right ventricular diastolic function leads to systemic venous hypertension, edema, hepatomegaly, and further compromise of left ventricular filling and cardiac output.
Finally skin care manufacturers purchase 20gm betnovate, molecular biologists use salicylates to activate genes that code for heat-shock proteins in the lampbrush chromosomes of Drosophila acne topical medications order 20gm betnovate mastercard, to influence mitogen-activated protein kinases skin care 40 year old buy betnovate 20 gm low cost, and to induce ceramide-mediated apoptosis in cancer cells acne paper quality betnovate 20 gm. By 1828, at the Pharmacologic Institute of Munich, Buchner isolated a tiny amount of the active glycoside, salicin, in the form of bitter-tasting yellow, needle-like crystals. Two years later, Leroux, in Paris, improved on the extraction procedure and obtained 1 ounce of salicin from 3 pounds of the bark. By 1838, Raffaele Pira of Pisa described how he obtained a pure substance from salicin by hydrolyzing the glycoside in a CrO3 -mediated oxidation via an aldehyde intermediate. Meadowsweet (Spiraea ulmaria) yielded ample quantities of an ether-soluble oil from which Spirsa ure, the same acide salicylique of Pira, was crystallized. Oil of wintergreen, a traditional remedy for aguish disorders, also was shown to contain the methyl ester of salicylic acid from which acide salicylique could be prepared. Forced to compete with the French and British dye industries, which supplied their textile mills with pigments imported from overseas colonies, the Germans responded by inventing cheap aniline dyes, creating in their train such giant enterprises as I. In 1876, Stricker and Ries reported the first successful treatment of acute rheumatism by sodium salicylate at doses of 5 to 6 g/day. Almost simultaneously, Maclagan reported his results with salicylic acid and salicin at similar dosage levels. Stricker and Ries and Maclagan found that salicylates reduce not only fever and pain but also redness and swelling. That anti-inflammatory property was next used to advantage by the Parisian Germain See, who, in 1877, introduced high-dose salicylates, both acid salicylique and salicin, as effective treatments for gout and "chronic poly-arthritis. In 1898, Felix Hofmann, an aniline dye chemist at the Friedrich Bayer-Eberfeld division of I. Farben, searched for less acidic derivatives to avoid gastric irritation and focused on acetyl derivatives of sodium salicylate. Competitors entered the field as markets expanded for other drugs that could reduce fever and pain. Based on anecdotal accounts from Alsace that a product formed from aniline treated with vinegar made a useful febrifuge, Karl Morner, in 1889, synthesized the material-acetanilide-and isolated its metabolites. Acetanilide itself, unfortunately, caused bone marrow depression and anemias in a distinct number of patients, so other derivatives were sought. Acetanilide and the widely used phenacetin are metabolized to N-acetyl- p-aminophenol, which by various anagramatic combinations yields the generic names acetaminophen in the United States and paracetamol in the United Kingdom. In 1955, acetaminophen acquired a trade name in the United States that was to make it famous: Tylenol-also from acetylp-aminophenol. Neither acetanilide nor phenacetin proved as useful as aspirin for treating rheumatic fever or rheumatoid arthritis because they were not anti-inflammatory. By comparison, trials of steroids versus aspirin and sodium salicylate showed that salicylates at doses high enough to yield plasma levels of 25 to 35 mg/dL (6 to 9 g/day) were as effective anti-inflammatory agents as cortisone or prednisone in rheumatic fever. Moreover, they found that platelets taken from volunteers given aspirin and indomethacin 1 hour before venipuncture failed to make prostaglandins in response to thrombin and that catecholamine-induced release of prostaglandins from canine spleens could be inhibited by indomethacin, albeit less consistently than by aspirin. The constitutive enzyme, cyclooxygenase 1, is a 70-kd homodimer localized to microsomal membranes. This enzyme catalyzes two reactions: the bis-dioxygenation 115 Figure 29-1 the inflammatory cascade. The endoperoxides, critical for platelet function, are transformed by platelets to a most potent vasoconstricting and platelet-aggregating substance, thromboxane A2 (TxA2). Because platelets make TxA2, which constricts the smooth muscle of blood vessels, and because blood vessel walls make prostacyclin I2, which powerfully relaxes blood vessels and inhibits platelet aggregation, the hunt was on for ways to inhibit the synthesis of thromboxane but not prostacyclin. Vane and his associates, in the 1970s, had amassed convincing evidence that the prostaglandin hypothesis of aspirin action was largely correct. Vane argued that stable prostaglandins not only were produced at sites of inflammation but also, alone or in concert with other mediators, could provoke all the cardinal signs of inflammation. By comparison, acetaminophen ineffectively inhibits prostaglandin synthesis by enzyme preparations from a variety of tissues but is effective against the synthetase from brain. And although non-acetylated salicylates are roughly 1/10 as potent as aspirin in vitro, studies of urinary prostaglandin metabolites showed that sodium salicylate effectively diminishes excretion of these metabolites in humans.