"750 mg lquin with visa, bacteria 80s ribosome".
R. Knut, M.A., M.D.
Co-Director, University of South Alabama College of Medicine
Patients with ascorbic acid deficiency also often show bruises on the limbs as a result of subcutaneous extravasation (leakage) of blood due to capillary fragility (Figure 4 antibiotics for uti septra generic lquin 500 mg with amex. Glycosylation: Some hydroxylysine residues are modified by glycosylation with glucose or glucosyl-galactose (see Figure 4 antibiotics heartburn lquin 250 mg with mastercard. Assembly and secretion: After hydroxylation and glycosylation virus vs bacterial infection order lquin 750 mg visa, three pro- chains form procollagen antibiotic quiz medical student purchase lquin 750 mg fast delivery, a precursor of collagen that has a central region of triple helix flanked by the nonhelical amino- and carboxyl-terminal extensions called propeptides (see Figure 4. The formation of procollagen begins with formation of interchain disulfide bonds between the C-terminal extensions of the pro- chains. The procollagen molecules move through the Golgi apparatus, where they are packaged in secretory vesicles. The vesicles fuse with the cell membrane, causing the release of procollagen molecules into the extracellular space. Extracellular cleavage of procollagen molecules: After their release, the procollagen molecules are cleaved by N- and C-procollagen peptidases, which remove the terminal propeptides, releasing triple-helical tropocollagen molecules. Formation of collagen fibrils: Tropocollagen molecules spontaneously associate to form collagen fibrils. They form an ordered, overlapping, parallel array, with adjacent collagen molecules arranged in a staggered pattern, each overlapping its neighbor by a length approximately three-quarters of a molecule (see Figure 4. Cross-link formation: the fibrillar array of collagen molecules serves as a substrate for lysyl oxidase. This Cu2+-containing extracellular enzyme oxidatively deaminates some of the lysine and hydroxylysine residues in collagen. The reactive aldehydes that result (allysine and hydroxyallysine) can condense with lysine or hydroxylysine residues in neighboring collagen molecules to form covalent cross-links and, thus, mature collagen fibers (Figure 4. Disruption in copper homeostasis causes copper deficiency (X-linked Menkes disease) or overload (Wilson disease). Degradation Normal collagens are highly stable molecules, having half-lives as long as several years. However, connective tissue is dynamic and is constantly being remodeled, often in response to growth or injury of the tissue. Breakdown of collagen fibers is dependent on the proteolytic action of collagenases, which are part of a large family of matrix metalloproteinases. For type I collagen, the cleavage site is specific, generating three-quarter and one-quarter length fragments. Collagen diseases: Collagenopathies Defects in any one of the many steps in collagen fiber synthesis can result in a genetic disease involving an inability of collagen to form fibers properly and, therefore, an inability to provide tissues with the needed tensile strength normally provided by collagen. More than 1,000 mutations have been identified in 23 genes coding for 13 of the collagen types. The following are examples of diseases that are the result of defective collagen synthesis. Osteogenesis imperfecta: this syndrome, known as brittle bone disease, is a genetic disorder of bone fragility characterized by bones that fracture easily, with minor or no trauma (Figure 4. The most common mutations cause the replacement of glycine (in GlyXY) by amino acids with bulky side chains. The resultant structurally abnormal chains prevent the formation of the required triple-helical conformation. It is characterized by multiple fractures at birth, short stature, spinal curvature leading to a "humped-back" (kyphotic) appearance, and blue sclerae. Elastic fibers composed of elastin and glycoprotein microfibrils are found in the lungs, the walls of large arteries, and elastic ligaments. They can be stretched to several times their normal length but recoil to their original shape when the stretching force is relaxed. Structure Elastin is an insoluble protein polymer synthesized from a precursor, tropoelastin, which is a linear polypeptide composed of about 700 amino acids that are primarily small and nonpolar (for example, glycine, alanine, and valine). Elastin is also rich in proline and lysine but contains scant hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine.
These studies have revealed new information about the polypeptide backbones of mucins (size of tandem repeats antibiotic resistance argument buy lquin 250 mg line, potential sites of N-glycosylation infection questionnaires cheap lquin 500 mg without prescription, etc) and ultimately should reveal aspects of their genetic control antibiotics with food 500 mg lquin fast delivery. The enzymes catalyzing this type of reaction are membrane-bound glycoprotein glycosyltransferases viro the virus buy 750 mg lquin amex. The factors that determine which specific serine and threonine residues are glycosylated have not been identified but are probably found in the peptide structure surrounding the glycosylation site. The enzymes assembling O-linked chains are located in the Golgi apparatus, sequentially arranged in an assembly line with terminal reactions occurring in the trans-Golgi compartments. Secretory mucins generally have an oligomeric structure and thus often have a very high molecular mass. Membrane-bound mucins participate in various cell-cell interactions (eg, involving selectins; see below). Many cancer cells form excessive amounts of mucins; perhaps the mucins may mask certain surface antigens on such cells and thus protect the cells from immune surveillance. Mucins also carry cancer-specific peptide and carbohydrate epitopes (an epitope is a site on an antigen recognized by an antibody, also called an antigenic determinant). The sugars of this compound are first assembled on the Dol-P-P backbone, and the oligosaccharide chain is then transferred en bloc to suitable Asn residues of acceptor apoglycoproteins during their synthesis on membrane-bound polyribosomes. To form high-mannose chains, only the Glc residues plus certain of the peripheral Man residues are removed. The phenomenon whereby the glycan chains of N-linked glycoproteins are first partially degraded and then in some cases rebuilt is referred to as oligosaccharide processing. Thus, the initial steps involved in the biosynthesis of the N-linked glycoproteins differ markedly from those involved in the biosynthesis of the O-linked glycoproteins. It is the major class of glycoproteins and has been much studied, since the most readily accessible glycoproteins (eg, plasma proteins) mainly belong to this group. The principal difference between this and the previous class, apart from the nature of the amino acid to which the oligosaccharide chain is attached (Asn versus Ser or Thr), concerns their biosynthesis. Complex, Hybrid, & High-Mannose Are the Three Major Classes of N-Linked Oligosaccharides There are three major classes of N-linked oligosaccharides: complex, hybrid, and high-mannose (Figure 474). The oligosaccharide branches are often referred to as antennae, so that bi-, tri-, tetra-, and A. The polyisoprenol used in eukaryotic tissues is dolichol, which is, next to rubber, the longest naturally occurring hydrocarbon made up of a single repeating unit. Schematic diagram of the pentasaccharide core common to all N-linked glycoproteins and to which various outer chains of oligosaccharides may be attached. The phosphate in dolichol phosphate is attached to the primary alcohol group at the left-hand end of the molecule. The reaction is catalyzed by oligosaccharide:protein transferase, a membraneassociated enzyme complex. Glycosylation occurs at the Asn residue of an AsnX-Ser/Thr tripeptide sequence, where X is any amino acid except proline, aspartic acid, or glutamic acid. Only about one-third of the Asn residues that are potential acceptor sites are actually glycosylated, suggesting that factors other than the tripeptide are also important. The transfer reaction and subsequent processes in the glycosylation of N-linked glycoproteins, along with their subcellular locations, are depicted in Figure 479. In the case of highmannose glycoproteins, the process may stop here, or up to four Man residues may also be removed. Four external Man residues are removed in reactions 4 and 5 by at least two different mannosidases. Late phase-To assemble a typical complex oligosaccharide chain, additional sugars must be added to the structure formed in reaction 7. Reactions 9, 10, and 11 involve the addition of Fuc, Gal, and NeuAc residues at the sites indicated, in reactions catalyzed by fucosyl, galactosyl, and sialyl transferases, respectively. The Golgi apparatus is composed of cis, medial, and trans cisternae; these can be separated by appropriate centrifugation procedures. Vesicles containing glycoproteins appear to bud off in the endoplasmic reticulum and are transported to the cis Golgi. The thick arrows indicate various nucleotide sugars involved in the oveall scheme. The major features of the biosynthesis of Nlinked glycoproteins are summarized in Table 4710 and should be contrasted with those previously listed (Table 479) for O-linked glycoproteins.
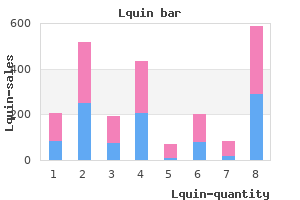
Fasting blood and urine samples of patient (individual) are collected to know fasting blood glucose level and urine glucose antimicrobial guidelines 500 mg lquin with mastercard. Alternatively patient may be given 1 gm of glucose per kg body weight dissolved in 200 ml water recently took antibiotics for sinus infection order lquin 750 mg without a prescription. Thereafter blood and urine samples are collected at every 30 minutes interval for 2 hours and 30 minutes antibiotics vertigo 750 mg lquin visa. The individuals fasting blood glucose level remains within 60-90 mg% range (OToluidine method) virus 3d model order lquin 750 mg without prescription. After oral test load of glucose blood glucose level reaches peak in one hour (110130 mg%) and it does not exceed renal threshold for glucose which is about 180 mg%. Thereafter blood glucose levels falls and reaches normal fasting level at the end of 2 hours. Further more, none of the urine samples collected during test period show glucose as blood glucose level remained within renal threshold value. The fasting blood glucose level is always above (130 mg%) and usually influenced by severity of diabetes mellitus. In mild diabetes, the fasting blood glucose level is less than 150 mg% whereas in severe diabetes it is higher than 180 mg%. Further after test dose of glucose increase in blood glucose level is higher than normal individual and blood glucose level does not return to normal level even after 2 hours which is characteristic of diabetes. Fasting blood glucose of an individual with impaired glucose tolerance is above 90 mg% but below 130 mg%. Further, the blood glucose level does not return to fasting level even after 2 hours and usually it is higher than 140 mg% but below 200 mg%. S e ve re diab e tes 3 00 2 50 2 00 B loo d g lu co se (m g%) 1 50 1 00 50 M ild d ia be the s I m p a ir e d g lu c o s e to le r a n c e N o rm al In c r e a se d to le ra n ce 0 30 60 90 1 20 1 50 Tim e (m in u tes). In a normal individual, the blood glucose level reaches peak in few minutes after glucose load is given then start decreasing by 20 to 30 minutes and returns to normal by 45 to 60 minutes. In case of decreased glucose tolerance blood glucose level does not return to normal after usual one hour. It is defined as a time in minutes required for peak blood glucose to get reduced to half. Long term arsenic exposure and incidence of non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Relationship between plasma measure of oxidative stress and metabolic control in non-insulin dependant diabetes mellitus, Diabetologia, 40, 647-654, 1997. Metabolic syndrome outside the site, a lateral approach to phosphotase inhibition. Give an account of metabolic changes that occur in liver, adipose tissue and skeletal muscle under well fed conditions. A 40-year-old man started experiencing excessive thirst, polyuria and loss of weight for past couple of weeks. During hunger strike by a major political party, a volunteer was brought to hospital in coma. Nucleotides are required for formation of co-enzymes of some members of vitamins B complex group. Some nucleotides act as carrier or donor of activated sugars, sulphates and nitrogenous compounds. Synthetic analogs of nucleosides and nitrogenous bases are anticancer and antiviral agents. Purines play major role in cardiovascular biology in normal and pathological conditions. Chemical nature of nucleotides Hydrolysis of nucleotides produce nitrogen bases, sugars and phosphate. The carbon (c) and nitrogen (N) atoms of purine ring are numberered in anti-clockwise direction. The structures of adenine and guanine along with their systematic names are shown in. Uric acid and xanthine tend to crystalize at physiological pH at high concentration. The structures of these pyrimidines along with their systematic names are shown in. They too exhibit keto-enol tautomerism as well as amino-imino tautomerism like purine bases.
The monoacylglycerols best antibiotic for sinus infection cipro buy lquin 750 mg otc, free fatty acids antimicrobial textiles buy lquin 500 mg low cost, cholesterol and lysophospholipids combine with bile salt micelles and form mixed micelles antibiotics for uti nhs cheap 250 mg lquin amex. These mixed micelles carry the products of lipid digestion to the brush border of mucosal cells where they are absorbed into intestinal epithelium bacteria battery lquin 750 mg lowest price. Solubilization Solubilization of products of lipid digestion is required for diffusion of these molecules from the liquid luminal contents to brush border of enterocyte. Bile salts increases the solubility of lipolytic products in the aqueous luminal phase by forming mixed micelles only. Decreased bile salt concentration leads to formation of large sized liquid crystalline vesicles or liposomes. Transport of Lipolytic Products into Enterocyte Until recently it is assumed that uptake of products of lipid digestion by enterocytes involves simple diffusion. Now it is known that specific transporters are involved in the uptake of some products of lipid digestion by enterocytes. It is an integral membrane protein anchored in the lipid bilayer through an hydrophobic domain. The active centre involved in the transport are exposed to external side of the membrane. Alpha glycerophosphate pathway is another alternative pathway for triglyceride resynthesis in enterocyte. Within the intestinal cells, monoacylglycerols and fatty acids are converted to triglycerides only. In addition lysophospholipids absorbed are converted to phospholipids by acylation. Triglycerides, cholesterol esters and phospholipids so formed in intestinal cells combines with protein to form lipoproteins, which are called as chylomicrons. Because of the absorption of dietary lipids the lymph appears milky and called as chyle. The absorbed short chain and medium chain fatty acids are transported into portal venous blood. Similarly, glycerol absorbed is also not utilized and enters portal venous blood. It is due to abnormal connection between Digestion and Absorption of Food 149 urinary tract and lymphatics of small intestine. It disappears when dietary fat is replaced with fat containing short chain and medium chain fatty acids. Chylothorax In the affected persons milky pleural fluid accumulates in pleural space due to abnormal connection between pleural space of lungs and lymphatics of small intestine. Like chyluria, chylothorax also disappears when dietary fat consist of only short and medium chain fatty acids. Triglycerides accumulates in intestinal cells due to lack of apo B-48 required for lipoprotein formation (chylomicrons). Cholestasis Lipid digestion and absorption is impaired in intra or extra hepatic cholestasis due to non availability of adequate amounts of bile salts, phospholipids and cholesterol. In cholestatic patients, liquid crystal vesicles are formed instead of mixed micelles. Proper biliary secretion of phospholipid is necessary for chylomicron formation in enterocyte and secretion of lipids into lymph. Elevated plasma level of plant sterol sitosterol is characteristic of this disorder. It is due to decreased activity of sterol transporter that secretes sterol into bile for elimation. Digestion and Absorption of Proteins Dietary proteins Food stuffs like cereals, grains, milk, eggs and meat contain proteins. Digestion of Proteins Hydrolysis of dietary proteins to aminoacids constitutes the process of protein digestion. Protein Digestion In the mouth Due to lack of protein splitting enzymes, no digestion of protein takes place in the mouth. The digestion of the denatured proteins is initiated by pepsin present in gastric juice. It is secreted by the chief cells of stomach in the 150 Medical Biochemistry form of inactive pro-enzyme pepsinogen.