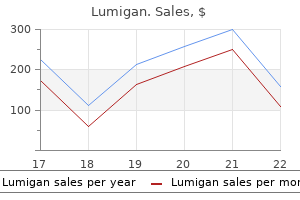
"Purchase 3ml lumigan overnight delivery, medications for migraines".
P. Sanford, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, Dell Medical School at The University of Texas at Austin
When the ratios of the different genotypes in a population have been determined symptoms ulcer cheap lumigan 3ml without prescription, their predicted ratios in the next generation can be compared with the observed values medications used to treat fibromyalgia buy lumigan 3ml otc. If the differences are significant and migration and non-random mating can be discounted k-9 medications buy cheap lumigan 3ml on line, then there is evidence that directional selection is occurring in the population treatment laryngomalacia infant best 3 ml lumigan. Selective breeding over many centuries has produced many different breeds, such as b, the Guernsey. Desired features include docility (making the animal easier to control), fast growth rates and high milk yields. Individuals showing one or more of these desired features to a larger degree than other individuals are chosen for breeding. Over many generations, alleles conferring the desired characteristics increase in frequency, while those conferring characteristics not desired by the breeder decrease in frequency. A bull cannot be assessed for milk production since this a sex-limited trait (note that this is not the same as sex-linked). It is important to realise that selective breeders have to consider the whole genotype of an organism, not just the genes affecting the desired trait, such as increased milk yield. Suppose that the chosen parents come from the same environment and are from varieties that have already undergone some artificial selection. It is likely that such parents share a large number of alleles of background genes, so the offspring will be adapted for the same environment. But suppose instead that one of the chosen parents comes from a different part of the world. It may show the trait being selected for, but it may not be welladapted to its environment. Black Sea Caspian Sea Assyria Mediterranean Sea Mesopotamia Phoenicia Euphrates Tigris Lower Egypt Persian Gulf Red Sea Upper Egypt Nile Figure 17. Crop improvement the same problem is seen when a cross is made between a cultivated plant and a related wild species. Although most species will not breed with a different species, some can be interbred to give fertile offspring. Such species are often those that do not normally come into contact with one another, because they live in different habitats or areas. The wild parent will have alleles that are not wanted and which have probably been selected out of the cultivated parent. It was not until the 20th century that we really understood how we can affect the characteristics of crop plants by artificial selection and selective breeding. But, although these early farmers knew nothing of genes and inheritance, they did realise that characteristics were passed on from parents to offspring. The farmers picked out the best plants that grew in one year, allowing them to breed and produce the grain for the next year. Over thousands of years, this has brought about great changes in the cultivated varieties of crop plants, compared with their wild ancestors. Today, selective breeding continues to be the main method by which new varieties of crop plants are produced. In some cases, however, gene technology is being used to alter or add genes into a species in order to change its characteristics. Much of it is grown to produce grains rich in gluten, which makes them good for making bread flour. For making other food products such as pastry, varieties that contain less gluten are best. Chapter 17: Selection and evolution Breeding for resistance to various fungal diseases, such as head blight, caused by Fusarium, is important, because of the loss of yield resulting from such infections. Successful introduction of an allele giving resistance takes many generations, especially when it comes from a wheat grown in a different part of the world. Its aim is to support the development of new varieties by screening seed collections for plants with traits such as disease resistance, or climate resilience (Figure 17. Any plant with a suitable trait is grown in large numbers and passed to the commercial breeders. This makes them easier to harvest and means they have higher yields (because they put more energy into making seeds rather than growing tall) (Figure 17. The shorter stems also make the plants less susceptible to being knocked flat by heavy rains, and means they produce less straw, which has little value and costs money to dispose of.
A gene is expressed when its protein product is synthesized medications you can take while breastfeeding purchase lumigan 3 ml on-line, and one requirement of the genetic material is that it direct the order in which amino acid units are added to the end of a growing protein molecule medicine nobel prize 2016 cheap 3ml lumigan visa. A genetic material must also be capable of undergoing occasional mutations in which the information it carries is altered symptoms 8 weeks pregnant buy discount lumigan 3ml line. Furthermore medicine with codeine purchase 3ml lumigan with amex, so that mutations will be heritable, the mutant molecules must be capable of being replicated as faithfully as the parental molecule. This feature is necessary to account for the evolution of diverse organisms through the slow accumulation of favorable mutations. This length is denoted 50 kb, where kb stands for kilobases (1 kb 1000 base pairs). The pink and green cylinders represent regions of the enzyme in which the amino acid chain is twisted in the form of a right-handed helix. Because the first three letters in the name of each restriction enzyme stand for the bacterial species of origin, these letters are printed in italics; the rest of the symbols in the name are not italicized. Most restriction enzymes recognize only one short base sequence, usually four or six nucleotide pairs. The nucleotide sequence recognized for cleavage by a restriction enzyme is called the restriction site of the enzyme. The enzyme TaqI yields cohesive ends consisting of two nucleotides, whereas the cohesive ends produced by the other enzymes contain four nucleotides. The former leave sticky ends because each end of the cleaved site has a small, single-stranded overhang that is complementary in base sequence to the other end (Figure 2. The type of electrophoresis most commonly used in genetics is gel electrophoresis. A thin slab of a gel, usually agarose or acrylamide, is prepared containing small slots (called wells) into which samples are placed. Liquid gel is allowed to harden with an appropriately shaped mold in place to form "wells" for the samples (purple). The separated fragments in a sample appear as bands, which may be either visibly colored or fluorescent, depending on the particular reagent used. The region of a gel in which the fragments in one sample can move is called a lane; this gel has seven lanes. It also indicates that the linear relationship breaks down for the largest fragments that can be resolved under a given set of conditions. For any one agarose concentration, except for the largest fragments, the distance migrated decreases as a linear function of the logarithm of fragment size. The numbers within the arrows are the approximate lengths of the fragments in kilobase pairs (kb). Numbers indicate fragments in order from largest (1) to smallest (6); the circled numbers on the maps correspond to the numbers beside the gel. Note: In Problem 2 at the end of this chapter (Guide to Problem Solving), we show how to use the results of a double digest to determine the particular order of fragments for a pair of restriction enzymes. Nucleic Acid Hybridization Most genomes are sufficiently large and complex that digestion with a restriction enzyme produces many bands that are the same or similar in size. What this means is that even though we know that the fragment we are interested in is 3 kb in length, it is only one of 17,000 fragments that are so similar in size that ours cannot be distinguished from the others by length alone. A more accurate analogy would be looking for a needle in a haystack that had been pitched into a swimming pool full of water. Clearly, we need some method by which the molecules in a gel can be immobilized and our specific fragment identified. In this section we examine how the two strands in a double helix can be "unzipped" to form single strands and how, under the proper conditions, two single strands that are complementary or nearly complementary in sequence can be "zipped" together to form a different double helix. Applications of this type include the tracking of genetic markers in pedigrees and the isolation of fragments containing a particular mutant gene. This allows the isolation of genes that have the same or related functions in multiple species. It is used to study aspects of molecular evolution, such as how differences in sequence are correlated with differences in function, and the patterns and rates of change in gene sequences as they evolve. The temperature at which 50 percent of the base pairs are denatured is the melting temperature, symbolized Tm.
This may happen passively treatment resistant depression discount 3 ml lumigan with visa, as certain materials move back and forth treatment of chlamydia order 3ml lumigan, or the cell may have special mechanisms that facilitate transport treatment 3rd degree burns generic 3 ml lumigan with amex. All cells spend the majority of their energy to maintain an imbalance of sodium and potassium ions between the interior and exterior of the cell medicine ball slams cheap 3 ml lumigan mastercard. Passive transport is a naturally occurring phenomenon and does not require the cell to exert any of its energy to accomplish the movement. In passive transport, substances move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. A physical space in which there is a range of concentrations of a single substance is said to have a concentration gradient. Selective Permeability Plasma membranes are asymmetric: the interior of the membrane is not identical to the exterior of the membrane. In fact, there is a considerable difference between the array of phospholipids and proteins between the two leaflets that form a membrane. On the interior of the membrane, some proteins serve to anchor the membrane to fibers of the cytoskeleton. There are peripheral proteins on the exterior of the membrane that bind elements of the extracellular matrix. Carbohydrates, 144 Chapter 5 Structure and Function of Plasma Membranes attached to lipids or proteins, are also found on the exterior surface of the plasma membrane. These carbohydrate complexes help the cell bind substances that the cell needs in the extracellular fluid. Recall that plasma membranes are amphiphilic: They have hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions. This characteristic helps the movement of some materials through the membrane and hinders the movement of others. Lipid-soluble material with a low molecular weight can easily slip through the hydrophobic lipid core of the membrane. Substances such as the fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K readily pass through the plasma membranes in the digestive tract and other tissues. Molecules of oxygen and carbon dioxide have no charge and so pass through membranes by simple diffusion. While some polar molecules connect easily with the outside of a cell, they cannot readily pass through the lipid core of the plasma membrane. Additionally, while small ions could easily slip through the spaces in the mosaic of the membrane, their charge prevents them from doing so. Ions such as sodium, potassium, calcium, and chloride must have special means of penetrating plasma membranes. Simple sugars and amino acids also need help with transport across plasma membranes, achieved by various transmembrane proteins (channels). A single substance tends to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until the concentration is equal across a space. For example, think about someone opening a bottle of ammonia in a room filled with people. The ammonia gas is at its highest concentration in the bottle; its lowest concentration is at the edges of the room. The ammonia vapor will diffuse, or spread away, from the bottle, and gradually, more and more people will smell the ammonia as it spreads. On the contrary, concentration gradients are a form of potential energy, dissipated as the gradient is eliminated. Within a system, there will be different rates of diffusion of the different substances in the medium. Factors That Affect Diffusion Molecules move constantly in a random manner, at a rate that depends on their mass, their environment, and the amount of thermal energy they possess, which in turn is a function of temperature. This movement accounts for the diffusion of molecules through whatever medium in which they are localized. A substance will tend to move into any space available to it until it is evenly distributed throughout it. After a substance has diffused completely through a space, removing its concentration gradient, molecules will still move around in the space, but there will be no net movement of the number of molecules from one area to another. This lack of a concentration gradient in which there is no net movement of a substance is known as dynamic equilibrium. While diffusion will go forward in the presence of a concentration gradient of a substance, several factors affect the rate of diffusion.
As you read treatment locator order lumigan 3 ml overnight delivery, take notes and organize what you learn about the classification of protists medicine used to treat bv order 3ml lumigan with visa, based upon the way they move symptoms type 1 diabetes lumigan 3ml with mastercard. Ciliophora Sarcodina Apicomplexa Zoomastigina Chapter 19 Protists 225 How does a paramecium feed and digest food Picture this Structure of a Paramecium Pellicle Cilia Oral groove Ectoplasm Gullet (rigid cytoplasm) Endoplasm (fluid cytoplasm) 1 anima sound medicine purchase 3 ml lumigan fast delivery. Highlight the structures of the paramecium that are involved in feeding and digestion. Trichocysts Macronucleus Food Micronucleus vacuoles Anal pore How do ciliates reproduce All known ciliates have two types of nuclei-the macronucleus and the micronucleus. The macronuclei control the everyday life functions such as feeding and maintaining water balance. Most ciliates exchange genetic information in a sexual process called conjugation. Conjugation is not sexual reproduction because new individuals do not result from it. After three of the new micronuclei dissolve, the remaining micronucleus undergoes mitosis. The micronuclei then combine to form a new diploid macronucleus with a new combination of genetic information. Most amoebas live in salt water, but some live in streams, the muddy bottoms of ponds, and in damp moss and leaves. Amoebas have an outer plasma membrane and an inner stiff membrane called ectoplasm. The cytoplasm contains a nucleus, food vacuoles, and sometimes contractile vacuoles. Amoebas excrete wastes and take in oxygen through their outer membranes by diffusion. Some species have a test-a hard, porous covering similar to a shell that surrounds the plasma membrane. In harsh living conditions, some amoebas form cysts that can survive until conditions improve. Spores are reproductive cells that form without fertilization and produce a new organism. In Africa, tsetse flies spread the disease when they feed on the blood of humans or other mammals. Restate the Main Point As you read this section, stop after each paragraph, and put the main ideas into your own words. They group algae by pigment types, method of food storage, and composition of the cell wall. The oil also helps diatoms float close to the surface, where they can absorb energy from the Sun. When a diatom is about one-quarter of the original size, sexual reproduction begins. The beating flagella cause dinoflagellates to spin as they move through the water. Algal blooms When dinoflagellates have plenty of food and favorable conditions, they reproduce in great numbers. Instead, they are covered by a flexible, tough outer pellicle, similar to a paramecium. Most chrysophytes are one-celled, but some form a group of cells that join together in close association called a colony. They usually reproduce asexually, and they live in both freshwater and salt water.