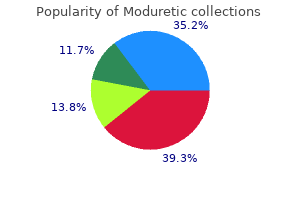
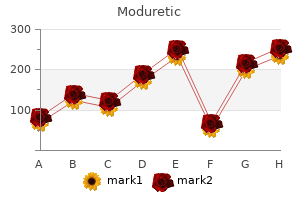
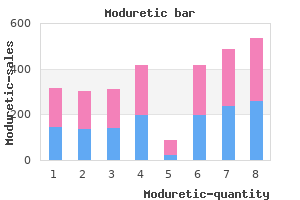
"Buy discount moduretic 50mg line, hypertension 14070".
R. Wilson, M.B.A., M.D.
Co-Director, Burrell College of Osteopathic Medicine at New Mexico State University
The magnitude of the problem is starkly illustrated by the demographics: approximately 4 blood pressure 9860 generic moduretic 50 mg amex. Food production increases resulting from the Green Revolution of the 1960s and 1970s have helped to close the gap between food supply and demand hypertension kidney specialists lancaster pa proven 50 mg moduretic. But conventional plant breeding techniques may not be adequate to keep pace with demand for both production increases and improvements in land use and environmental quality hypertension diagnosis code moduretic 50mg on line. The principle goal of this report is to provide a review of the literature addressing the comparative environmental benefits and safety of the three most widely planted biotechnology-derived crops: soybean hypertension renal disease cheap 50mg moduretic overnight delivery, corn (commonly referred to as maize), and cotton. To evaluate adequately the potential benefits and safety of agricultural biotechnology the authors provide a comprehensive literature review and place the information in context by comparing recent advances in biotechnology-derived soybean, corn, and cotton with currently available traditional varieties of those same crops. The peer-reviewed literature, regulatory assessments, nongovernmental organizations, and the popular media have raised questions repeatedly about the environmental safety of biotechnology-derived crops. To answer these questions relative to soybean, corn, and cotton, the authors of this report evaluate the environmental impacts of commercially available biotechnology-derived crops in relation to the current agricultural practices for crop and pest management in conventionally bred crops. Changes in pesticide use patterns - Does the adoption of biotechnology-derived soybean, corn, and cotton impact the use of pesticides and, if so, do these changes alter farmer practices in ways that affect water quality or soil health? Soil management and conservation tillage Does adoption of biotechnology-derived soybean, corn, and cotton lead to changes in the adoption of no-till and other conservation tillage practices or otherwise impact soil erosion, moisture retention, soil nutrient content, water quality, fossil fuel use, and greenhouse gasses? Crop weediness - Do biotechnology-derived soybean, corn, and cotton acquired weediness traits? Pest resistance - Do biotechnology-derived soybean, corn, and cotton possess plant-protectant traits to which pests will become resistant and, if so, is the development of resistance to these traits different from development of resistance to conventional chemical and microbial pesticides? Pest population shifts - Do biotechnologyderived soybean, corn, and cotton cause changes in weed or secondary insect pest populations that impact the agricultural system or ecology of the surrounding environment? Human exposure - Do the traits of herbicide tolerance and resistance to pest insects in biotechnology-derived soybean, corn, or cotton pose any new or different safety concerns in comparison with conventionally bred crops that have similar traits? The literature most pertinent for this comprehensive review was identified through a series of literature database searches and in the course of professional practice (meetings, conferences, and peer-to-peer networking). Prior to the sections on soybean, corn, and cotton, an overview of modern biotechnology is provided for those readers who are less familiar with the use of modern laboratory methods to transfer traits or characteristics from one living entity to another. Crop-specific information and conclusions are addressed in the sections on soybean, corn, and cotton. The literature review has been supported through contributions from the United Soybean Board. Review and comment of the report was provided by individuals from agricultural scientific societies, academic institutions, and nonprofit organizations. Overview of Modern Biotechnology To appreciate the environmental benefits of agricultural biotechnology in the midst of public concerns, one should focus on the traits produced in the context of their environment rather than the techniques for crop improvement. Regardless of the specific trait intended for enhancement, the process of transforming different crop species generally involves common strategies and molecular methods. However, concerns about agricultural biotechnology can be alleviated, in part, by an improved understanding of the biochemical basis for the enhanced traits and the techniques used. Thus, the following section is, in part, a brief historical overview of the biochemical basis and genetic sources of the currently registered and commercial herbicide tolerance and pest-protected traits, and the mechanics of plant transformation. Three principle mechanisms are responsible in all instances where pest resistance evolves. These include increased ability to detoxify the pesticide; altered biochemical site of interaction with the pesticide. In the case of detoxification, the proteins involved are enzymes that possess an enhanced capacity for breaking down the herbicide. Biochemical sites attacked by a herbicide also may be enzymes or, alternatively, receptors that trigger a cascade of physiological reactions. Altered enzymes and receptors of tolerant or resistant plants have less affinity than their "normal" counterparts for binding the herbicide. The glyphosate tolerance trait is used in field crops for weed control, but the glufosinate tolerance trait has its practical utility as a selection marker to help produce the commercial insect-protected plants. Herbicide Tolerance Plant species have long been known to be highly variable in their response to herbicides.
Syndromes
- Allergic reaction to the contrast dye
- Talk therapy
- The other approach is called endovascular stent grafting. This procedure can be done without making a large cut in your abdomen, so you may get well faster. If you have certain other medical problems, this may be a safer approach. Endovascular repair is rarely done for a leaking or bleeding aneurysm.
- Be aware of risks connected with recreation such as shooting a gun, driving snowmobiles, or other similar activities.
- Blood tests
- Pseudoxanthoma elasticum
- Urine output, decreased
- Sore throat
A yellow fever epozootic in Zika Forest pulse pressure 12080 buy 50mg moduretic with mastercard, Uganda hypertension va disability purchase moduretic 50 mg with amex, during 1972: part 2: monkey serology arrhythmia and alcohol discount moduretic 50mg visa. Hemagglutination inhibition with arboviruses: relationship between titers and source of erythrocytes arteria 3d medieval worldbuilder classic buy 50 mg moduretic with mastercard. Neutralizing antibodies for certain viruses in the sera of human beings residing in northern Natal. Antibodies against certain arboviruses in sera from human beings and domestic animals from the south-western and north-western regions of the Cape Province of South Africa. Epidemic of dengue-4 virus in Yap State, Federated States of Micronesia, and implication of Aedes hensilli as an epidemic vector. Genetic and serologic properties of Zika virus associated with an epidemic, Yap State, Micronesia, 2007. Cao-Lormeau V-M, Roche C, Aubry M, Teissier A, Lastere S, Daudens E, Mallet H-P, Musso D, Aaskov J. Recent emergence of dengue virus serotype 4 in French Polynesia results from multiple introductions from other South Pacific islands. Serosurvey of dengue, Zika and other mosquito-borne viruses in French Polynesia, abstr 765. Vandenbogaert M, Cao-Lormeau V-M, Diancourt L, Thiberge J-M, Sall A, Kwasiborski A, Musso D, Desprиs P, Manuguerra J-C, Caro V. Tognarelli J, Ulloa S, Villagra E, Lagos J, Aguayo C, Fasce R, Parra B, Mora J, Becerra N, Lagos N, Vera L, Olivares B, Vilches M, Fernбndez J. Dengue-1 virus isolation during first dengue fever outbreak on Easter Island, Chile. Roth A, Mercier A, Lepers C, Hoy D, Duituturaga S, Benyon E, Guillaumot L, Souares Y. Concurrent outbreaks of dengue, chikungunya and Zika virus infections-an unprecedented epidemic wave of mosquito-borne viruses in the Pacific 20122014. Zika virus in Brazil and the danger of infestation by Aedes (Stegomyia) mosquitoes. Outbreak of exanthematous illness associated with Zika, chikungunya, and dengue viruses, Salvador, Brazil. Undiagnosed illness-Brazil (northeast, Rio de Jeineiro): Zika virus suspected, request for information. Detection of four dengue serotypes suggests rise in hyperendemicity in urban centers of Brazil. Arboviral diseases in the western Brazilian Amazon: a perspective and analysis from a tertiary health & research center in Manaus, State of Amazonas. High level of vector competence of Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus from ten American countries as a crucial factor in the spread of chikungunya virus. Updating the geographical distribution and frequency of Aedes albopictus in Brazil with remarks regarding its range in the Americas. Tappe D, Rissland J, Gabriel M, Emmerich P, Gьnther S, Held G, Smola S, Schmidt-Chanasit J. The invasive mosquito species Aedes albopictus: current knowledge and future perspectives. Rapid risk assessment: Zika virus disease epidemic: potential association with microcephaly and Guillain-Barrй syndrome. Zammarchi L, Stella G, Mantella A, Bartolozzi D, Tappe D, Gьnther S, Oestereich L, Cadar D, Muсoz-Fontela C, Bartoloni A, SchmidtChanasit J. Zika virus infections imported to Italy: clinical, immunological and virological findings, and public health implications. The 2007 epidemic outbreak of chikungunya virus infection in the Romagna region of Italy: a new perspective for the possible diffusion of tropical diseases in temperate areas? Review of West Nile virus epidemiology in Italy and report of a case of West Nile virus encephalitis. Epidemiology of West Nile disease in Europe and in the Mediterranean Basin from 2009 to 2013.
Their study indicates that only 12% of farmers in the region adopted the biotechnology-derived cotton hypertension education materials 50mg moduretic with mastercard. Fifty-seven percent of the farmers having greater than 10 ha adopted Bt cotton compared with 7% of those with less than 2 heart arrhythmia 4 year old purchase moduretic 50 mg without a prescription. The authors indicate hypertensive retinopathy effective 50mg moduretic, however arrhythmia epidemiology purchase moduretic 50mg amex, that due to the short period of time addressed in the study no definitive conclusions of adoption dynamics can be drawn. Biotechnology-derived cotton has been approved for commercial planting in the above-mentioned countries. Despite vocal opposition against biotechnologyderived cotton, adoption through unapproved means is becoming commonplace in some parts of the developing world. In particular, biotechnology-derived cotton is rapidly entering into farm operations prior to receipt of local approval in several countries in Asia India, Thailand, and Indonesia (Buffin and Jewel 2001). Thailand field tested Bt cotton in 1997 from seeds brought into the country in 1995. However, although Bt cotton has not been commercialized in Thailand, studies in 1999 demonstrated the presence of Bt cotton on farms outside the approved test sites. The approval of biotechnology-derived cotton cultivars in early 2002 by the Indian government demonstrates that farmer demand for the technology was outpacing the ability of regulatory institutions to manage the early adoption process. The original commercial release scheduled for June 2001 was stalled by pressure groups. However, it was discovered that Bt cotton had been sold as a hybrid in some regions of India for three years. It is estimated that Bt cotton is planted prior to regulatory approval in India on 10,000 ha. Monsanto, a life science company developing biotechnology-derived crops, brought Bt cotton into India in 1996 to work with a local seed producer to develop cotton varieties optimized for India. By July 2000, the seed producer received approval to plant 150 ha to produce seed for 85 field testing, which continues today. In 1996, total global biotechnology-derived crop area was an estimated 800,000 ha, of which Bt comprised an estimated 27%. Herbicide-tolerant cotton comprised less than 1% of total biotechnology-derived crop area. By 2000, the global area of biotechnology-derived cotton increased to an estimated 44. Biotechnology-derived Crops: 2000, 1999, 1998;in stacked Global Status Note a included James, Clive. Note a included in stacked variety United States production the United States is the second largest producer of cotton, and the largest producer of biotechnologyderived cotton. Between the years 1996 and 2000, estimated biotechnology-derived cotton area in the United States increased from approximately 1. Over the same period total estimated cotton acreage planted in the United States for both Pima and Upland cotton increased from 14,633,500 a. Stark (1997) conducted an economic study of biotechnology-derived cotton in Georgia. The results indicated that Bt cotton outperformed the non-Bt variety with a high yield of 1,378 pounds of lint compared with a high of 1,239 pounds for the non-Bt cotton. The low yield of Bt cotton was 746 pounds of lint compared with 706 for the non-Bt cotton. The average yield across all field sites of Bt cotton was 1,027 pounds, and 923 pounds for the non-Bt cotton. The number of pesticide spray applications per acre for the Bt cotton was a high of 5, and for the non-Bt cotton, 10. The fewest number of sprays on the Bt cotton was zero compared with one for the non-Bt cotton. Wier, Mullins, and Mills (1998) indicated that in a study in Mississippi over three years, Bollgard had an economic advantage over the non-Bollgard cotton. For the three-year study, Bollgard cotton had greater lint yields than the non-Bollgard cotton. Interestingly, the Bollgard varieties in year two and three actually had greater costs associated with insect control. Nevertheless, the economic advantage for the three years 1995-97 for Bollgard cotton was $82. In the same study, Bollgard comparisons were done over three regions and averages for the three years were compared.
Students in such programs are blood pressure medication what does it do buy moduretic 50 mg with visa, like most retarded children hypertension renal failure generic moduretic 50 mg, able to live with their own families and have the benefits of family life as well as a variety of needed services in a habilitative setting blood pressure medication usa generic moduretic 50 mg otc. This provision may be the treatment of choice for direct educational service for seriously handicapped children for whom transportation may be hazardous prehypertension young adults purchase moduretic 50mg line, those who have multiple problems, retarded children identified at an early age for whom preschool home activity is planned, and children who are hospitalized for medical treatments. Programs in residential settings in which educational and other habilitative services are provided in a single setting away from family or natural home. Such 24-hour care settings may be small units located in ordinary neighborhoods or larger facilities (usually subdivided into units) located on several acres of land. Although they may not be a part of the school system, and thus supported by some govern mental agency other than the educational system, they are supported by tax funds. A small proportion of the retarded population is in private residential schools and may be supported by either tax funds through a contract or by the family. The residential living setting has been considered by many professionals as the most restrictive of the alternatives. Therefore, other alternatives for provision of services are usually given first consideration. In making decisions, specialists must recognize the variability of programs within each type of provision and decide on Clinical Applications ll7 an individual basis. As a general rule, the less handicapped the child, the less restrictive is the educational alternative. Speech and language handicaps are particularly prevalent, especially for moderately to profoundly retarded persons. The degree of speech and language delay or disability is related to the degree of retardation. Most severely retarded and all profoundly retarded persons demonstrate severe language delay and will develop only minimal communication skills of any type, even as adults and with intensive training. One approach in recent years that has led to improvement in the development of communication for such persons was the design of techniques to teach some system of sign language or meaningful gestures. Efforts to improve spoken language of severely and profoundly retarded people had been minimally effective; the recent development of various alternative forms of communication has resulted in considerable improvement in adaptation through communication with careproviders and peers. In one such system, Bliss symbols, pictorial representations of words are used; for example, a valentine heart represents emotion and additional symbols indicate the type of emotion. Other systems may be boards with many pictures representing objects or events of daily life, and nonverbal individuals can point to the pictures to facilitate communication with others and thus increase their range of interpersonal contacts. Staff members in educational and institutional settings have been highly inventive in devising boards that depict relevant aspects of life, and a large number of the communication boards in use are made to meet the needs of particular individuals, especially those with serious motor handicaps. Other communication facilitators include electronic devices or modified typewriters and computers that can be manipulated with minimal use of muscles. Some severely retarded individuals have been taught to use small toy-like objects to communicate; these are 118 Classification in Mental Retardation usually designed for specific persons and may include such items as a cup, a spoon, or other object that represents needs. In contrast to severely and profoundly retarded individuals, moderately to mildly retarded people are likely to be able to develop useful communication skills, including spoken language. The communication level ultimately reached by retarded individuals, however, may be somewhat limited. Language training by speech and language specialists or teachers having access to language consultants may be provided for a large proportion of the moderately retarded population; for mildly retarded people the development of language skills is likely to be the responsibility of parents and regular or special education teachers. Speech or language disability combined with mental retardation is the most common of all the dual disabilities, according to federal reports. Identification of the level of retardation provides guidelines for decision-making about the type of services most likely to be effective, determination of age at which progress may be expected, and reasonable long-term goals. The development of improved language skills may make other changes in level of functioning possible so that individuals may move from a more severe to a less severe level of functioning. Some individuals with mild retardation may use newly developed language skills to increase other skills and thus may lose the designation of mental retardation. Special services in the area of motor-skills training and remediation are commonly needed by mentally retarded students, particularly those who are more seriously retarded.