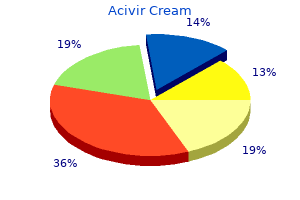
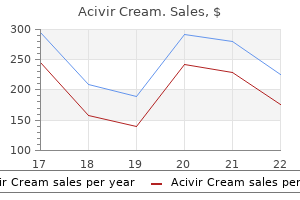
"Cheap acivir cream 10 gr online, hiv infection rate nigeria".
N. Silas, MD
Program Director, UTHealth John P. and Katherine G. McGovern Medical School
Anindividual still may be substantially limited in a major life activity hiv infection rates in heterosexuals buy discount acivir cream 10 gr online, notwithstanding the use of a mitigating measure like medicine antiviral cream contain generic 10 gr acivir cream amex, which may only lessen the symptomsofanimpairment most common hiv infection symptoms cheap 10 gr acivir cream free shipping. A reasonable accommodation includes "modifications or adjustments to the work environment antiviral immune booster buy acivir cream 10 gr free shipping. Fair Employment and Housing Commission, the employees demonstrated that because of respiratory disorders, exposure to tobacco smoke limited their abilitytobreathe. Astheabovecasesillustrate,disabilitylawsuitscan be an effective way for an individual who meets the legal definition of "disabled" to get relief from secondhand smoke exposure in the workplace. However,becausethenumberofpeoplewhoqualify for these federal protections is limited, disability lawsuitsarenotanidealvehicleforadvocatesseeking workplace-smoking restrictions that protect a broad groupofemployees. Duty to Provide a Safe Workplace In most jurisdictions, employers have a legal duty to provide employees a reasonably safe work environment. The employee was severely allergic to tobacco smoke and was forced to leave work on several occasions after becoming physically ill due to secondhand smoke exposure. In other casesdecidedmorerecentlythanShimp,courtshave agreedthatemployerscanbreachthedutytoprovide asafeworkplaceiftheyfailtomaintainasmokefree work environment. However, if an employee is not seeking money damages but instead is seeking an injunction. Employeescanpursueatleastfourpolicy strategies to eliminate secondhand smoke in the workplace:passingstateorlocallaws;enactingstate occupational health and safety agency regulations; changing collective bargaining agreements; and adoptingvoluntaryrulesbytheemployer. Given this legal risk, employers should voluntarily adopt smokefree workplace policies and supportstateorlocallegislationrequiringsmokefree workplaces. Traynor ProfessorofLaw,attheUniversityofCalifornia,Boalt Hall School of Law for his help in conceptualizing thisarticle,andMeliahThomasforconductinglegal research that formed the basis for the article. The authorswishtothankKerryCork,DougBlankeand Christopher Banthin for their editing assistance and productionwork. Glantz, Cardiovascular Effects of Secondhand Smoke: Nearly as Large as Smoking, 111 circUlAtion 268, 2685 (2005); Suzaynn Schick & Stanton Glantz, Philip Morris Toxicological Experiments with Fresh Sidestream Smoke: More Toxic than Mainstream Smoke, 1 tobAcco control 96, 96 (2005). Wortley, Exposure to Secondhand Smoke in the Workplace: Serum Cotinine by Occupation, J. States clearly have the constitutional authority to enact such a law because there is no specially protected right to smoke and smokers are not a specially protected class of people. Graff, Tobacco Control Legal Consortium, There is No Constitutional Right to Smoke: 2008 (2008), available at. Glantz, Effect of Smoke-Free Workplaces on Smoking Behaviour: Systematic Review, 25 B. Occupational Safety and ealth Administration proposed a federal indoor air quality rule in 199, but withdrew the proposed rule seven years later largely due to pressure from the tobacco industry. Fox, An Assessment of the Current Legal Climate Concerning Smoking in the Workplace, 1 St. Vallone, Employer Liability for Workplace Environmental Tobacco Smoke: Get out of the Fog, 0 vAl. Paul, Minnesota, fields requests for legal technical assistance and coordinates the delivery of services by the collaborating legal resource centers. Our legal technical assistance includes help with legislative drafting; legal research, analysis and strategy; training and presentations; preparation of friend-of-the-court legal briefs; and litigation support. Department of Justice and prepared the following final report: Document Title: A National Overview of Prostitution and Sex Trafficking Demand Reduction Efforts, Final Report Michael Shively, Ph. In a prior study, Abt Associates found that the use of anti-demand approaches was more widespread throughout the United States than previously thought. We also found that little research or descriptive information was available about the vast majority of interventions. It was also evident that communities attempting to address demand had usually done so with little guidance from the collective experience of others; consequently, some initiatives had struggled or failed when faced with problems that had been solved elsewhere. The project was designed to develop a descriptive overview of antidemand tactics employed throughout the United States and to provide practitioners with actionable information to assist them in starting, improving, or sustaining initiatives. To share what has been learned, the project has generated several key products, one of which is the present report, A National Overview of Prostitution and Sex Trafficking Demand Reduction Efforts, which summarizes the research activities and presents findings.

When the prevalence of iron deficiency anemia reaches the 2030% level in the age-gender group under evaluation antiviral detox 10 gr acivir cream with visa, it is likely to be more effective hiv infected person symptoms trusted 10 gr acivir cream, and possibly more efficient hiv infection fever cheap 10 gr acivir cream with visa, to provide universal supplementation to that entire group rather than to screen for individual case management purposes hiv infection statistics europe acivir cream 10 gr online. Anemia response to treatment for malaria must be considered, along with treatment of hookworm, in areas with a known incidence of these conditions (16, 61). It also seems likely that the iron in multimicronutrient home fortifica- tion formulations will not increase morbidity, but there is insufficient current evidence to be absolutely sure of this. Several reports and reviews emphasize the importance of adequate iron stores in the development of infants and young children (75, 76). The same necessity to avoid iron deficiency and nutritional anemia applies also to women of reproductive age, preferably before they become pregnant. There have been sporadic attempts, through social marketing, to have poor clients buy iron/folic acid supplements. These have rarely been sustainable, although there are some promising current experiences in several Asian countries, for example, Cambodia, the Philippines and Vietnam (77). It is, however, unlikely to be a useful approach for the very poorest and most marginalized, where supplementation remains the option of choice. Iron fortification has been an important contributor to improved iron status and, most likely, B vitamins in industrialized countries (78) and, probably, Latin America (79) although the chemical and physical form of iron used in national fortification programs has been questioned as to efficacy (41). As has recently been noted with magnesium sulphate (a cheap drug for use in preeclampsia) "even when low cost, effective treatments exist, drug availability for many common health problems remains poor in many settings, limiting progress towards achieving the millennium development goals. Add to this the apparent lack of conviction in health workers regarding the usefulness of the intervention, and other barriers such as unaffordable primary user fees, distance from health system clinics, and the not infrequent abusive treatment by healthcare providers (8183). In fact, some health workers Global perspectives on nutritional anemia control 369 when questioned thought that iron supplements might actually be harmful by increasing the amount of blood and size of fetus, with the attendant risks in marginalized areas distant from obstetric care (personal observation in Indonesia and Zambia, Darnton-Hill 1997). Public and private sector in the prevention of anemia Chief among the constraints in the fight against anemia and other micronutrient deficiencies is the limited willingness of governments (and donors) to invest sufficiently in order to improve diets and reduce social inequities. This is because such action requires large, long term investments to improve the supply, distribution, and consumption of animal and vegetable foods, and needs, especially to target those who are in greatest need. Similarly, health systems in the countries most affected are seriously under resourced (73). These factors involve not only problems of access and related cost, since the highest undernutrition rates are usually found among those in remote rural areas who are more difficult to reach, but also because those living in remote rural communities are usually peripheral to the concerns of the urban political class. It is clear, however, that this is a complex task which requires various parts of society to collaborate in order to succeed. The role that the food and health industries can play in improving the nutritional status of a population is important for all the key strategies, from efforts to improve the supply, distribution, and consumption of animal and vegetable food, to fortification and supplementation. Reduction in rates of anemia and other micronutrient deficiencies are more likely to be achieved through a combination of the three key approaches of dietary improvement, supplementation and fortification, while also aiming to reduce social inequities (given that nutritional anemias are most often a consequence of poverty). Fortification can offer a partial solution in the medium and long term, but this requires: wheat or other food producers to work with the pharmaceutical companies in producing micronutrient mixes; consumers and the public health community to put pressure on government to adopt legislation and regulations on voluntary or mandatory fortification of foods; and effective communication of the importance of this approach through the media and schools in order for people to know that they should demand it. There is a great deal of attention currently focused on expanding fortification to developing and transitional economies (14, 41, 86, 87). Likewise, supplementation programs should be seen as an opportunity also to promote improved diets, since supplementation is a perhaps less sustainable means of helping address deficiencies due to inadequate food intake and/or other factors. In comparing four weekly iron and folic acid supplementation programs in Cambodia, for example, the most successful one included (in addition to weekly iron and folic acid supplements), vitamin A capsules and deworming tablets taken every six months; the program attempted also to address water quality and sanitation problems, and the fact that children often go to school without breakfast (77). In many developing countries, the private health and nongovernmental sectors may have 370 I. Cavalli-Sforza multiple advantages in delivering health care interventions such as micronutrient supplementation over poorly resourced government services. Such advantages include the existence of better functioning facilities (and in some places, the only clinics available); A better image, including among the poor, and the (often undeserved) reputation for providing better health care; A drugs and supplements distribution network and the interest in ensuring it functions well; the ability to advertise their products and services. Nevertheless, governments must still be held responsible for the wellbeing of the very poorest whom the World Bank, amongst others, has identified as being at particular disadvantage in an increasingly globalized world (89). The government health services, on the other hand, have a large network of experienced staff in regular contact with their public and the opportunity to develop complementary strategies with other government and nongovernment structures, such as schools, workplaces, and municipalities. The dialogue between the health ministries and the food industry now taking place in many countries also offers the opportunity to integrate the prevention of chronic diseases by limiting the consumption of foods high in fat, sugar, and salt, with the prevention of micronutrient deficiencies through the promotion of diets rich in fruits and vegetables, and fortification. Countries where government and mass organizations both work closely with communities offer a great opportunity for synergistic approaches to supplementation. Half the profit of the sales goes to a revolving fund, one quarter to the woman selling the supplements, and the rest to social marketing activities to further promote sales.
The Board 61 did not intend that an entity would identify significantly more promised goods and services that result in performance obligations than under existing revenue guidance except that certain material rights that are not identified as deliverables under existing revenue guidance will be identified as performance obligations under the new revenue standard antiviral neuraminidase inhibitor discount 10 gr acivir cream visa. The Board decided to amend Topic 606 to state that immaterial items are not required to be assessed as promised goods or services for purposes of identifying performance obligations (that is hiv infection management purchase acivir cream 10 gr without prescription, for purposes of applying Step 2 of the revenue model in Topic 606) hiv infection gay top buy acivir cream 10 gr fast delivery. The Board decided that an entity is required to consider whether a promised good or service is material only at the contract level because it would be unduly burdensome to require an entity to aggregate and determine the effect on its financial statements of those items or activities determined to be immaterial at the contract level hiv infection diagnosis and treatment buy generic acivir cream 10 gr on-line. This notion of determining material promised goods or services at the contract level also is used in Topic 606 for significant financing components and customer options for additional goods or services. As it is used in paragraph 606-10-25-16A, the term immaterial refers to the general notion of materiality. That is, an entity should consider the relative significance or importance of a particular promised good or service in the contract to the arrangement with the customer as a whole. In applying this notion, an entity should consider both the quantitative and the qualitative nature of the promised goods or services in the contract. An entity is not required to allocate revenue to promised goods or services that are immaterial in the context of the contract. Assessing whether promised goods or services are immaterial at the contract level will require the use of judgment. Assessing the materiality of promised goods or services in a contract with a customer includes consideration of quantitative and qualitative factors. If multiple goods or services in a contract are individually immaterial in the context of the contract, but those individually immaterial items are material in the aggregate to the contract, then an entity should not disregard those (or all of those) goods or services when identifying performance obligations. The Board decided that the guidance in paragraph 606-10-25-16A does not apply to customer options for additional goods and services when those 62 options provide a customer with a material right. The Board determined that when assessing whether optional goods and services provide the customer with a material right, an entity would apply the guidance in paragraphs 606-10-55-42 through 55-43. The entity would apply the guidance in those paragraphs to determine whether an option gives rise to a material right that a customer will not receive without entering into that contract. The Board decided to include guidance in Topic 606 that requires an entity to accrue the costs, if any, to transfer immaterial goods or services to the customer in instances in which the costs will be incurred after the satisfaction of the performance obligation (and recognition of revenue) to which those immaterial goods or services relate. The Board concluded that this will more appropriately align the recognition of revenue and costs in the financial statements. While the proposed Update, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606): Identifying Performance Obligations and Licensing, did not include this requirement, it included a similar notion in the basis for conclusions. On the basis of stakeholder feedback, the Board decided to include the requirement in the Codification. That guidance states that if revenue is recognized upon substantial completion of the terms specified in the arrangement related to the unit of accounting at issue, all related costs of performance or delivery should be accrued. The Board also observed that the cost accrual requirement only applies to items that are determined to be promises to the customer in the contract. Some items that a few stakeholders have discussed in the context of this requirement may not constitute promises to the customer and, therefore, would not be subject to the guidance in paragraph 606-10-25-16A. For example, an entity typically would not be required to accrue costs for answering general questions about a product. The operation of a call desk for general inquiries that is available broadly is an example of an activity that is not fulfilling a promise to a customer. In practice, this could be a more costly approach than the approach adopted in this Update, and the Board expects it will not significantly change the quality of the information reported to financial statement users. The guidance in paragraph 606-10-25-16 states that an implied promise in a contract with a customer may exist if a promise creates a valid expectation of the customer that an entity will transfer a good or service to the customer. Stakeholders have diverse views about whether and when Topic 606 requires shipping and handling activities (collectively referred to as shipping) that occur after the transfer of control of the good to the customer to be accounted for as a promised service or as a fulfillment activity. Under existing revenue guidance, many entities do not account for shipping provided in conjunction with the sale of their goods as an additional deliverable. Requiring shipping to be accounted for as a promised service would be a significant change in practice for many entities because shipping generally is not a deliverable under existing guidance for arrangements involving the sale of goods. At present, there are many manufacturers, retailers, and others that do not consider their arrangements to include multiple deliverables (that is, a good and a shipping service). Consequently, they do not have the systems, processes, and internal controls to account for those arrangements as multiple-element arrangements. Requiring shipping to be identified as a performance obligation separate from the transfer of the good might diminish the usefulness of the information provided to financial statement users because users may combine the two pieces of revenue for their analyses.
Syndromes
- Hypothyroidism
- Shaving
- Brain tumors can be treated with medicines called mTOR inhibitors (sirolimus, everolimus).
- Emotional stress
- Hypersplenism (swollen spleen)
- Flush across the cheeks
- Careful monitoring
- Tissue and blood typing to make sure your body will not reject the donated liver
Colony stimulating factorCytokine that stimulates the growth of immature leukocytes in the bone marrow anti viral hand wipes acivir cream 10 gr low price. Committed/progenitor Parent or ancestor cells that differentiate into cells one cell line hiv infection parties cheap acivir cream 10 gr mastercard. Common coagulation One of the three interacting pathways in the pathway coagulation cascade antiviral nhs acivir cream 10 gr low price. The common pathway includes three rate-limiting steps: (1) activation of factor X by the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways antiviral fruit discount 10 gr acivir cream fast delivery, (2) conversion of prothrombin to thrombin by activated factor X, and (3) cleavage of fibrinogen to fibrin. Compensated hemolytic A disorder in which the erythrocyte life span is disease decreased but the bone marrow is able to increase erythropoiesis enough to compensate for the decreased erythrocyte life span; anemia does not develop. Complement Any of the eleven serum proteins that when sequentially activated causes lysis of the cell membrane. Erythrocyte hemolysis results from the precipitation of hemoglobin in the form of heinz bodies, which damages the cell membrane and causes cell rigidity. Contact group A group of coagulation factors in the intrinsic pathway that is involved with the initial activation of the coagulation system and requires contact with a negatively charged surface for activity. Continuous flow analysisAn automated method of analyzing blood cells that allows measurement of cellular characteristics as the individual cells flow singly through a laser beam. Contour gating Subclassification of cell populations based on two characteristics such as size (x-axis) and nuclear density (y-axis) and the frequency (zaxis) of that characterized cell type. A line is drawn along the valley between two peaks to separate two cell populations. Coverglass smear Blood smear prepared by placing a drop of blood in the center of one coverglass, then placing a second coverglass on top of the blood at a 45° angle to the first coverglass. Cryopreservation the maintaining of the viability of cells by storing at very low temperatures. Cyanosis Develops as a result of excess deoxygenated hemoglobin in the blood, resulting in a bluish color of the skin and mucous membranes. Cytochemistry Chemical staining procedures used to identify various constituents (enzymes and proteins) within white blood cells. Useful in differentiating blasts in acute leukemia, especially when morphologic differentiation on romanowsky stained smears is impossible. Cytokine Protein produced by many cell types that modulates the function of other cell types; cytokines include interleukins, colony stimulating factors, and interferons. This occurs because the primary hemostatic plug is not adequately stabilized by the formation of fibrin. A laboratory test used to detect the presence of antibody and/or complement that is attached to the erythrocyte. Dцhle bodies An oval aggregate of rough endoplasmic reticulum that stains light gray blue (with Romanowsky stain) found within the cytoplasm of neutophils and eosinophils. It is associated with severe bacterial infection, pregnancy, burns, cancer, aplastic anemia, and toxic states. The antibody reacts with erythrocytes in capillaries at temperatures below 15°C and fixes complement to the cell membrane. Upon warming, the terminal complement components on erythrocytes are activated, causing cell hemolysis. Downey cell An outdated term used to describe morphologic variations of the reactive lymphocyte. Drug-induced hemolytic Hemolytic anemia precipitated by ingestion of anemia certain drugs. Dutcher bodies Intranuclear membrane bound inclusion bodies found in plasma cells. Dysfibrinogenemia Dyshematopoiesis Dysplasia Dyspoiesis A hereditary condition in which there is a structural alteration in the fibrinogen molecule. Abnormal development of blood cells frequently characterized by asynchrony in nuclear to cytoplasmic maturation and/or abnormal granule development. A spiculated erythrocyte with short, equally spaced projections over the entire outer surface of the cell.