"Buy prograf 0.5mg with mastercard, hiv infection stages".
T. Trompok, M.B. B.CH., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Co-Director, Dell Medical School at The University of Texas at Austin
Energy-enhanced smokeless products such as Revved Up contain stimulants (caffeine jurkat hiv infection generic prograf 1mg visa, ginseng) stages of hiv infection medscape cheap prograf 0.5mg without a prescription, taurine hiv infection onset 0.5mg prograf mastercard, and vitamins B and C hiv infection rates female to male order prograf 5mg on line. Some forms of tombol contain khat (Catha edulis), a plant that contains cathinone, an alkaloid with amphetamine-like stimulant properties, which purportedly causes euphoria, excitement, and loss of appetite. Research is also needed into the role of microorganisms (bacteria and mold) in altering product chemistry. Categorizing the products into groups with similar properties may provide a means of determining the health effects associated with particular product chemistries. Smokeless tobacco products vary greatly in chemical composition and, in some cases, contain extremely high levels of total nicotine, free nicotine, and carcinogens. Another matter of concern is the addition of stimulants to tobacco products, such as the addition of caffeine to moist snuff products. Maintenance of toxicants below certain feasible, but not necessarily safe, thresholds demonstrates that the tobacco industry has the ability to use manufacturing controls to reduce toxicants as recommended by the World Health Organization156; however, only one company has set its own voluntary toxicant reduction standards. Lyon, France: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2007 [cited 2012 April 24]. Lyon, France: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2004 [cited 2012 April 24]. Developing smokeless tobacco products for smokers: an examination of tobacco industry documents. Unintentional child poisonings by ingestion of conventional and novel tobacco products. Proceedings of an international symposium, Tata Institute of Fundamental Research. Studies on tobacco specific nitrosamines and other carcinogenic agents in smokeless tobacco products. Unusually high levels of carcinogenic tobaccospecific nitrosamines in Sudan snuff (toombak). Accidental fatal poisoning by Nicotiana glauca: identification of anabasine by high performance liquid chromatography/photodiode array/mass spectrometry. Influence of temperature and humidity on the accumulation of tobacco-specific nitrosamines in stored burley tobacco. Tobacco-specific nitrosamines: formation from nicotine in vitro and during tobacco curing and carcinogenicity in strain A mice. Sources of and technical approaches for the abatement of tobacco specific nitrosamine formation in moist smokeless tobacco products. Tobacco-specific nitrosamine accumulation and distribution in flue-cured tobacco alkaloid isolines. Endogenous nitrosation in the oral cavity of chewers while chewing betel quid with or without tobacco. Leaf chemistry: basic chemical constituents of tobacco leaf and differences among tobacco types. Microbial community structure and dynamics of dark fire-cured tobacco fermentation. Larsson L, Szponar B, Ridha B, Pehrson C, Dutkiewicz J, Krysinska-Traczyk E, et al. Bacillus species are present in chewing tobacco sold in the United States and evoke plasma exudation from the oral mucosa. Florianpolis, Brazil: Federal University of Santa Catarina Publishing House; 1996. Food of the gods: the search for the original tree of knowledge: a radical history of plants, drugs, and human evolution. Urinary levels of volatile organic carcinogen and toxicant biomarkers in relation to lung cancer development in smokers.
Diseases
- Pseudopapilledema blepharophimosis hand anomalies
- Primary pulmonary hypertension
- Anonychia onychodystrophy brachydactyly type B
- Anton syndrome
- Berry aneurysm, cirrhosis, pulmonary emphysema, and cerebral calcification
- Jones Hersh Yusk syndrome
- BAER
- Genetic diseases, inborn
- Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, very long chain, deficiency of
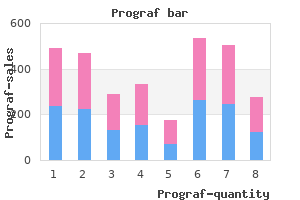
Yet data to precisely quantify these differences in disease risk and to identify the factors that drive them are lacking hiv infection statistics worldwide order 0.5 mg prograf otc. Smokeless tobacco use and marketing present distinct public health challenges in different countries and regions antiviral yify effective prograf 1mg. Changes in product marketing antiviral for eyes purchase prograf 0.5 mg free shipping, patterns of use hiv infection medscape buy prograf 0.5mg line, and tobacco control programs and interventions may have very different results in these different environments. In some high-income countries where restrictions on public smoking have increased and smoking prevalence has decreased, tobacco companies have marketed oral tobacco products to smokers. However, the impact of this trend on smoking behavior, and possible dual or poly-tobacco use, remains uncertain. At the same time, multinational tobacco companies have an increasing presence among low- and middle-income countries with both smoked and smokeless products. Prices are lower, warning labels are weaker, surveillance is less developed, fewer proven interventions are available, and fewer resources are devoted to prevention and control programs. The Global Challenge of Smokeless Tobacco Significant challenges exist in monitoring the use and health effects of smokeless tobacco. The Global Challenge of Smokeless Tobacco Chapter 1 introduces and provides a framework for this report, summarizes its chapters, and sets out its major conclusions. Smokeless tobacco use prevalence varies significantly across individual countries and regions, between youth and adults, and between males and females. Among youth and adults, males generally show higher prevalence of use than females. However, among adults, use by women is similar to or greater than use by men in some countries, including Bangladesh, Thailand, Cambodia, Malaysia, Vietnam, and some African countries, such as South Africa, Mauritania, and Sierra Leone. Although data were available to measure overall prevalence for many countries, longitudinal data and data on patterns of use are lacking in most regions. Premade products range from manufactured products made in factories or large production facilities to cottage industry products made in market stalls or shops. The chapter builds on previous reports and systematic reviews that have provided thorough assessments of the evidence. The Economics of Smokeless Tobacco Chapter 5 summarizes the literature and available data on the economics of smokeless tobacco. Little is known about the comparability of tax levels between smoked and smokeless products. The current best practice for cigarette taxation favors the use of a specific excise tax that is regularly adjusted for inflation. A standard unit may be based on dosage (average amount of a product used in a single session), the weight of the dry tobacco leaf used in a product, or the weight of a product (weight of the tobacco, water content, and all other additives). Lack of standardization complicates not only tax collection but also scientific research, as it hinders the use of econometric methods. These marketing strategies may have an adverse public health impact if they encourage dual use or use of multiple tobacco products, discourage cessation, or encourage new tobacco use initiation. In low- and middle-income countries, product innovations may also make sale and use of products more convenient. For example, in India the gutka industry has promoted a packaged ready-to-use product based on a traditional custom-made mixture. Products are designed to appeal to targeted consumers, they are offered at a desirable price, and they are promoted effectively using multiple communication and placement channels. Understanding consumer perceptions of and responses to novel products is essential to assessing the public health impact of changing product and marketing strategies. Greater monitoring and research is needed regarding marketing practices in low- and middle-income countries. Prevention and Cessation Interventions Chapter 7 describes evidence-based prevention and treatment programs that have been tested in a range of countries. The interventions vary from community, to organizational, to individual levels of treatment.
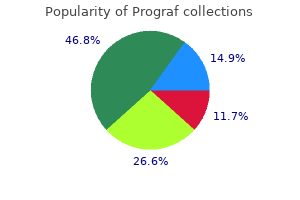
Ongoing efforts to improve vaccine uptake across the lifespan and among persons at increased risk for vaccine-preventable diseases or their complications should be sustained anti viral anti fungal herbs cheap 1mg prograf otc. Increasing uptake of currently available vaccines supports investments in new vaccines by increasing the projected market for new products process of hiv infection and how it affects the body prograf 5 mg low cost. Historically antiviral uk purchase prograf 0.5 mg otc, vaccine innovation has been driven by disease epidemiology anti viral fungal fighter best 5 mg prograf, burden, and severity. However, for some high priority vaccine 18 Encouraging Vaccine Innovation: Promoting the Development of Vaccines that Minimize the Burden of Infectious Diseases in the 21st Century targets, public-private partnerships are central to facilitating development. Vaccines for pandemic influenza preparedness or biodefense, such as smallpox and anthrax vaccines, are purchased solely by the government as there is no viable commercial interest or market. Public-private partnerships are important to facilitate development of high-priority products. Conclusion Much progress has been made in understanding the complex scientific issues inherent in making a vaccine; adapting regulatory needs to a changing environment; and supporting policies that facilitate progress and innovation. Catalytic investments in some areas as identified above may further propel innovations toward licensure and delivery. For example, a systematic, evidence-based process to assess and communicate public health needs for new and improved vaccines, including a critical review of disease epidemiology, the merits of individual targets, gaps in information, and efforts to address these gaps could spur innovation. Understanding the issues facing key stakeholders and their respective roles and contributions to the vaccine network could also help unify and focus efforts on several vaccine targets while strengthening the U. As a result of continuous development and innovation, vaccines have had a profound impact, protecting Americans across the lifespan. This report outlines challenges and opportunities facing the vaccine enterprise that, if addressed, could spur continued progress and innovation toward the availability of future vaccines to improve public health in the 21st century. Vaccine Enterprise Components Basic & Applied Research Description Improve the knowledge base regarding the antigenic components of infectious agents, underlying mechanisms of infectious disease, the human immune system, and host-pathogen interactions. Develop the "target product profile", a high level summary of characteristic traits and key features of the product. Develop a clinical program that involves studies in humans to determine the effects of vaccines for safety, immunogenicity, and efficacy through a staged process. Product Development* Regulatory Evaluation and Licensure Recommendations Provide recommendations for use to indicate which civilian populations for Introduction should receive a vaccine and under what conditions. Vaccine Uptake Support the immunization delivery system to ensure all individuals across the lifespan have access to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practice-recommended vaccines and vaccinations and monitor the impact of vaccine uptake, safety, and effectiveness. The entire portfolio of vaccines in clinical development in the United States is available at clinicaltrials. The table provided here is reproduced from the source and include only infectious disease vaccine candidates. In order to receive an orphan designation, a qualifying drug or biologic must be intended for the treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of a rare disease or condition that affects usually fewer than 200,000 people in the United States. Phase 1-Researchers test the investigational drug or biologic in a small group of people, usually between 20 and 100 healthy adult volunteers, to evaluate its initial safety and tolerability profile, determine a safe dosage range, and identify potential side effects. Phase 2-The investigational drug or biologic is given to volunteer patients, usually between 100 and 500, to determine whether it is effective, identify an optimal dose, and to further evaluate its short-term safety. Phase 3-The investigational drug or biologic is given to a larger, more diverse patient population, often involving between 1,000 and 5,000 patients (but sometimes many more), to generate statistically significant evidence to confirm its safety and effectiveness. Breakthrough Therapy designation is based on the Designation following criteria: 1) the product is intended to be used alone or in combination with one or more drugs to treat a serious or life-threatening disease or condition and 2) Preliminary clinical evidence indicates that the product may demonstrate substantial improvement on a clinically significant study endpoint(s) over available therapies. The Food and Drug Administration Modernization Act of 1997 mandates the Agency to , at the request of the sponsor, facilitate the development and expedite review of drugs, including biological products, intended to treat serious or life-threatening diseases or conditions and that demonstrate the potential to address unmet medical needs. Fast Track adds to existing programs, such as accelerated approval, the possibility of a "rolling review" for an application. Numerous vaccines have been approved that received Fast Track Designation, including vaccines for the prevention of cervical cancer and cholera. Numerous vaccines have been approved that had Priority Review status, including vaccines to prevent cervical cancer, invasive meningococcal serogroup B disease, cholera, and pneumococcal conjugate vaccines. Such approval may be subject to verification of clinical benefit through additional studies conducted after approval (Phase 4 studies). Since its creation, the accelerated approval program has been used to approve numerous vaccines, including those to prevent influenza, Haemophilus influenzae Type b (Hib) and invasive meningococcal disease caused by Neisseria meningitidis serogroup B.
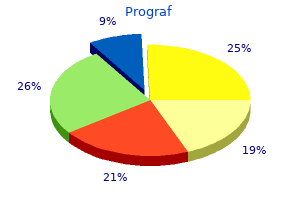
Prions and prion-like proteins (see Chapter 4 for a definition of prion- 118 Stanford University Biosafety Manual like proteins) are highly resistant to conventional decontamination hiv infection guidelines discount prograf 5mg with amex, and laboratories are strongly encouraged to use only disposable equipment stages of hiv infection and their symptoms safe prograf 5mg. Specific procedures for decontamination and disposal must be followed when working with prions and prion-like proteins hiv infection rate dallas effective 5 mg prograf. But hiv infection cd4 count order prograf 0.5 mg visa, worse than that, they make their brains and their nerves work too hard; they fatigue their heads and become irritable, or nervous, as it is called, being excited to gayety or anger without sufficient cause. Sometimes, indeed, their brains become altogether deranged, and are no longer able to act properly; the persons are then insane, or lunatic. It is by no means true, however, that the professions and sedentary occupations furnish all of the cases of insanity. Currently, Stanford University contracts with an outside vendor for this; call the vendor (number is found at ehs. The Principal Investigator should present a receipt verifying that the paraformaldehyde decontamination procedure has been completed by the contracted biosafety cabinet certifier. The former contents must be decontaminated by autoclaving or disposed of in a biohazard bag. Cryostats and liquid nitrogen storage equipment must also be emptied and contents properly disposed of. Specimens stored in a cold room or an incubator in an adjacent tissue culture room should be autoclaved or disposed of in a biohazard bag. The outer surface of all equipment and any work surface must be decontaminated with a suitable disinfectant. An autoclave is suitable for the treatment of certain types of medical waste but not all types. The following items of medical waste must not be autoclaved: Chapter 12: Lab Deactivation & Equipment Disposal Items for Lab Deactivation Laboratories which utilize biological materials must notify the Biosafety program prior to terminating work to ensure that the laboratory has been decontaminated and that the biological material has been secured or properly disposed. If the Principal Investigator intends to cease work, he or she must notify Biosafety at least 60 days prior to the set departure/closing date. This will allow Biosafety to consult with the Principal Investigator and perform a walkthrough of the lab to provide recommendations on the most expeditious way to prepare for the move and the final termination of the biohazardous work in the lab (Figure 1). A final Lab Deactivation Chapter 12: Lab Deactivation & Equipment Disposal 121 Figure 1. Schedule a wipe test with Health Physics to ensure that the equipment is free from residual radioactive contamination. Make sure that the equipment was not used to store water reactive chemicals, corrosives or strong oxidizers that may incompatibly react during the decontamination process. If the internal compartments of a piece of equipment are grossly contaminated with biohazardous material, label or tag the equipment as potentially biohazardous. Notify the Biosafety Manager and a decision will be made whether the Disposal of Used Lab Equipment Used laboratory equipment, such as incubators, refrigerators and freezers, must be thoroughly decontaminated prior to disposal or release to surplus property (Figure 2). Laboratory equipment that was used in conjunction with biological research may have residual contamination resulting from chemicals and/or radioactive materials. Freezer in Need of Clean-Out Chapter 12: Lab Deactivation & Equipment Disposal 123 equipment is safe for disposal. Additional guidance related to the proper deactivation and move-out of Stanford University laboratories is available at: stanford. Determination of whether a pathogen has a potential for serious detrimental impact on managed (agricultural, forest, grassland) or natural ecosystems should be made by the Principal Investigator and the Institutional Biosafety Committee, in consultation with scientists knowledgeable of plant diseases, crops, and ecosystems in the geographic area of the research (Section V-M). All procedures shall be performed in accordance with accepted greenhouse practices that are appropriate to the experimental organism.