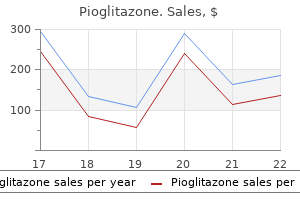
"Generic 45 mg pioglitazone visa, blood glucose 436".
E. Rathgar, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, University of Nevada, Las Vegas School of Medicine
An extensive evidence review was conducted diabetes type 2 carb counting generic pioglitazone 15mg without prescription, focusing on 2006 through October 2012 and selected other references through March 2014 diabetex pgx with mulberry generic 45 mg pioglitazone fast delivery. Key search words included but were not limited to the following: age diabetes diagnostic test generic pioglitazone 15mg visa, antiarrhythmic diabetes mellitus type 1 prevention trusted 45mg pioglitazone, atrial fibrillation, atrial remodeling, atrioventricular conduction, atrioventricular node, cardioversion, classification, clinical trial, complications, concealed conduction, cost-effectiveness, defibrillator, demographics, epidemiology, experimental, heart failure, hemodynamics, human, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, meta-analysis, myocardial infarction, pharmacology, postoperative, pregnancy, pulmonary disease, quality of life, rate control, rhythm control, risks, sinus rhythm, symptoms, and tachycardia-mediated cardiomyopathy. References selected and published in this document are representative and not all-inclusive. The new guideline incorporates new and existing knowledge derived from published clinical trials, basic science, and comprehensive review articles, along with evolving treatment strategies and new drugs. The data from that report were reviewed by the writing committee and incorporated where appropriate (7a,7b). Some recommendations from earlier guidelines have been eliminated or updated as warranted by new evidence or a better understanding of earlier evidence. Table 2 lists these publications and statements deemed pertinent to this effort and is intended for use as a resource. Under the guidance of the Task Force, the Heart Rhythm Society was invited to be a partner organization and provided representation. The writing committee also included a representative from the Society of Thoracic Surgeons. Reproduced with permission from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (44). Sympathetic activation and vagal withdrawal such as that with exertion or illness accelerates the ventricular rate. Loss of atrial contraction may markedly decrease cardiac output, particularly when diastolic ventricular filling is impaired by mitral stenosis, hypertension, Downloaded From: content. Overall, cardiac output may decrease and filling pressures may increase compared with a regular rhythm at the same mean rate. Atrial tachycardias are characterized by an atrial rate of $100 beats per minute (bpm) with discrete P waves and atrial activation sequences. Focal atrial tachycardia is characterized by regular, organized atrial activity with discrete P waves, typically with an isoelectric segment between P waves (Figure 1) (64,65). In multifocal atrial tachycardia, the atrial activation sequence and P-wave morphology vary (64). Atrial Flutter and Macroreentrant Atrial Tachycardia Early studies designated atrial flutter with a rate of 240 bpm to 340 bpm as "type I flutter," and this term has commonly been applied to typical atrial flutter (65,68). It is now recognized that tachycardias satisfying either of these descriptions can be due to reentrant circuits or rapid focal atrial tachycardia. Typical atrial flutter is a macroreentrant atrial tachycardia that usually proceeds up the atrial septum, down the lateral atrial wall, and through the cavotricuspid (subeustachian) isthmus between the tricuspid valve annulus and inferior vena cava, where it is commonly targeted for ablation. The atrial rate is typically 240 bpm to 300 bpm, but conduction delays in the atrial circuit due to scars from prior ablation, surgery, or antiarrhythmic drugs can slow the rate to <150 bpm in some patients (65). P-wave morphologies are shown for common types of atrial flutter; however, the P-wave morphology is not always a reliable guide to the reentry circuit location or the distinction between common atrial flutter and other macroreentrant atrial tachycardias. Atrial flutter is often a persistent rhythm that requires electrical cardioversion or radiofrequency catheter ablation for termination. Complex reentry circuits with >1 reentry loop or circuit can occur and often coexist with common atrial flutter. These arrhythmias are not abolished by ablation of the cavotricuspid isthmus, but recognition and distinction of these arrhythmias from common atrial flutter usually requires electrophysiological study with atrial mapping (65). These structural abnormalities can heterogeneously alter impulse conduction and/or refractoriness, generating an arrhythmogenic substrate. The atria are more sensitive to profibrotic signaling and harbor a greater number of fibroblasts than the ventricles. Atrial stretch activates the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, which generates multiple downstream profibrotic factors, including transforming growth factor-beta 1. Additional mechanisms, including inflammation and genetic factors, can also promote atrial fibrosis. Human studies show a strong correlation between regions of low voltage on electroanatomic mapping and areas of late enhancement on magnetic resonance imaging.
The gender specific difference in the premenopausal adult circulation is consistent with higher work capacity and superior athletic performance in male compared with female subjects diabetes diet don'ts buy 15mg pioglitazone overnight delivery. A consistent and predictable change occurs around the female menopause managing diabetes kidneys 15 mg pioglitazone sale, and a decade later in males blood glucose newborn cheap 30 mg pioglitazone with amex, suggestive of an endocrine influence on blood pressure diabetes in dogs type 2 purchase pioglitazone 45 mg line, and arguing for a male menopause. The greater work capacity of the male circulation prior to menopause has implications for athletic performance and combat roles. Recently, intraoperative blood pressure variability has been shown to predict postoperative morbidity and mortality in cardiac bypass surgery1. Risk factors for increased variability have not been identified, but data suggests that intraoperative instability may be the result of preoperative antihypertensive treatment2. In this study, we have looked at the effect of preoperative antihypertensive regimens upon intraoperative blood pressure variability. Selection criteria included hypertensive patients on single drug therapy preoperatively who had nonemergent surgery with an arterial line. Operative records were analyzed for the percent of total case time that systolic blood pressure was above 135mmHg and/or below 90mmHg. This range was derived from previously established systolic pressure ranges that were associated with poor outcomes in previous trials1. Comparison of demographics, co morbidities, and intraoperative vasopressor requirement was also completed. They also had less high-end variability compared with diet controlled patients with a trend towards less overall variability. In conclusion, antihypertensive patients treated with beta-blockers preoperatively had less intraoperative systolic blood pressure variability. This effect could be explained by a preponderance of younger males in the beta blocker group. Intraoperative systolic blood pressure variability predicts 30-day mortality in aortocoronary bypass surgery patients. Hemodynamic effects of anesthesia in patients chronically treated with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. However, these recommendations are largely based on single-center studies and expert opinion. We therefore conducted a populationbased study to evaluate the outcomes of elective intermediate-tohigh risk non-cardiac surgery following stent insertion. Approximately 34% (n=2725) underwent stent insertion within two years before surgery, of whom 905 (33%) received drug-eluting stents. For comparison, we assembled a separate cohort of 341,350 individuals, aged 40 years or older, who underwent major elective surgery during the time period and had not undergone coronary revascularization. The primary outcome was postoperative 30-day major adverse cardiac events (mortality, hospital readmission for acute coronary syndrome or repeat coronary revascularization). As shown in the Figure, when the interval between stent insertion and surgery was less than 30days, event rates were high for bare-metal (6. In addition to suggesting that practice guidelines be re-evaluated, these findings will help inform clinical decision-making when weighing the risks of operative versus non-operative therapy in patients being considered for major elective non-cardiac surgery following recent coronary stent insertion. For comparison, the horizontal dashed lines represent event rates for individuals who did not undergo coronary revascularization within 10 years before non-cardiac surgery, and had been stratified by their Revised Cardiac Risk Index scores. Although there have been many reports indicating the relationship between the autonomic nervous system balance and arrhythmia, the effect of remifentanil on arrhythmia induction has not been clarified. The anesthesia maintenance was accomplished with propofol 6-10 mg/kg/h and remifentanil 0. If programmed cardiac stimulation, isoproterenol infusion, or their combination were not effective in arrhythmia induction, remifentanil administration was discontinued. Patients whose arrhythmia could not be induced even after remifentanil discontinuation were defined as induction-impossible cases. The mechanisms of Non-Reentry arrhythmia include automaticity and triggered activity. The incidence of induction-impossible cases in non-Reentry group was higher than in Reentry group (13 (18. We investigated the incidence, factors, and outcome measures associated with weight gain following cardiac surgery that have not been extensively studied before.
Step 2-Initial incision A lateral incision is made diabetic diet how many carbs per meal generic pioglitazone 15mg on-line, curved from the femoral shaft and middle of the greater trochanter with slight posterior curve above the greater trochanter diabetes test times purchase 45mg pioglitazone visa. The distal extent will depend on the distal extent of foreign material within the femur and surgical approach blood sugar insulin pioglitazone 15 mg amex. Step 3-Exposing Tissue Divide the subcutaneous tissue down to the fascia diabetic diet zone discount pioglitazone 45 mg without a prescription, split the fascia in line with its fibers curving posteriorly above the greater trochanter into the gluteus maximus. Position a Charnley retractor to hold the deep fascia open exposing the underlying tissues. At this point, based on preoperative findings, surgeon preference and previous experience, an anterior lateral, posterior lateral, transtrochanteric or extended trochanteric osteotomy approach may be chosen. Whatever the choice, every effort must be made to leave soft tissue attached to the bone so that it will not be devascularized. This is particularly so in the case of an extended trochanteric approach, in which case care should be taken to leave the abductors and vasti attached to the trochanteric and lateral cortex of the femur. A minimum of three synovial soft tissue biopsies should be sent for bacteriologic study. Step 4-Component Removal Before any of the Prostalac components are prepared or used, remove all existing implanted components, cement and any other foreign material. If there is doubt as to the adequacy of cement removal, an intraoperative radiograph can be helpful at this point. Step 5-Acetabular Preparation Reaming of the acetabulum is not recommended in most cases. It may potentially remove valuable bone and irregularities that are useful for interference fixation of the cement mantle used later in the case. Using manual tools, remove all foreign material and soft tissue down to bleeding bone and take care to identify and remove any hidden pieces of bone cement (Figure 2). Proper mixing of the antibiotics and bone cement is critical to the success of this device. The safety and potential benefit of the Prostalac hip has only been demonstrated when used with tobramycin sulfate and vancomycin hydrochloride at the indicated doses. Then add liquid monomer and carefully mix all ingredients by hand with a spatula, pressing the bone cement around the sides of the bowl until all ingredients are blended together (Figure 4). The antibiotic-loaded bone cement consistency will be slightly different than bone cement without antibiotics. This bone cement procedure is intended to achieve stable, but not rigid fixation by interdigitation and interference fit with the irregularities of the surrounding bone. It also allows easy removal during the second stage, without bone attached (Figure 5). Insert the Prostalac cup into the cement mantle at an appropriate location and at an orientation of 45 degrees of abduction and 20 degrees of anteversion. Use a cup impactor with a 28 mm head impactor to position the cup and apply pressure until the cement has hardened (Figure 6). Step 8-Femoral Preparation Utilize the Endurance broaches to prepare the femoral envelope for optimal fit of the Prostalac hip (Figure 7). To confirm stem size selection, stem trials should be used to determine if a short or long stem is to be used. Continue broaching using progressively larger broaches until reaching the broach size that corresponds to the templated implant size. Figure 7 Figure 6 Figure 5 7 Surgical Technique Step 9-Trial Reduction Trial neck segments and trial modular heads are available to use with the broach, to assess joint stability and range of motion. Perform a trial reduction with a +5 Prostalac head trial to allow for two up or one down adjustment in neck length without using a skirted femoral head. Refer to the chart at the back of this surgical technique for detailed base offset, neck length and leg length adjustment information. Note: the Prostalac trial head is slightly smaller in diameter than the final head to allow easy reduction and dislocation since the acetabular component is a snap-fit design. Trial Neck Selection Stem Size Broach Size Trial Neck 120 mm Std 120 mm High 150, 200, 240 mm Std 1 to 5 1 to 5 3 Size 1 Standard Size 1 High Size 3 Revision Step 10-Femoral Mold Preparation A. Mold selection (Figure 8) 120 mm Standard/High Offset Short Stems Choose the short mold that matches the last broach size used. Figure 8 150, 200, 240 mm Long Stems Choose the left or right size 3 long mold to match the infected side of the hip. Mold Preparation (Figure 9) Before using the Prostalac molds, apply a thin layer of sterile mineral oil inside the mold to allow easy removal of the implant after the cement has hardened around the implant.
Thepatientshouldbereferredto genetics for a dysmorphology evaluation and appropriate testing diabetes in dogs hereditary 15mg pioglitazone free shipping. Therefore diabetes mellitus facts statistics buy 30 mg pioglitazone fast delivery,theriskincreaseswith 13 Chapter 13 Genetics: Metabolism and Dysmorphology 347 diabetes prevention funding 45 mg pioglitazone for sale. Inthechildhoodcerebralform diabetes mellitus type 2 normal value best pioglitazone 15mg,onsetoccurs between ages 4 and 12 years with school failure, behavior, vision and hearing changes progressing to total disability and decerebration within 2 years of symptom onset. Presentation:Disorderofcoppermetabolismthatpresentswith hepatic, neurologic, renal and psychiatric complications including chronicliverdisease,jaundice,cirrhosis,dysarthria,poor coordination, depression and occasionally intellectual deterioration. Diagnosticevaluation:Lowserumcopperandceruloplasmin concentrations with increased urinary copper excretion and hepaticcopperconcentration. Therefore,karyotypeanalysisisstillindicatedinaneuploidysyndromes, both to provide a diagnosis, and to provide accurate genetic counseling. Features:Intrauterinegrowthrestrictionandpolyhydramnios,small for gestational age at birth, clenched hands with overlapping fingers, hypoplastic nails, short sternum, prominent occiput, low-set and structurally abnormal ears, micrognathia, rockerbottom feet, congenital heart disease, cystic and horseshoe kidneys,seizures,hypertonia,significantdevelopmentaland cognitive impairments. Features:Defectsofforebraindevelopment(holoprosencephaly), severe developmental disability, low-set malformed ears, cleft lip and palate, microphthalmia, aplasia cutis congenita, polydactyly (mostfrequentlyofthepostaxialtype),narrowhyperconvexnails, apneic spells, cryptorchidism, congenital heart defects. Thediagnosisshouldbeconsideredinafemale fetus with hydrops, increased nuchal translucency, cystic hygroma, orlymphedema. Otherfeaturesmayincludeshortstature,gonadal dysgenesis with amenorrhea and lack of a pubertal growth spurt, broad chest with hypoplastic or inverted nipples, renal abnormalities, webbed neck, hypertension, congenital heart disease(mostcommonlybicuspidaorticvalveandcoarctationof theaorta),andhypothyroidism. Intelligenceisusuallynormal,but patients are at risk for cognitive, behavioral, and social disabilities. Adolescentandadultmalesmay present with infertility and hypoandrogenism with eunuchoid body habitus,gynecomastiaandsmalltestes. Connective tissue diseases27,37,38 ExamplesincludeMarfansyndrome,Loeys-Dietzsyndrome,familial thoracic aortic aneurysm disease, bicuspid aortic valve and aneurysm syndromes,Ehlers-Danlossyndrome,Shprintzen-Goldbergsyndrome, cutis laxa syndromes, arterial tortuosity syndrome, Stickler syndrome (descriptionofalloftheseisbeyondthescopeofthischapter). Presentation:Myopia,ectopialentis(60%),dilatationoftheaorta atlevelofsinusesofValsalva,predispositiontoaortictearand rupture, mitral valve prolapse, enlargement of proximal pulmonary artery,pneumothorax,boneovergrowthandjointlaxity,extremities disproportionatelylongforsizeoftrunk,pectuscarinatumor excavatum, scoliosis, pes planus. Healthsupervision:Annualophthalmologicexamination;annual echocardiography unless aortic root diameter exceeds 4. Themostcommon forms are the classical and hypermobility types, while the vascular typeinvolvesthehighestrisk. FeaturesofEhlers-Danlossyndrome may include smooth, velvety, hyperextensible skin, widened scars, easybruising,jointhypermobilitywithrecurrentdislocations, chronicjointorlimbpainandapositivefamilyhistory. Epidemiology:Autosomaldominantcondition;1/2cases spontaneous or de novo genetic mutations. Stenosis at the foramen magnum in infancy increases the risk of death;lumbarspinalstenosismaypresentinchildhood,butis Chapter 13 Genetics: Metabolism and Dysmorphology 353 morecommoninadulthood. Diagnosticevaluation:Clinicaldiagnosisbasedoncharacteristic physical exam described above and radiographic findings including a contracted skull base, square shaped pelvis with small sacrosciaticnotch,shortvertebralpedicles,rhizomelicshortening of long bones, trident hands, proximal femoral radiolucency and chevron shape of distal femoral epiphysis. Features:Primarycraniosynostosisresultsfromprematurefusion of the cranial sutures, an event which usually occurs prenatally. Scaphocephaly occurs from premature closer of the sagittal suture and is the most common form of craniosynostosis. Frontal plagiocephaly is the next most common form and results from premature fusion of a coronal and sphenofrontal suture. Earlytreatmentandmanagement may decrease the risk of associated complications such as hydrocephalus and cognitive impairment. Features:Characterizedbyseverehypotoniaandfeeding difficulties in infancy, followed by an insatiable appetite in later 13 Chapter 13 Genetics: Metabolism and Dysmorphology A. Squamosal suture Frontal bones Parietal bones Occipital bone Temporal bone B A 1 A C C D 2 D D E 2 E 1 A D 4 F 3 353. Developmentaldelaysinmotorand language abilities are present, and all affected individuals have somedegreeofintellectualdisability. Shortstatureiscommon; males and females have hypogonadism, and in most, infertility.